Table of Contents
Introduction
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is an antimetabolite chemotherapeutic drug used in the treatment of various solid tumors, including colorectal, breast, head and neck, and gastrointestinal cancers. Mechanism of Action of 5-Fluorouracil centers on its ability to inhibit DNA and RNA synthesis, leading to impaired cell proliferation. As a pyrimidine analog, 5-FU interferes with rapidly dividing cancer cells, making it an essential drug in oncology practice.
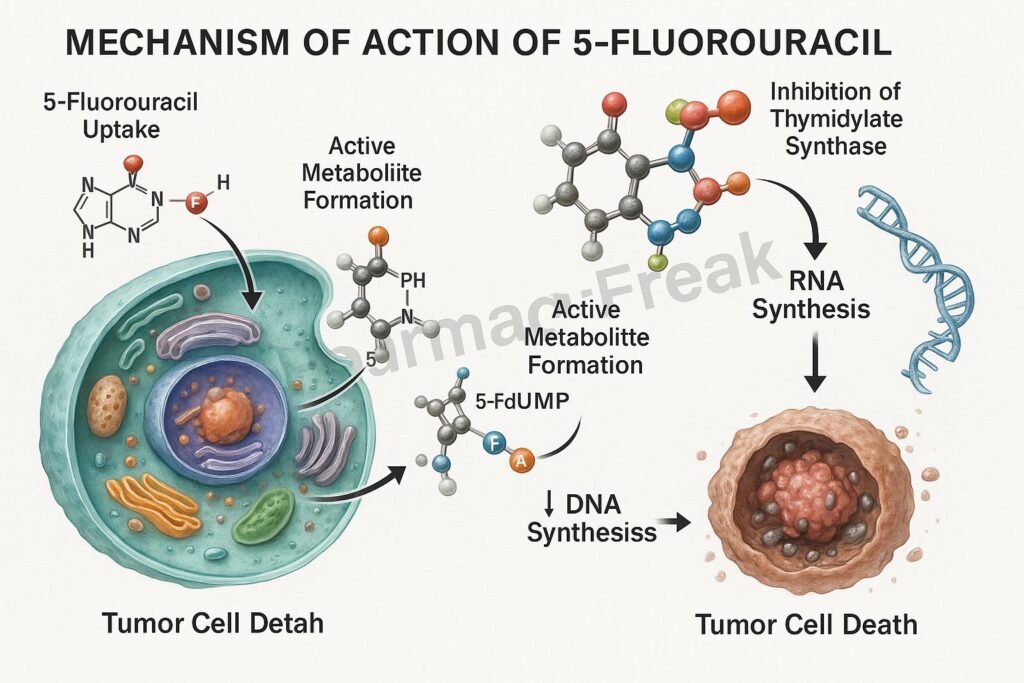
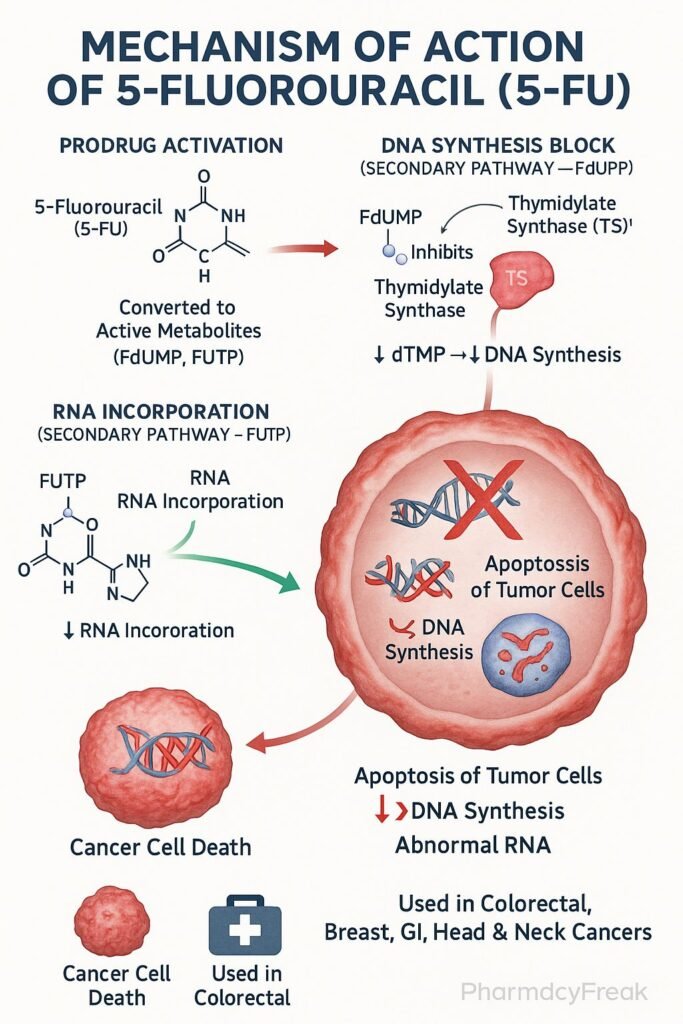
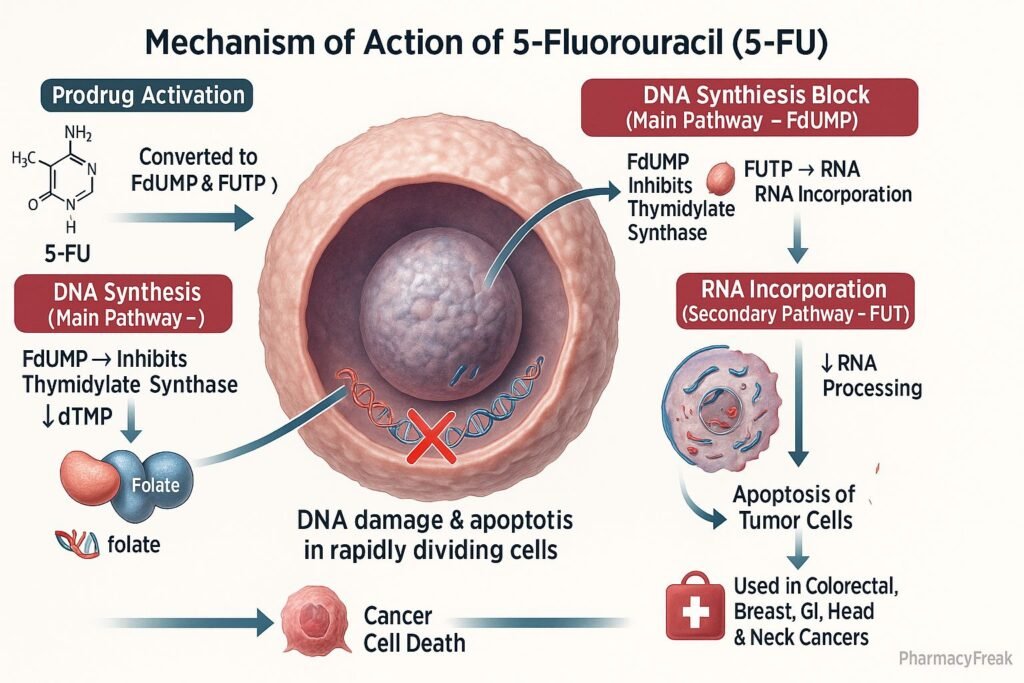
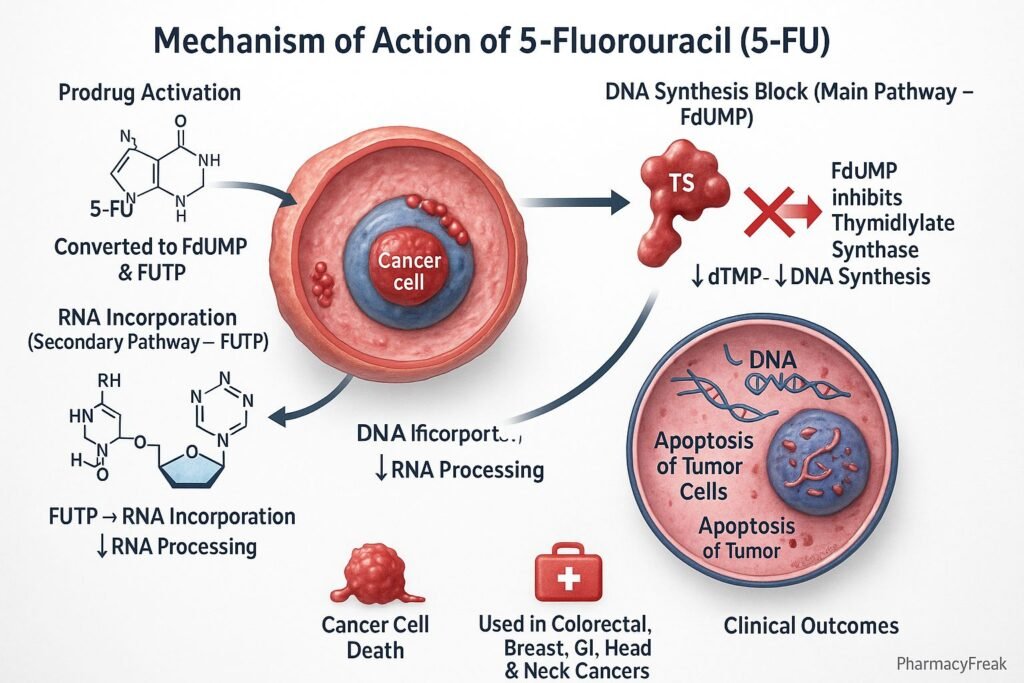
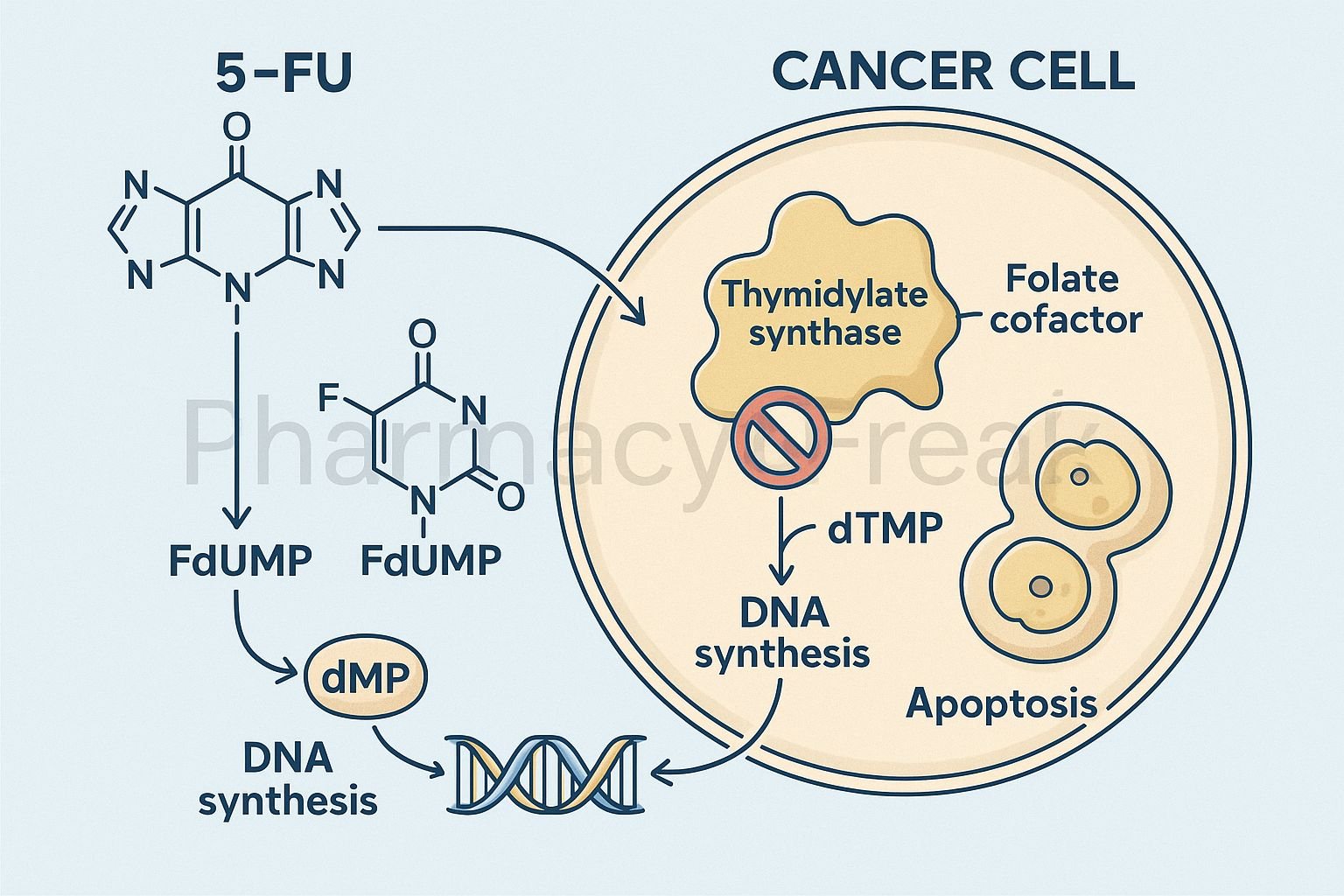
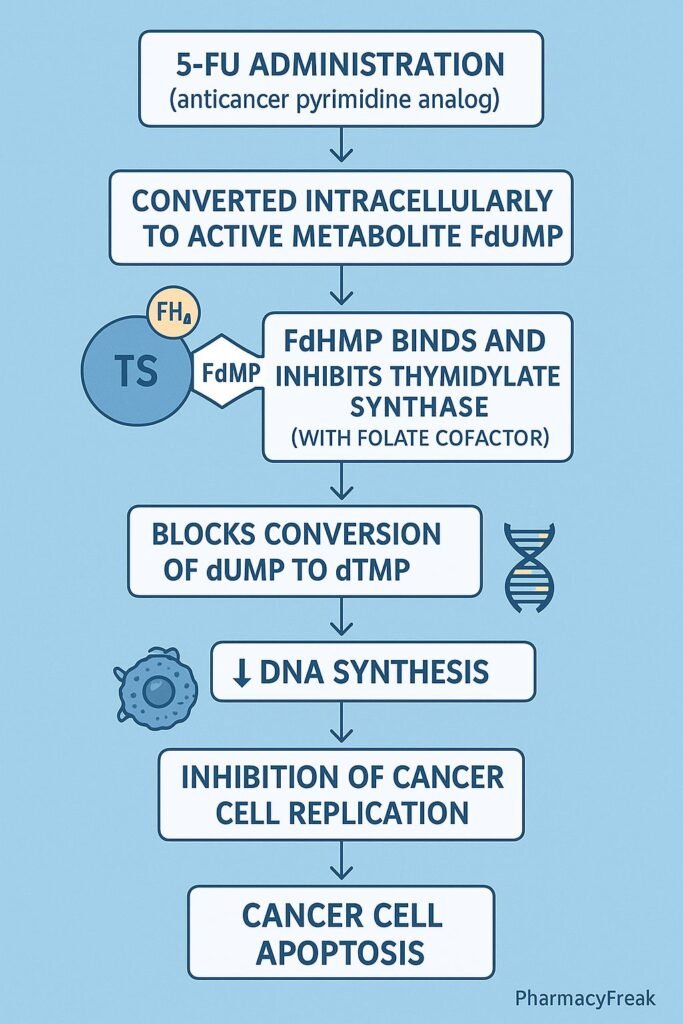
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
- Conversion to Active Metabolites
- 5-FU is a prodrug that undergoes intracellular activation.
- It is converted to fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP) and fluorouridine triphosphate (FUTP).
- Inhibition of Thymidylate Synthase
- FdUMP binds irreversibly to thymidylate synthase.
- This blocks the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP).
- Result: depletion of thymidine triphosphate (dTTP), an essential DNA building block.
- DNA Synthesis Inhibition
- Lack of dTTP prevents proper DNA replication and repair.
- Leads to DNA strand breaks and apoptosis in rapidly dividing cells.
- RNA Incorporation
- FUTP is incorporated into RNA in place of uridine triphosphate (UTP).
- This disrupts RNA processing, stability, and protein synthesis.
- Overall Effect
- Inhibition of both DNA and RNA synthesis.
- Selectively affects rapidly proliferating cancer cells.
Pharmacokinetics
- Administration: Intravenous (most common) or topical (for skin cancers).
- Absorption: Poor oral bioavailability due to rapid degradation.
- Distribution: Widely distributed in body tissues.
- Metabolism: Primarily metabolized in the liver by dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD).
- Excretion: Mainly renal.
- Half-life: 10–20 minutes (very short, continuous infusion often used).
Clinical Uses
- Colorectal cancer (first-line chemotherapy agent).
- Breast cancer.
- Gastric, pancreatic, and esophageal cancers.
- Head and neck cancers.
- Basal cell carcinoma and actinic keratosis (topical use).
Adverse Effects
- Common: Myelosuppression, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mucositis, alopecia.
- Less common: Hand-foot syndrome (palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia).
- Serious: Cardiotoxicity (angina, arrhythmias), neurotoxicity, severe toxicity in patients with DPD deficiency.
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) | Methotrexate | Cytarabine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug class | Pyrimidine analog (antimetabolite) | Folate antagonist (antimetabolite) | Pyrimidine analog (antimetabolite) |
| Target | Thymidylate synthase, RNA | Dihydrofolate reductase | DNA polymerase |
| Effect on DNA | ↓ dTMP → impaired DNA synthesis | ↓ purine and thymidylate synthesis | Inhibits DNA chain elongation |
| Effect on RNA | Incorporated into RNA | No direct RNA effect | No major RNA effect |
| Clinical uses | GI cancers, breast, topical use | Leukemia, lymphoma, solid tumors | Leukemia, lymphoma |
MCQs
1. 5-Fluorouracil belongs to which drug class?
a) Alkylating agent
b) Antimetabolite
c) Topoisomerase inhibitor
d) Mitotic inhibitor
Answer: b) Antimetabolite
2. Which enzyme is inhibited by 5-FU?
a) Dihydrofolate reductase
b) Thymidylate synthase
c) DNA polymerase
d) RNA polymerase
Answer: b) Thymidylate synthase
3. What is the main effect of FdUMP?
a) Inhibition of dUMP → dTMP conversion
b) RNA chain elongation
c) DNA polymerase inhibition
d) ATP synthesis blockade
Answer: a) Inhibition of dUMP → dTMP conversion
4. Which active metabolite of 5-FU is incorporated into RNA?
a) FdUMP
b) FUTP
c) dUMP
d) dTMP
Answer: b) FUTP
5. What is the most serious toxicity associated with 5-FU in DPD deficiency?
a) Severe myelosuppression
b) Hypertension
c) Pulmonary fibrosis
d) Retinopathy
Answer: a) Severe myelosuppression
6. Which of the following cancers is NOT typically treated with 5-FU?
a) Colorectal cancer
b) Pancreatic cancer
c) Breast cancer
d) Small-cell lung cancer
Answer: d) Small-cell lung cancer
7. The topical form of 5-FU is used for:
a) Ovarian carcinoma
b) Basal cell carcinoma
c) Prostate cancer
d) Lymphoma
Answer: b) Basal cell carcinoma
8. Which enzyme metabolizes 5-FU?
a) CYP3A4
b) Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD)
c) Xanthine oxidase
d) Monoamine oxidase
Answer: b) Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD)
9. Hand-foot syndrome is an adverse effect of:
a) Vincristine
b) 5-Fluorouracil
c) Bleomycin
d) Cisplatin
Answer: b) 5-Fluorouracil
10. 5-FU primarily interferes with which cellular process?
a) Protein folding
b) DNA and RNA synthesis
c) Mitosis
d) Oxidative phosphorylation
Answer: b) DNA and RNA synthesis
FAQs
Q1. Is 5-FU a cell cycle–specific drug?
Yes, it is S-phase specific, affecting DNA synthesis.
Q2. Why is leucovorin sometimes given with 5-FU?
Leucovorin enhances binding of FdUMP to thymidylate synthase, increasing efficacy.
Q3. What is the main dose-limiting toxicity of 5-FU?
Myelosuppression.
Q4. Can 5-FU cause cardiotoxicity?
Yes, rare cases of angina, arrhythmias, and myocardial ischemia occur.
Q5. Why is DPD deficiency important in 5-FU therapy?
Patients with DPD deficiency cannot metabolize 5-FU efficiently, leading to severe toxicity.
Q6. How is 5-FU administered?
Mainly intravenously; topical formulations exist for dermatological use.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
- Katzung Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
- Cancer Chemotherapy Clinical Guidelines
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com