Table of Contents
Introduction
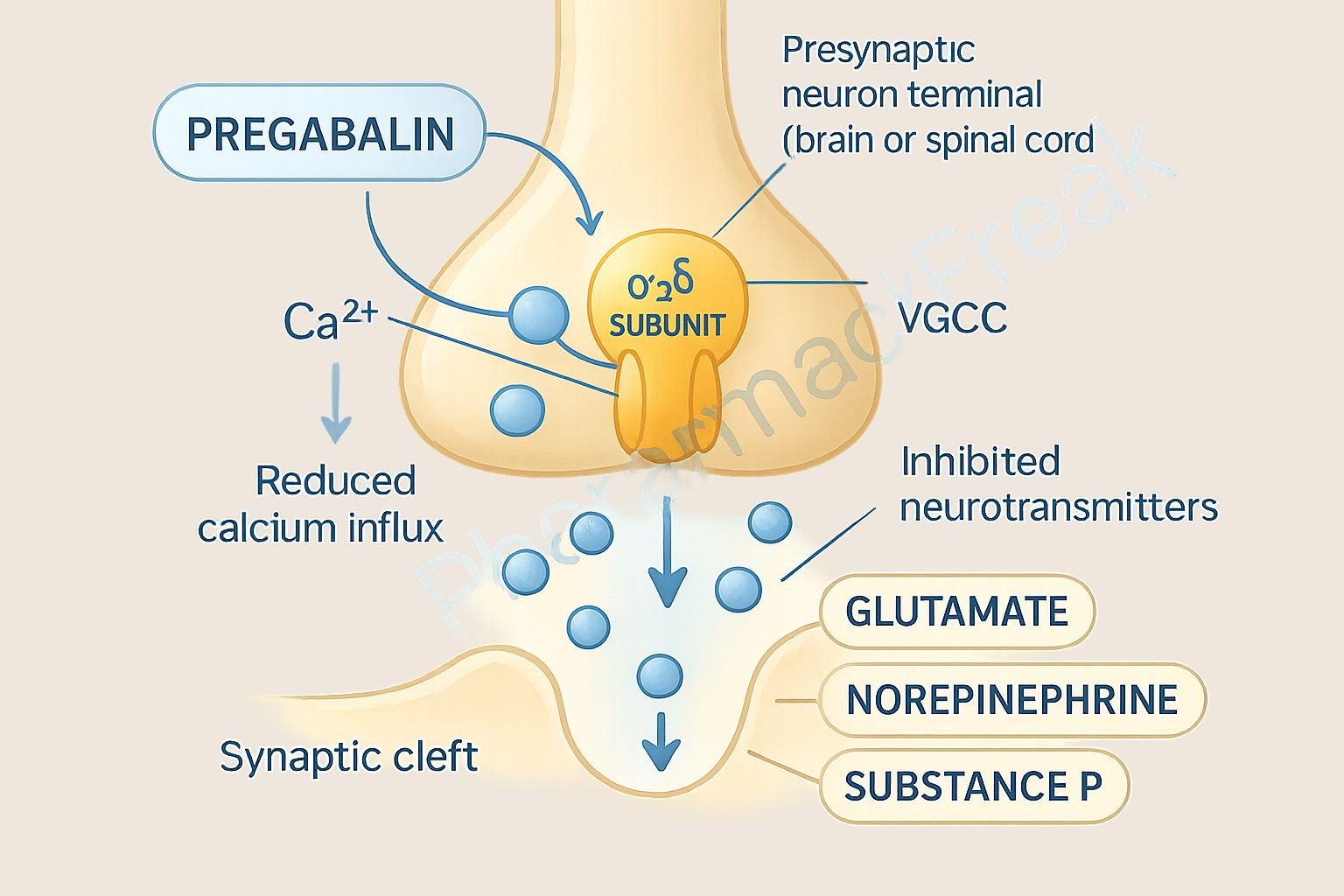
Pregabalin, marketed under the brand name Lyrica, is a centrally acting agent approved for neuropathic pain, epilepsy, and generalized anxiety disorder. Although structurally similar to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), pregabalin does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it exerts its effects by modulating calcium channels in the central nervous system, leading to decreased neurotransmitter release and neuronal excitability.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
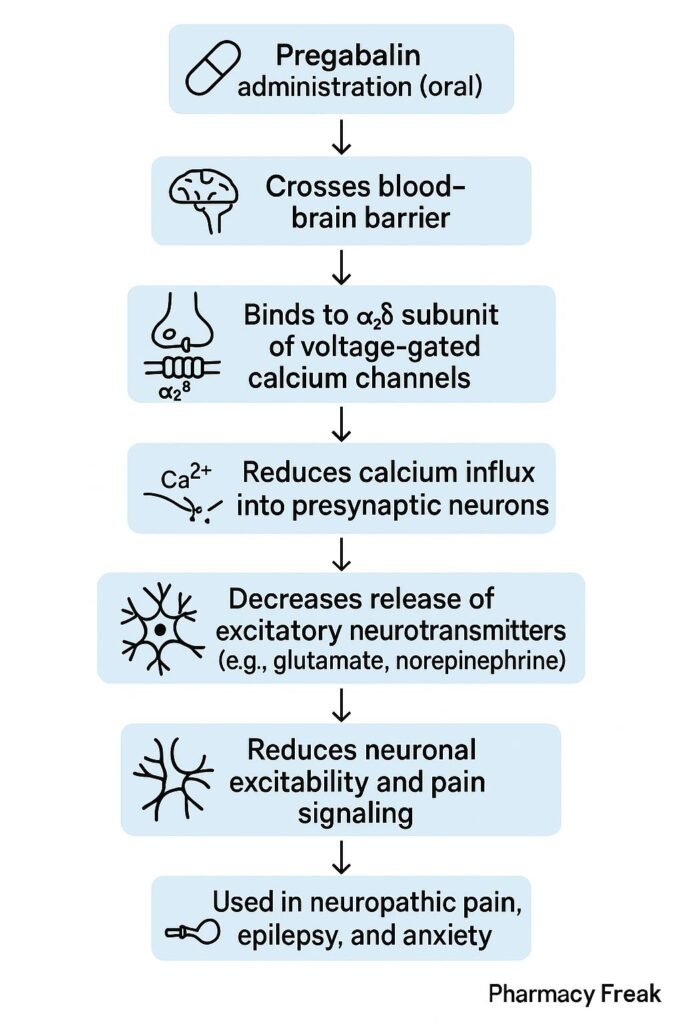
1. Binding to α2δ Subunit of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels
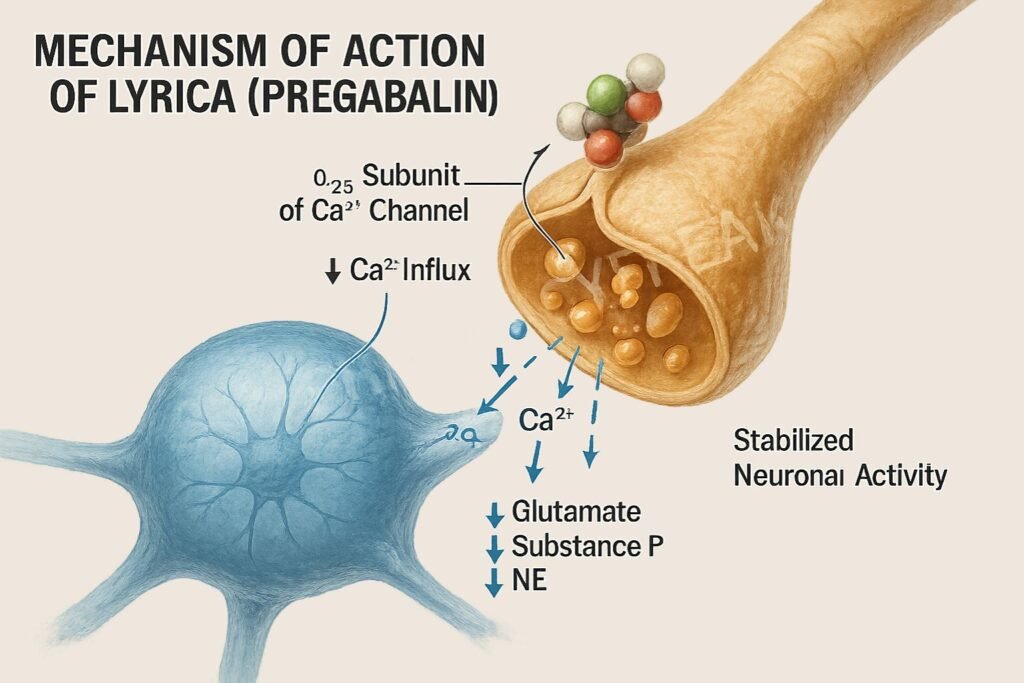
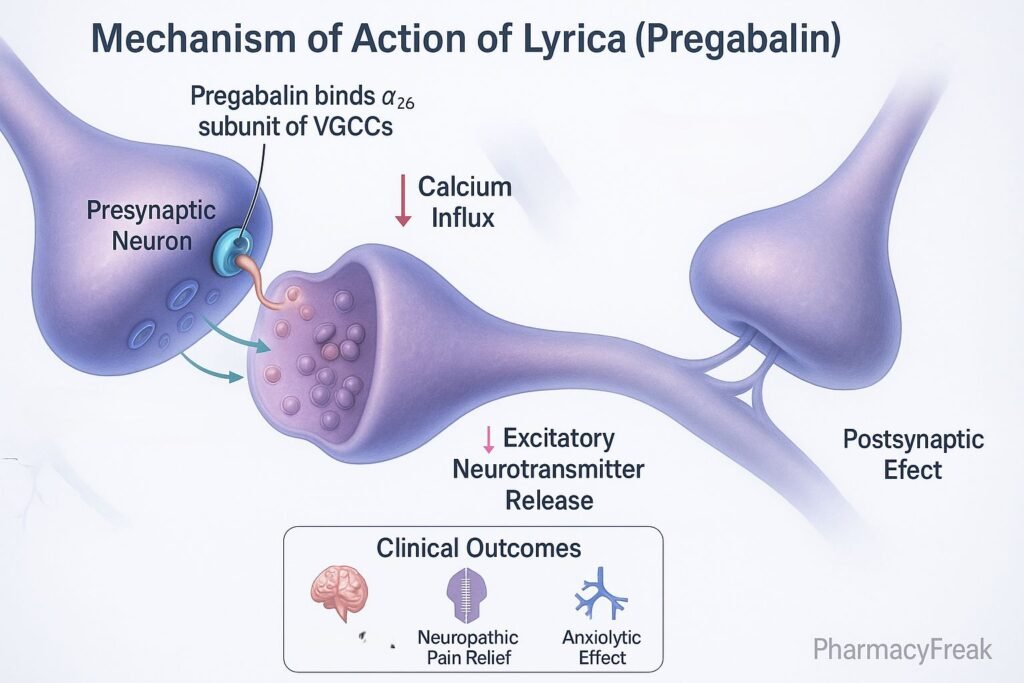
Pregabalin binds with high affinity to the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in presynaptic neurons.
2. Inhibition of Calcium Influx
This binding reduces the influx of calcium into the nerve terminals upon depolarization.
3. Decreased Release of Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Reduced calcium entry leads to decreased release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate, norepinephrine, substance P, and CGRP.
4. Reduction of Neuronal Excitability
By inhibiting excitatory transmission, pregabalin stabilizes overactive neurons, leading to analgesic, anticonvulsant, and anxiolytic effects.
5. Indirect GABAergic Effects
Although it does not directly act on GABA receptors, it may indirectly enhance GABAergic tone.
Pharmacokinetics
- Route of Administration: Oral
- Bioavailability: >90% (independent of dose)
- Time to Peak Plasma: ~1 hour (fasting)
- Half-Life: 6.3 hours
- Protein Binding: Negligible
- Metabolism: Minimal (not metabolized by liver enzymes)
- Excretion: Renal (unchanged drug)
Clinical Uses
- Neuropathic pain (diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia)
- Fibromyalgia
- Partial-onset seizures (adjunctive therapy)
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Spinal cord injury-related neuropathic pain
Adverse Effects
- Dizziness
- Somnolence
- Peripheral edema
- Weight gain
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Ataxia
- Contraindications: Known hypersensitivity; dose adjustment needed in renal impairment
Comparative Analysis
| Parameter | Pregabalin (Lyrica) | Gabapentin |
|---|---|---|
| Target | α2δ subunit of calcium channels | α2δ subunit of calcium channels |
| Bioavailability | >90% | Variable (30–60%) |
| Dosing Schedule | BID or TID | TID |
| Onset of Action | Faster | Slower |
| Anxiolytic Effect | Present | Minimal |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Pregabalin binds to which of the following?
a) GABA-A receptor
b) NMDA receptor
c) α2δ subunit of calcium channels
d) Sodium channels
Answer: c) α2δ subunit of calcium channels
2. What is a common side effect of pregabalin?
a) Hypotension
b) Weight gain
c) Bradycardia
d) Renal stones
Answer: b) Weight gain
3. Pregabalin is effective in all except:
a) Neuropathic pain
b) Fibromyalgia
c) Absence seizures
d) Generalized anxiety disorder
Answer: c) Absence seizures
4. How is pregabalin eliminated from the body?
a) Hepatic metabolism
b) Pulmonary excretion
c) Renal excretion (unchanged)
d) Biliary excretion
Answer: c) Renal excretion (unchanged)
5. Pregabalin shows its therapeutic effects by:
a) Inhibiting serotonin reuptake
b) Enhancing GABA binding directly
c) Reducing excitatory neurotransmitter release
d) Blocking dopamine receptors
Answer: c) Reducing excitatory neurotransmitter release
FAQs
Q1. Is pregabalin a GABA agonist?
No, it is structurally similar but does not bind to GABA receptors.
Q2. Can pregabalin be used for anxiety?
Yes, it is approved for generalized anxiety disorder in several countries.
Q3. Is there a risk of dependence with pregabalin?
Yes, especially with prolonged use or high doses.
Q4. What is the difference between pregabalin and gabapentin?
Pregabalin has higher bioavailability, faster onset, and anxiolytic effects.
Q5. Should pregabalin be tapered off?
Yes, abrupt discontinuation can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- Prescribing information for Lyrica (Pregabalin)
- Clinical guidelines for neuropathic pain and anxiety
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com