Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Pyridine is a six-membered nitrogen heteroaromatic (C₅H₅N) isoelectronic with benzene, with a ring sp²-N that is basic (conjugate-acid pKₐ ≈ 5.2). It serves as a solvent, ligand, mild base/nucleophile, and core scaffold in many pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Brand Names
Not applicable.
Name
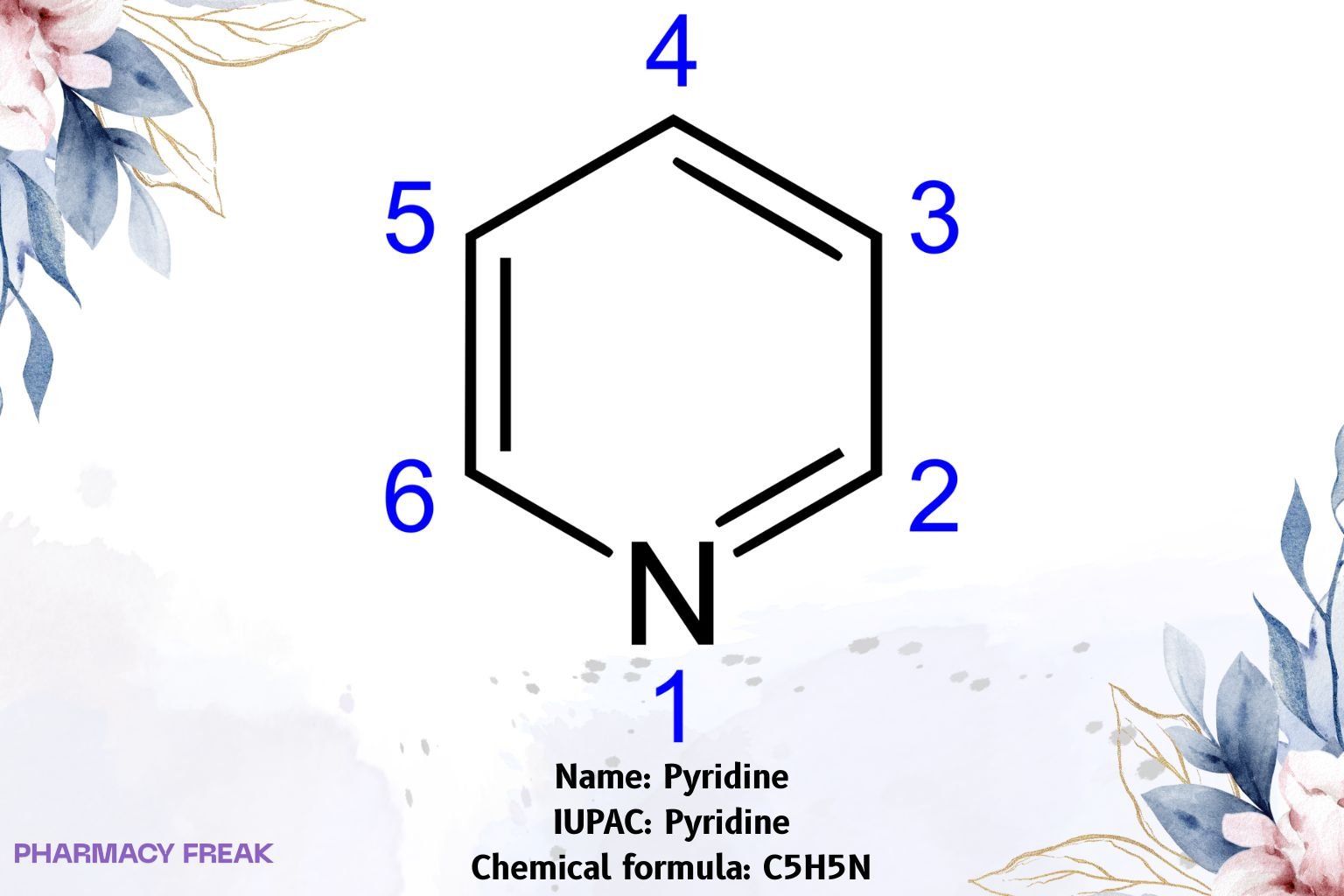
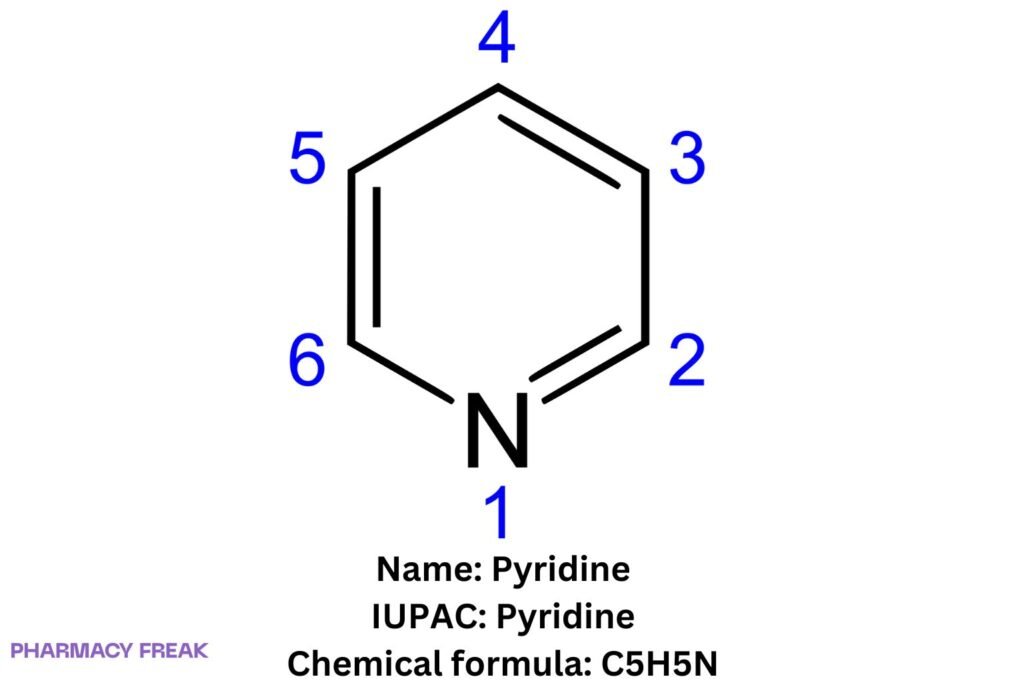
Pyridine
Background
Aromatically stabilized azabenzene; lone pair on ring nitrogen is orthogonal to the π-system (non-aromatic lone pair) → Lewis basicity and metal coordination. Characteristic reactivity: electrophilic substitution at C-3, nucleophilic substitution at C-2/C-4, N-oxidation (→ pyridine N-oxide), N-alkylation (→ pyridinium salts).
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Industrial chemical; laboratory solvent/reagent; ligand; pharmacophore motif
Structure
Weight
~79.10 g/mol
Chemical Formula
C₅H₅N
Synonyms
Azabenzene; Azine (historic); 1-Azabenzene; Pyridin
External IDs
CAS: 110-86-1; PubChem CID: 1049
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Not a therapeutic agent (parent chemical); widely used as solvent/reagent and structural motif in drugs.
Associated Conditions
Not applicable.
Associated Therapies
Not applicable.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Not applicable at drug level; industrial exposure governed by occupational safety standards.
Pharmacodynamics
Chemical—Lewis base/H-bond acceptor; forms pyridinium salts with acids; coordinates metals via ring N.
Mechanism of action
Chemical properties only: aromatic π-system with sp²-N lone pair available for protonation/coordination; directs reactivity patterns (EAS at C-3; NAS at C-2/C-4).
Absorption / Distribution / Protein binding / Metabolism / Elimination / Half-life / Clearance
Not applicable (chemical class usage).
Adverse Effects / Toxicity
Outside scope of blog’s structural brief; consult safety datasheets for exposure limits.
Pathways
Representative transformations: N-alkylation → pyridinium salts; N-oxidation → N-oxides; Chichibabin amination (NAS at C-2); Friedländer/Hantzsch syntheses use pyridine chemistry as scaffold routes.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Not applicable.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Not applicable (parent chemical); as a ligand/base, can alter metal-catalysis outcomes and acid–base equilibria.
Food Interactions
Not applicable.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
None.
Drug Categories
Heteroaromatic ring system; Nitrogen base; Ligand; Solvent/reagent
Chemical Taxonomy
Monocyclic aromatic with one ring nitrogen (1-aza-benzene); planar sp² network; pyridyl (C₅H₄N–) is the substituent group.
Affected organisms
Not applicable
5. Chemical Identifiers
CAS number
110-86-1
InChI Key
FNNPIMENNRUQGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C5H5N/c1-2-4-6-5-3-1/h1-5H
IUPAC Name
Pyridine
SMILES
n1ccccc1
6. References
IUPAC Gold Book — definition and basicity concepts for pyridine; heteroaromatic nomenclature.
NIST Chemistry WebBook — pyridine identifiers (CAS, InChI, InChIKey), spectroscopic constants.
PubChem Compound Summary (CID 1049) — formula C₅H₅N, molar mass ~79.10 g/mol, canonical SMILES/InChI.
Carey & Sundberg, Advanced Organic Chemistry — reactivity patterns (EAS at C-3; NAS at C-2/C-4), N-oxide and pyridinium chemistry.
March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry — aromaticity, directing effects, and pyridine basicity (conjugate-acid pKₐ ≈ 5.2).

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com