Table of Contents
Introduction
Sugammadex is a novel reversal agent specifically designed to antagonize the effects of aminosteroid non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers, such as rocuronium and vecuronium. It belongs to the class of selective relaxant binding agents (SRBAs) and represents a significant advancement over traditional acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Sugammadex offers rapid and effective reversal of neuromuscular blockade without cholinergic side effects.
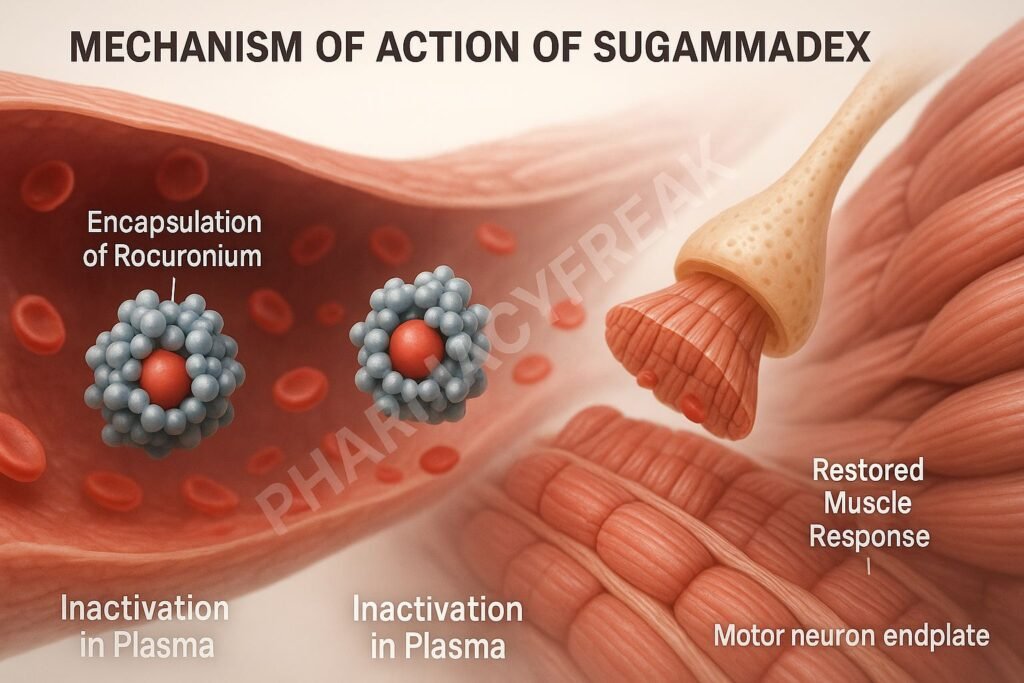
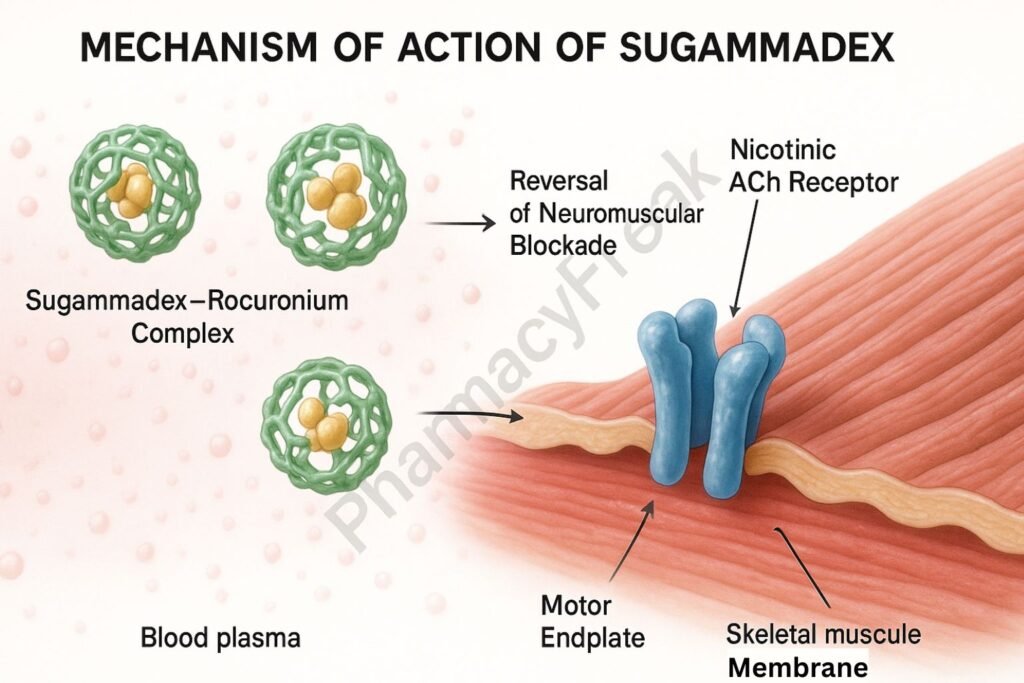
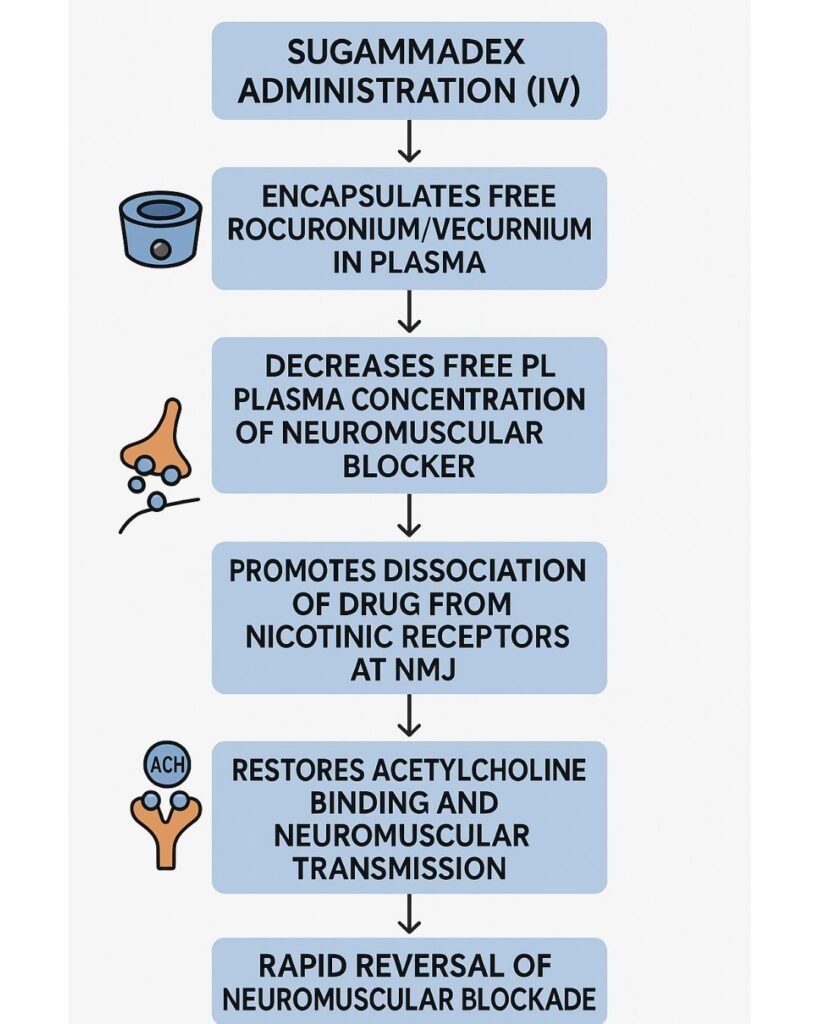
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
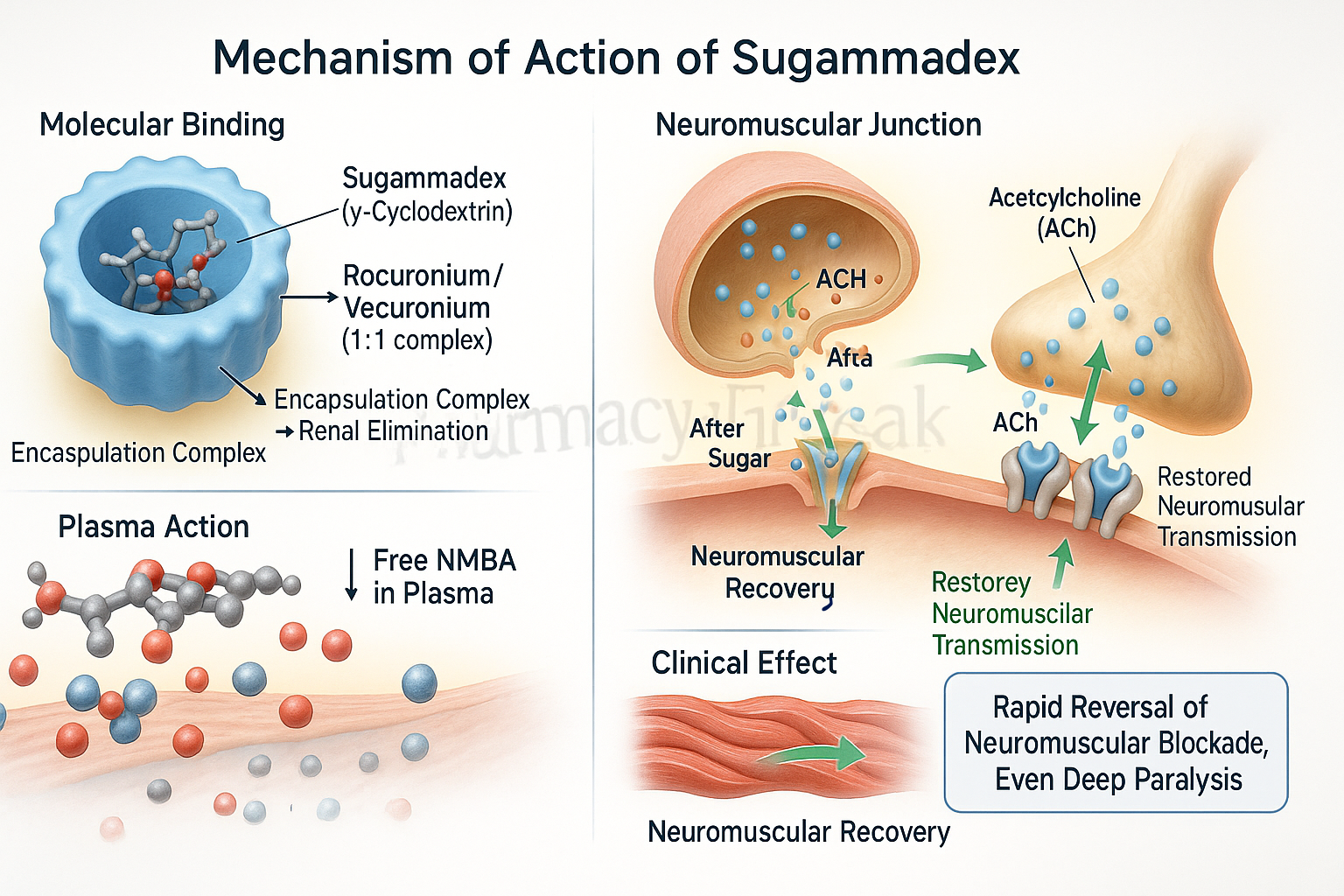
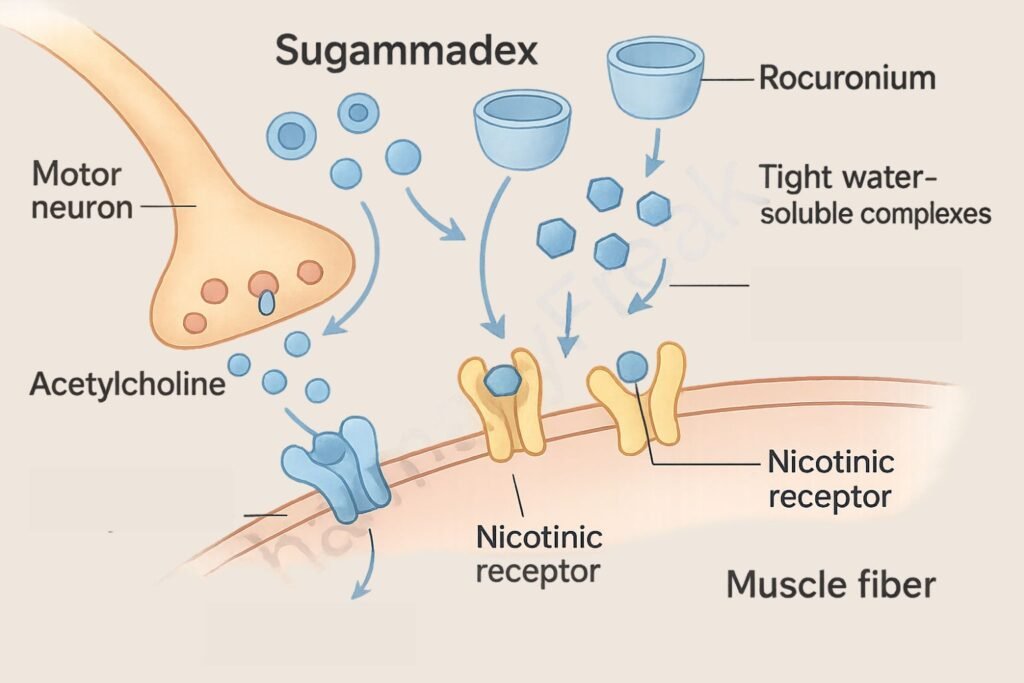
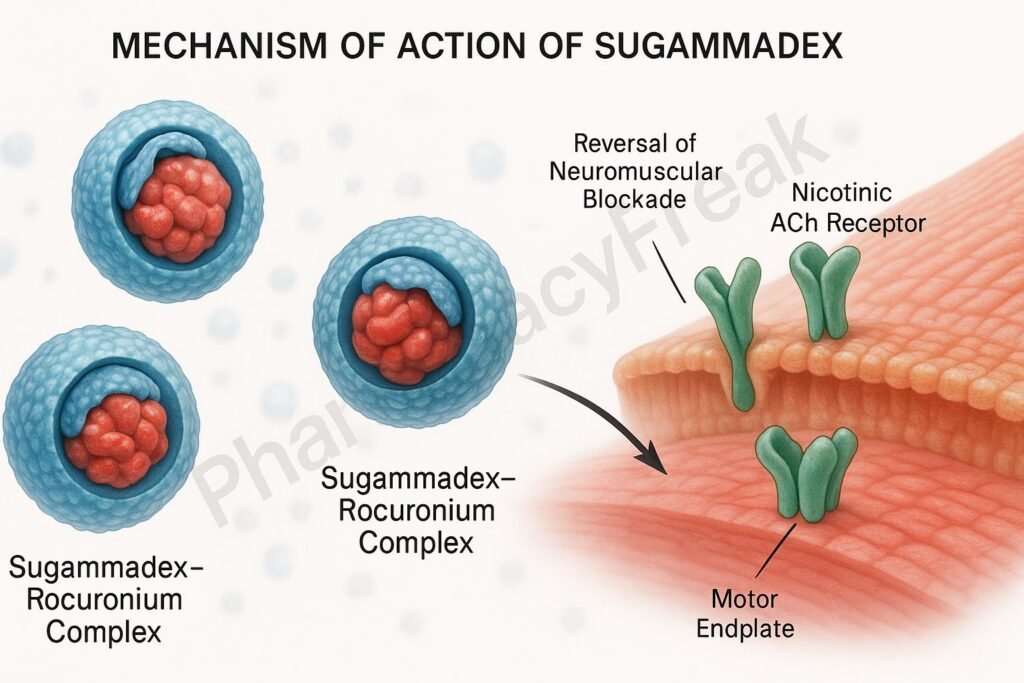
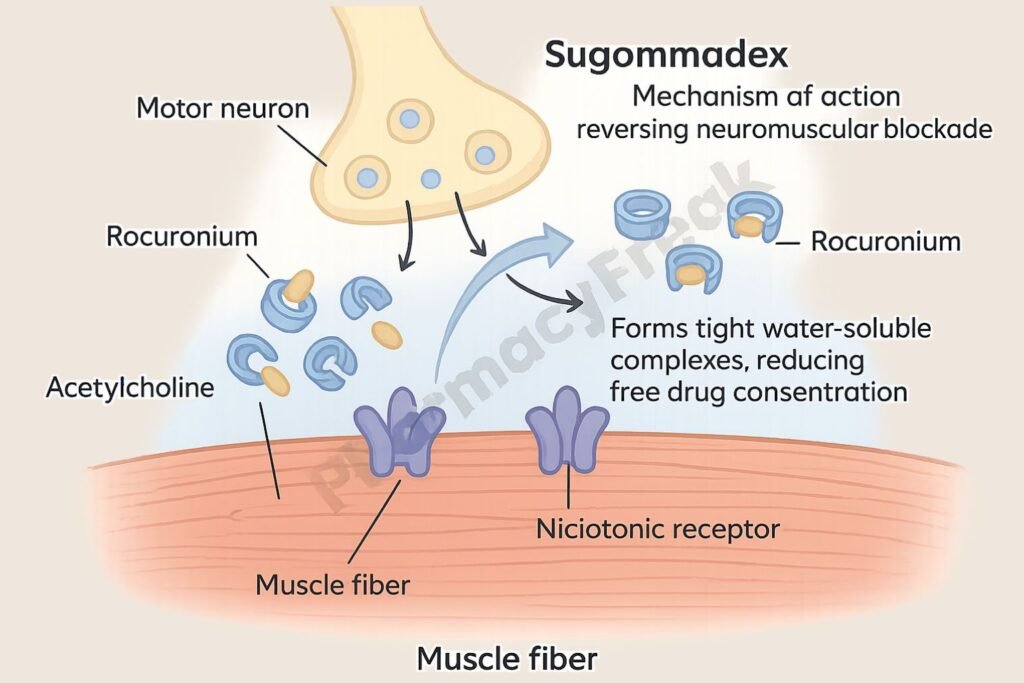
1. Encapsulation of Aminosteroid NMBAs
Sugammadex is a modified γ-cyclodextrin that binds tightly and selectively to rocuronium and vecuronium molecules.
2. Formation of a Stable Complex
Upon administration, sugammadex encapsulates free molecules of the NMBA in the plasma, creating a water-soluble complex.
3. Reduction of Free NMBA Concentration
This results in a steep concentration gradient, pulling rocuronium or vecuronium from the neuromuscular junction back into the plasma.
4. Restoration of Neuromuscular Transmission
As the free NMBA is cleared from the receptor site, acetylcholine can again bind and restore muscle function.
5. Rapid and Complete Reversal
The process is fast, predictable, and does not require anticholinergics for mitigation of side effects.
Pharmacokinetics
- Route of Administration: Intravenous
- Bioavailability: 100% (IV)
- Onset of Action: Within 3 minutes
- Half-Life: 2 hours
- Protein Binding: Negligible
- Metabolism: Not metabolized
- Excretion: Renal (unchanged drug)
Clinical Uses
- Reversal of neuromuscular blockade induced by rocuronium or vecuronium
- Used in general anesthesia settings when rapid recovery of muscle function is needed
Adverse Effects
- Bradycardia
- Hypotension
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hypersensitivity reactions (rare but serious)
- Anaphylaxis
- Prolonged coagulation parameters (transient)
- Contraindications: Severe renal impairment, known hypersensitivity
Comparative Analysis
| Parameter | Sugammadex | Neostigmine |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Rocuronium, Vecuronium | All non-depolarizing agents |
| Onset of Action | ~3 minutes | ~10–15 minutes |
| Mechanism | Encapsulation | Acetylcholinesterase inhibition |
| Cholinergic Side Effects | None | Yes (requires anticholinergic) |
| Excretion | Renal (unchanged) | Renal and hepatic |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Sugammadex is primarily used to reverse which drug?
a) Succinylcholine
b) Atracurium
c) Rocuronium
d) Cisatracurium
Answer: c) Rocuronium
2. What is the core structure of sugammadex?
a) β-cyclodextrin
b) γ-cyclodextrin
c) Polyethylene glycol
d) Amino acid peptide
Answer: b) γ-cyclodextrin
3. Which side effect is least likely with sugammadex compared to neostigmine?
a) Bradycardia
b) Nausea
c) Dry mouth
d) Hypotension
Answer: c) Dry mouth
4. How is sugammadex primarily excreted?
a) Biliary
b) Renal
c) Hepatic
d) Pulmonary
Answer: b) Renal
5. Sugammadex forms a complex with which class of muscle relaxants?
a) Depolarizing agents
b) Benzodiazepines
c) Aminosteroid non-depolarizing agents
d) Barbiturates
Answer: c) Aminosteroid non-depolarizing agents
FAQs
Q1. Can sugammadex be used for succinylcholine reversal?
No, it is ineffective against depolarizing neuromuscular blockers like succinylcholine.
Q2. Does sugammadex require co-administration of atropine?
No, it does not cause cholinergic side effects and thus does not need anticholinergics.
Q3. Is sugammadex safe in renal impairment?
Use is not recommended in severe renal dysfunction due to renal elimination.
Q4. How quickly does sugammadex act?
It typically reverses neuromuscular blockade within 3 minutes.
Q5. Does sugammadex interfere with hormonal contraceptives?
Yes, a transient reduction in progesterone levels may occur; advise additional contraception for 7 days.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- Prescribing information for Sugammadex
- Clinical anesthesia guidelines and reviews
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com