Table of Contents
Introduction
Metronidazole is a unique antibiotic and antiprotozoal agent that exerts its action by damaging DNA in anaerobic organisms. It’s a first-line treatment for anaerobic bacterial infections, Clostridium difficile, and protozoal infections like Giardiasis and Trichomoniasis. It is especially important for medical and pharmacy students in the US preparing for USMLE, NCLEX, NAPLEX, and GPAT, due to its broad clinical use, adverse effect profile, and unique mechanism among antibiotics.
Mechanism of Action of Metronidazole: Step-by-Step
- Passive diffusion into anaerobic organisms
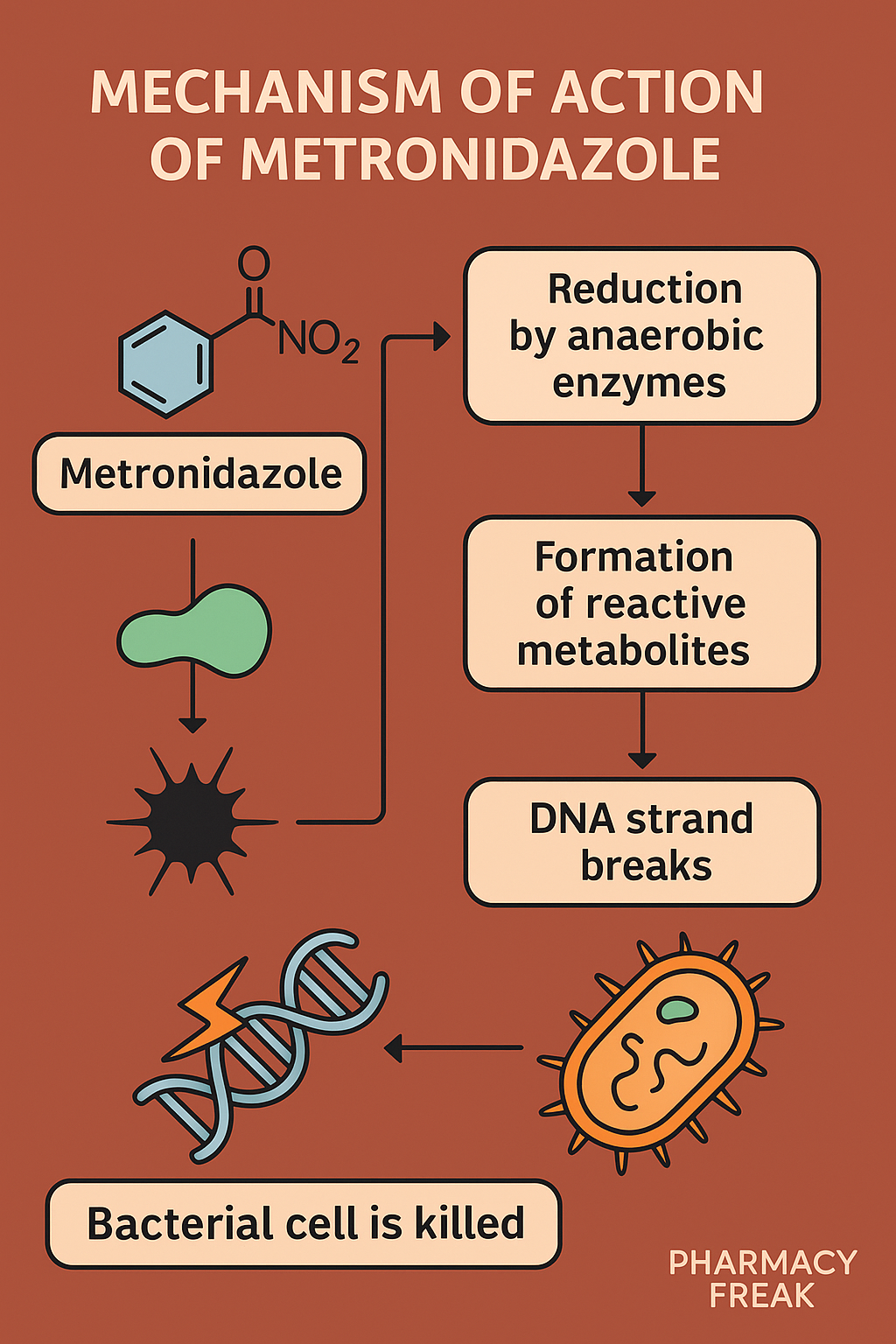
Metronidazole enters microbial cells by passive diffusion, as it is a lipophilic molecule. - Reduction of nitro group in anaerobic environment
In anaerobes and protozoa, low redox potential allows the nitro group of metronidazole to be reduced by ferredoxin-like proteins. - Formation of reactive free radicals
This reduction generates nitroso free radicals, which are cytotoxic. - Disruption of DNA structure
The reactive radicals bind to DNA, causing strand breaks, loss of helical structure, and inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis. - Cell death
The cumulative DNA damage leads to cell death, making metronidazole bactericidal and protozoacidal. - Selective toxicity
Mammalian cells do not have the enzymes necessary to reduce metronidazole, ensuring selective targeting of pathogens.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Metronidazole
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bioavailability | ~100% (excellent oral absorption) |
| Half-life | ~8 hours |
| Protein binding | ~10–20% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (via CYP enzymes) |
| Excretion | Urine (~60–80% as metabolites) |
| CNS penetration | Good (used in brain abscesses) |
Clinical Uses of Metronidazole
- Anaerobic infections (Bacteroides, Clostridium spp.)
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD)
- Trichomoniasis
- Giardiasis
- Amebiasis
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Intra-abdominal and pelvic infections (with other agents)
- Brain abscesses (anaerobic coverage)
Adverse Effects of Metronidazole
- Metallic taste
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort
- Headache and dizziness
- Peripheral neuropathy (with prolonged use)
- Disulfiram-like reaction (with alcohol)
- Darkened urine
- CNS toxicity (rare)
Comparative Analysis: Metronidazole vs Tinidazole
| Feature | Metronidazole | Tinidazole |
|---|---|---|
| Half-life | ~8 hours | ~12–14 hours |
| Duration of therapy | Longer (5–10 days) | Shorter (single dose to 3 days) |
| GI side effects | More common | Less common |
| Alcohol interaction | Strong disulfiram-like reaction | Same risk |
Practice MCQs
Q1. Metronidazole acts by:
a. Inhibiting peptidoglycan synthesis
b. Inhibiting folate synthesis
c. Disrupting bacterial DNA via radicals ✅
d. Inhibiting 50S ribosome
Q2. Which organisms activate metronidazole?
a. Aerobic bacteria
b. Gram-positive cocci
c. Anaerobes ✅
d. Fungi
Q3. A classic adverse effect with alcohol and metronidazole is:
a. Hypoglycemia
b. Red man syndrome
c. Disulfiram-like reaction ✅
d. Serotonin syndrome
Q4. Metronidazole is first-line for:
a. Syphilis
b. Clostridium difficile ✅
c. MRSA
d. TB
Q5. Which of the following is a protozoal indication for metronidazole?
a. Leishmaniasis
b. Trichomoniasis ✅
c. Malaria
d. Trypanosomiasis
Q6. What is the bioavailability of metronidazole?
a. 40%
b. 60%
c. ~100% ✅
d. <10%
Q7. Peripheral neuropathy occurs with:
a. Short use
b. Long-term use ✅
c. IV only
d. Rectal administration
Q8. How is metronidazole excreted?
a. Hepatic
b. Pulmonary
c. Renal ✅
d. Sweat
Q9. Can metronidazole be used in brain infections?
a. No
b. Yes, due to good CNS penetration ✅
c. Only topically
d. Only rectally
Q10. Which class best describes metronidazole?
a. Antifungal
b. Aminoglycoside
c. Nitroimidazole ✅
d. Glycopeptide
FAQs
Q1: Is metronidazole safe during pregnancy?
It is generally safe in the second and third trimesters, but caution is advised in the first trimester.
Q2: Why avoid alcohol with metronidazole?
It causes a disulfiram-like reaction — flushing, nausea, vomiting, and palpitations.
Q3: Can metronidazole be used in combination therapy?
Yes, it is often combined with cephalosporins or aminoglycosides for polymicrobial infections.
Q4: How long is metronidazole therapy for trichomoniasis?
Usually 2–5 days, or sometimes a single 2g dose.
Q5: Can it treat H. pylori?
Yes, metronidazole is part of triple therapy in H. pylori eradication protocols.
References
- KD Tripathi – Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
- Goodman & Gilman – The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
- Sparsh Gupta – Review of Pharmacology
- NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547677/

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com
