Table of Contents
Introduction
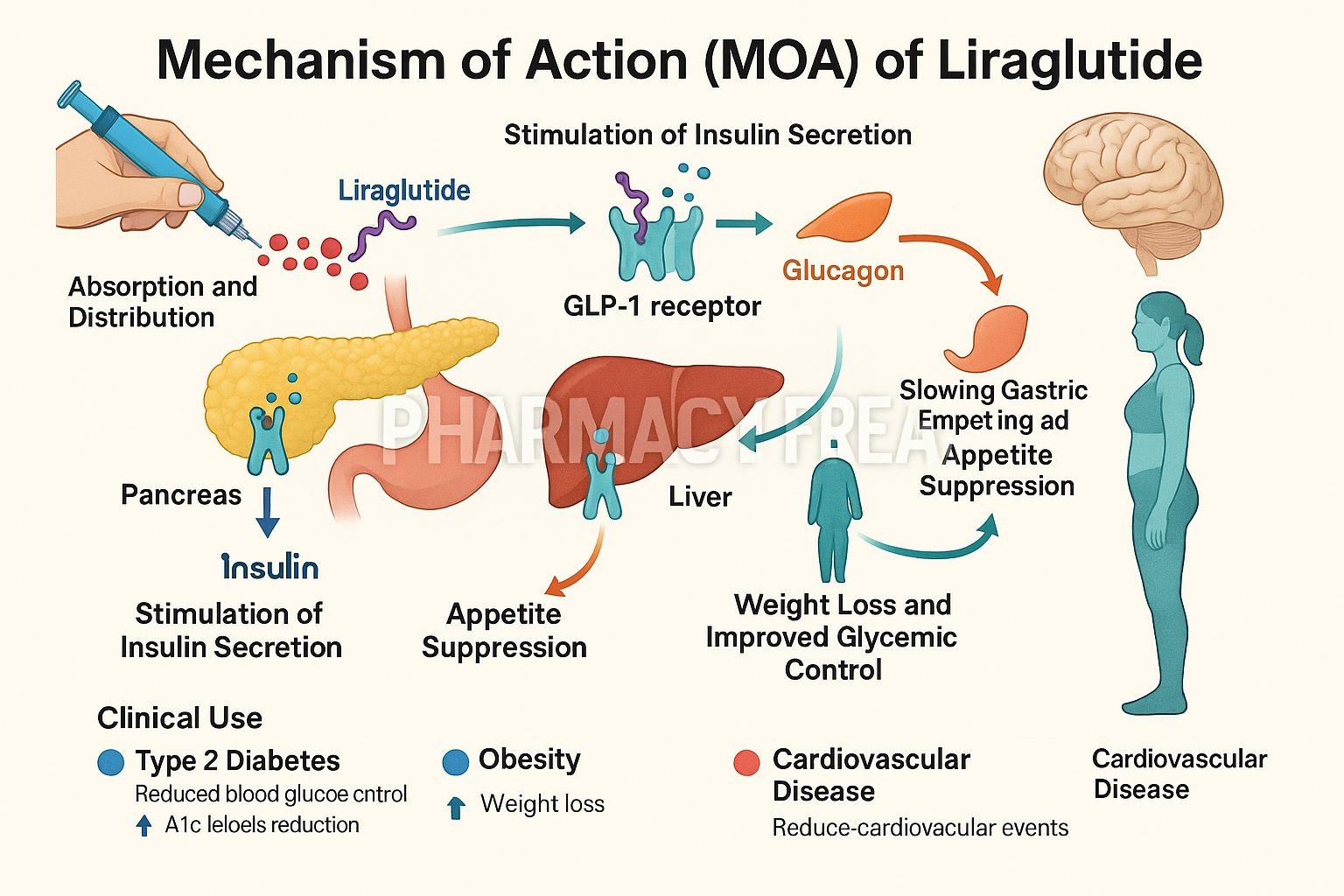
Liraglutide is a long-acting GLP‑1 receptor agonist, injected once daily. It’s used for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and chronic weight management, and also approved for reducing cardiovascular risk in patients with T2DM and established heart disease. It mimics the effects of endogenous GLP‑1 to improve glycemic control and promote satiety.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
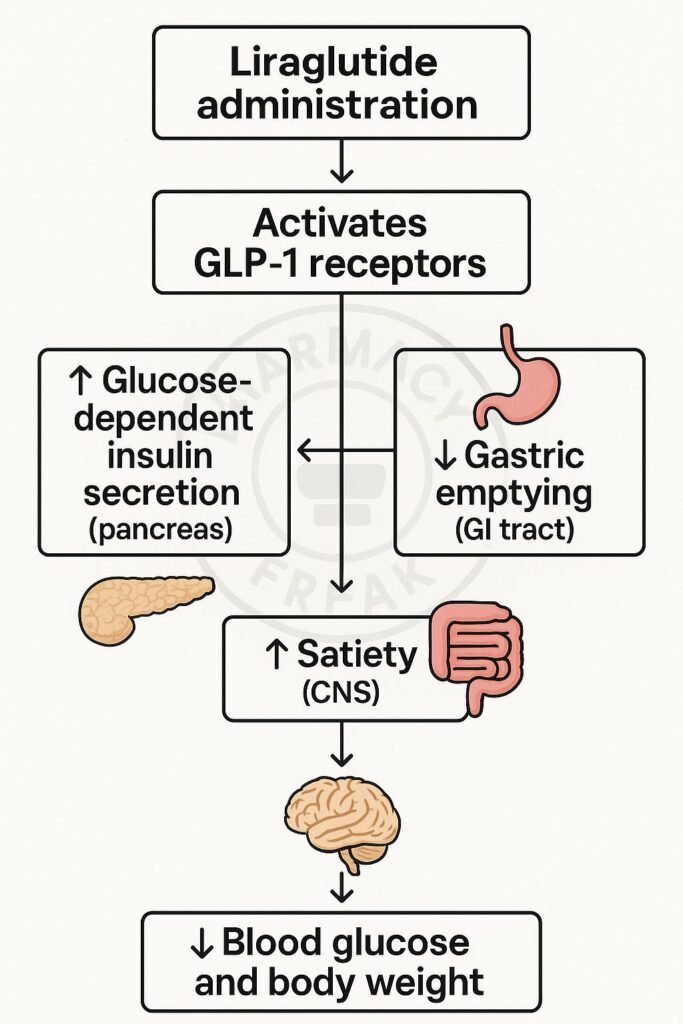
- GLP‑1 receptor activation
Liraglutide binds to GLP‑1 receptors located on pancreatic β‑cells, α‑cells, the brain, and gastrointestinal tract. - Glucose-dependent insulin secretion
When blood glucose levels are high, it enhances insulin release from β‑cells. - Glucagon suppression
It reduces glucagon secretion from α‑cells in hyperglycemic states. - Delayed gastric emptying
It slows gastric motility, reducing postprandial glucose spikes. - Appetite reduction and satiety
It activates satiety centers in the hypothalamus, leading to decreased caloric intake and weight loss. - Cardiovascular protection
It improves endothelial function, reduces inflammation, and lowers blood pressure—offering CV benefits in diabetic patients.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Subcutaneous injection, once daily |
| Absorption | ~55–65% |
| Time to Peak (Tmax) | 8–12 hours |
| Protein Binding | ~98–99% |
| Metabolism | Proteolysis into small peptides |
| Half-life | ~13 hours |
| Excretion | Urine and feces |
Clinical Uses
- Glycemic control in type 2 diabetes
- Chronic weight management in obesity/overweight
- Reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in T2DM with cardiovascular disease
Adverse Effects
- Gastrointestinal complaints: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation
- Rare: pancreatitis
- Slight increase in heart rate
- Injection-site reactions
- Not recommended in patients with personal/family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or MEN2
Comparative Analysis
| Agent | Duration | Dosing | Weight Impact | Cardiovascular Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liraglutide | Medium-acting | Daily | Moderate weight loss | Proven CV risk reduction |
| Semaglutide | Long-acting | Weekly | Larger weight loss | Robust CV benefits |
| Dulaglutide | Long-acting | Weekly | Moderate weight loss | CV protection |
MCQs
- Liraglutide acts primarily on which receptor?
a) GIP b) GLP‑1 c) DPP‑4 d) SGLT2
Answer: b) GLP‑1 - It enhances insulin secretion that is:
a) Glucose-independent b) Glucose-dependent c) Suppressed d) Unaffected
Answer: b) Glucose-dependent - The effect on gastric emptying is:
a) Accelerated b) Unchanged c) Delayed d) Inhibited only at night
Answer: c) Delayed - A key cardiovascular benefit of liraglutide is:
a) Increased LDL b) Improved endothelial function c) Elevated BP d) Pro-arrhythmic effect
Answer: b) Improved endothelial function - Liraglutide is administered:
a) Weekly injection b) Daily injection c) Oral tablet d) Daily infusion
Answer: b) Daily injection - Protein binding of liraglutide is:
a) 50% b) 75% c) ~98% d) 100%
Answer: c) ~98% - Which patient should avoid liraglutide?
a) History of medullary thyroid carcinoma b) T2DM without CV disease c) Overweight without diabetes d) T2DM with CKD
Answer: a) History of medullary thyroid carcinoma - The half-life is approximately:
a) 4 hours b) 13 hours c) 24 hours d) 7 days
Answer: b) 13 hours - Liraglutide’s weight loss is due to:
a) Increased basal metabolic rate b) Appetite reduction c) Increased fat absorption d) Renal glucose loss
Answer: b) Appetite reduction - Compared to dulaglutide and semaglutide, liraglutide is:
a) Daily dosing b) Oral c) Weekly dosing d) Injectable monthly
Answer: a) Daily dosing
FAQs
1. How soon does liraglutide reduce blood sugar?
Improvement in glycemic control is typically seen within 1–2 weeks after starting treatment.
2. Does it cause hypoglycemia when used alone?
No—it has minimal hypoglycemia risk when not combined with insulin or insulin secretagogues.
3. Can liraglutide aid weight loss?
Yes—patients may lose 5–10% of body weight over several months.
4. Is liraglutide safe in patients with renal impairment?
Yes—no dose adjustment is needed in mild-to-moderate renal dysfunction.
5. How often is thyroid function monitored?
Routine monitoring is not required unless there is family or personal history of thyroid cancer.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th Edition
- KD Tripathi. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 8th Edition
- DrugBank: Liraglutide pharmacology summary
- StatPearls: GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
- PubMed review: Cardiovascular effects of liraglutide

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com