Table of Contents
Introduction
Ipilimumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody classified under immune checkpoint inhibitors. It plays a pivotal role in cancer immunotherapy by targeting cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), a regulatory molecule that downregulates immune responses. By blocking CTLA-4, ipilimumab enhances T-cell activation and proliferation, leading to a more robust antitumor immune response. It has been approved for treating metastatic melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, and other malignancies.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
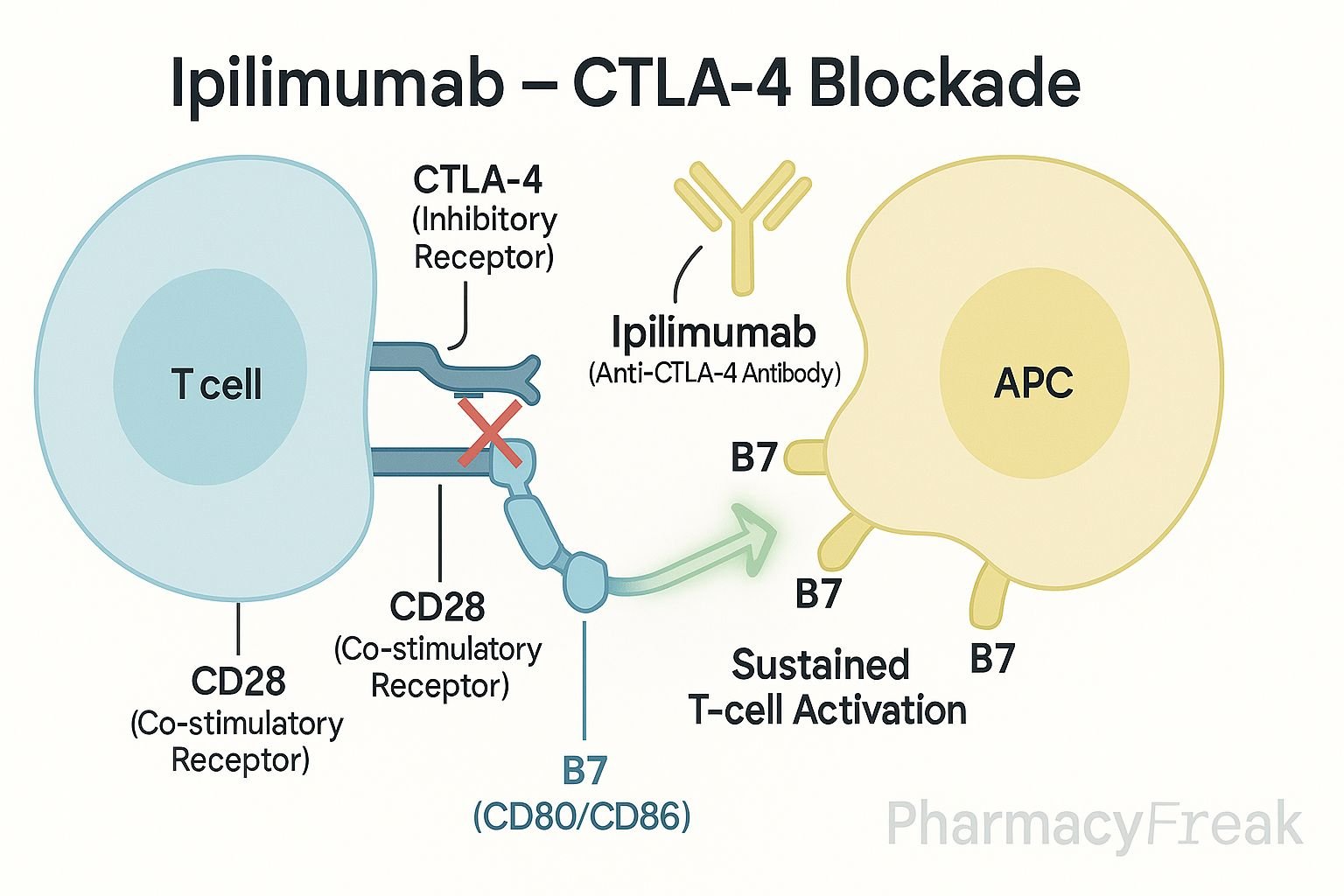
1. CTLA-4 Receptor Expression on T-cells
CTLA-4 is upregulated on activated T-cells and competes with CD28 for binding to B7 molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
2. Inhibitory Signal Transmission
When CTLA-4 binds to B7 (CD80/CD86), it sends an inhibitory signal to T-cells, reducing their activation.
3. Ipilimumab Binding to CTLA-4
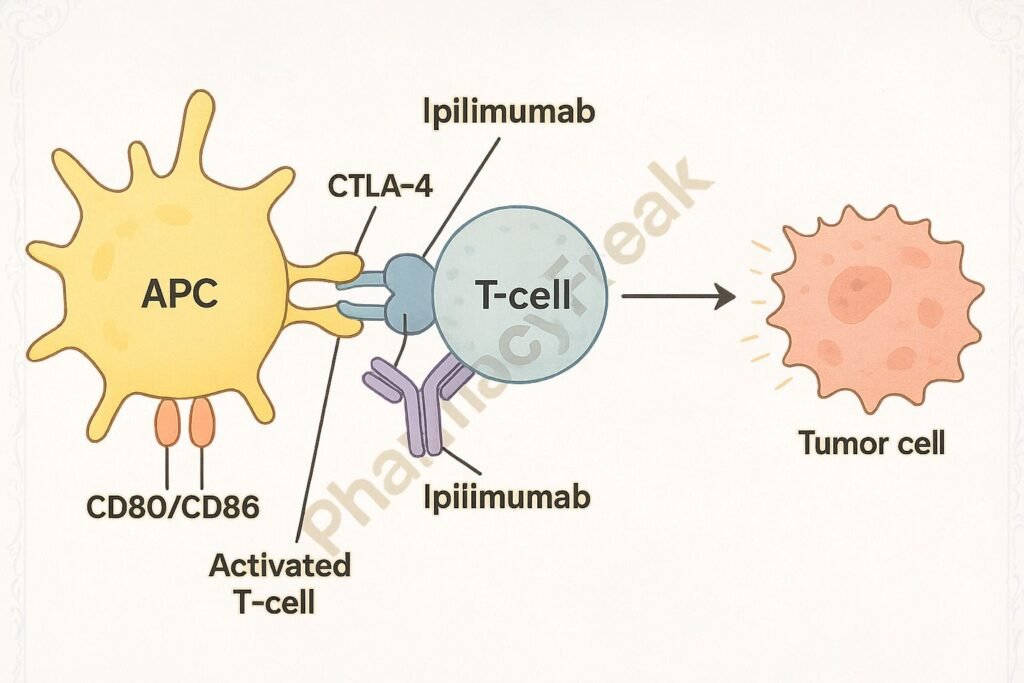
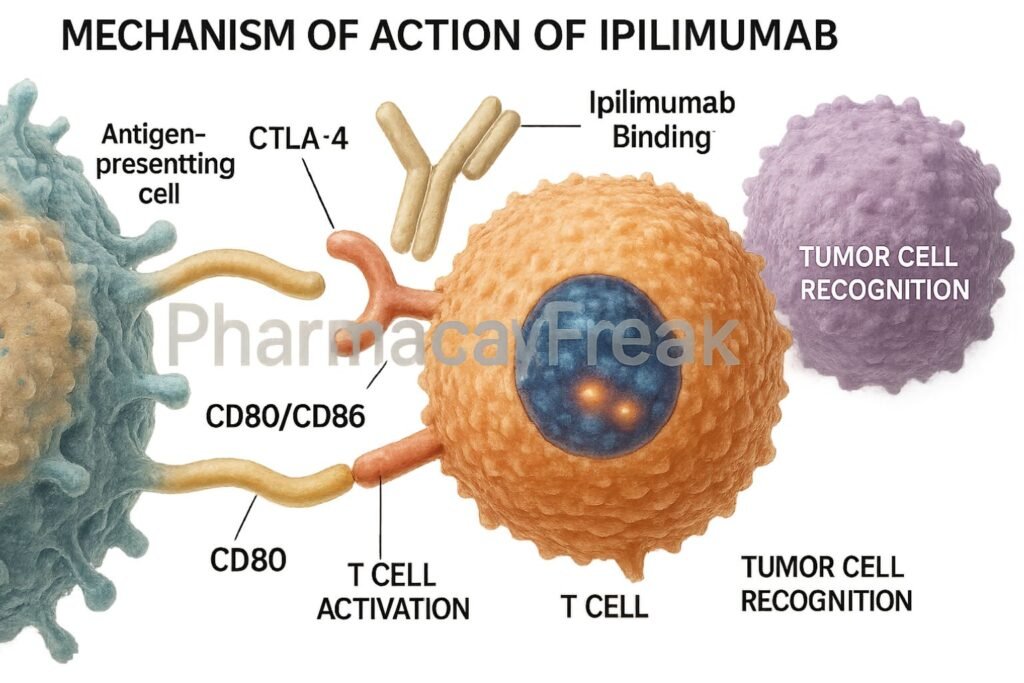
Ipilimumab selectively binds to CTLA-4, preventing its interaction with B7 molecules.
4. Enhanced CD28 Co-stimulation
By blocking CTLA-4, the co-stimulatory signal through CD28 and B7 is enhanced, promoting T-cell activation and proliferation.
5. Augmentation of Antitumor Immunity
Activated T-cells infiltrate tumors and mount an immune response against cancer cells.
6. Memory T-cell Development
Ipilimumab promotes the formation of memory T-cells, providing sustained immune surveillance.

Pharmacokinetics
- Route of Administration: Intravenous infusion
- Bioavailability: 100% (IV)
- Volume of Distribution: ~7.21 L
- Half-Life: ~15.4 days
- Metabolism: Catabolized into peptides and amino acids (like other IgG antibodies)
- Excretion: Not renally or hepatically cleared; degraded by reticuloendothelial system
Clinical Uses
- Unresectable or metastatic melanoma
- Advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in combination with nivolumab
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in combination regimens
- Colorectal cancer (MSI-H/dMMR) in combination with nivolumab
Adverse Effects
- Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs):
- Colitis
- Hepatitis
- Endocrinopathies (thyroiditis, hypophysitis)
- Dermatitis
- Pneumonitis
- Infusion Reactions
- Fatigue, nausea, rash
Management: Prompt corticosteroid therapy is often required to mitigate irAEs.
Comparative Analysis
| Parameter | Ipilimumab | Nivolumab |
|---|---|---|
| Target | CTLA-4 | PD-1 |
| T-cell Activation Phase | Early (priming phase) | Later (effector phase) |
| Indications | Melanoma, RCC, NSCLC | Melanoma, NSCLC, HCC, CRC |
| Adverse Events Profile | More irAEs | Generally fewer irAEs |
| Route of Administration | IV | IV |
| Combination Use | Common with Nivolumab | Common with Ipilimumab |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What is the main target of ipilimumab?
a) PD-1 receptor
b) CTLA-4 receptor
c) CD28 receptor
d) CD80/CD86 ligands
Answer: b) CTLA-4 receptor
2. Ipilimumab promotes T-cell activation by:
a) Blocking CD28
b) Inhibiting B7 expression
c) Blocking CTLA-4 interaction with B7
d) Activating PD-L1
Answer: c) Blocking CTLA-4 interaction with B7
3. Which of the following is an immune-related adverse effect of ipilimumab?
a) Nephrotoxicity
b) Hepatitis
c) Cardiomyopathy
d) Ototoxicity
Answer: b) Hepatitis
4. How is ipilimumab administered?
a) Subcutaneous
b) Oral
c) Intramuscular
d) Intravenous
Answer: d) Intravenous
5. Which drug is often combined with ipilimumab in cancer therapy?
a) Methotrexate
b) Nivolumab
c) Cisplatin
d) Pembrolizumab
Answer: b) Nivolumab
FAQs
Q1. How does ipilimumab differ from PD-1 inhibitors?
Ipilimumab acts at the early priming phase of T-cell activation by blocking CTLA-4, whereas PD-1 inhibitors act later at the effector phase.
Q2. Can ipilimumab be used alone?
Yes, but it is more commonly used in combination with other checkpoint inhibitors like nivolumab for enhanced efficacy.
Q3. What are common immune-related adverse events of ipilimumab?
Colitis, hepatitis, thyroiditis, and dermatitis are frequently observed.
Q4. Does ipilimumab require renal dose adjustment?
No, it does not undergo renal clearance.
Q5. How are severe irAEs managed during ipilimumab therapy?
Systemic corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- Clinical trials and FDA prescribing information for Ipilimumab
- Oncology treatment guidelines and immunotherapy reviews
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com