Table of Contents
Introduction
Flomax is the brand name for tamsulosin, a selective α₁-adrenergic receptor antagonist used primarily in the management of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It is highly exam-relevant due to its receptor selectivity, uroselective action, and reduced cardiovascular adverse effects compared with nonselective α-blockers.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
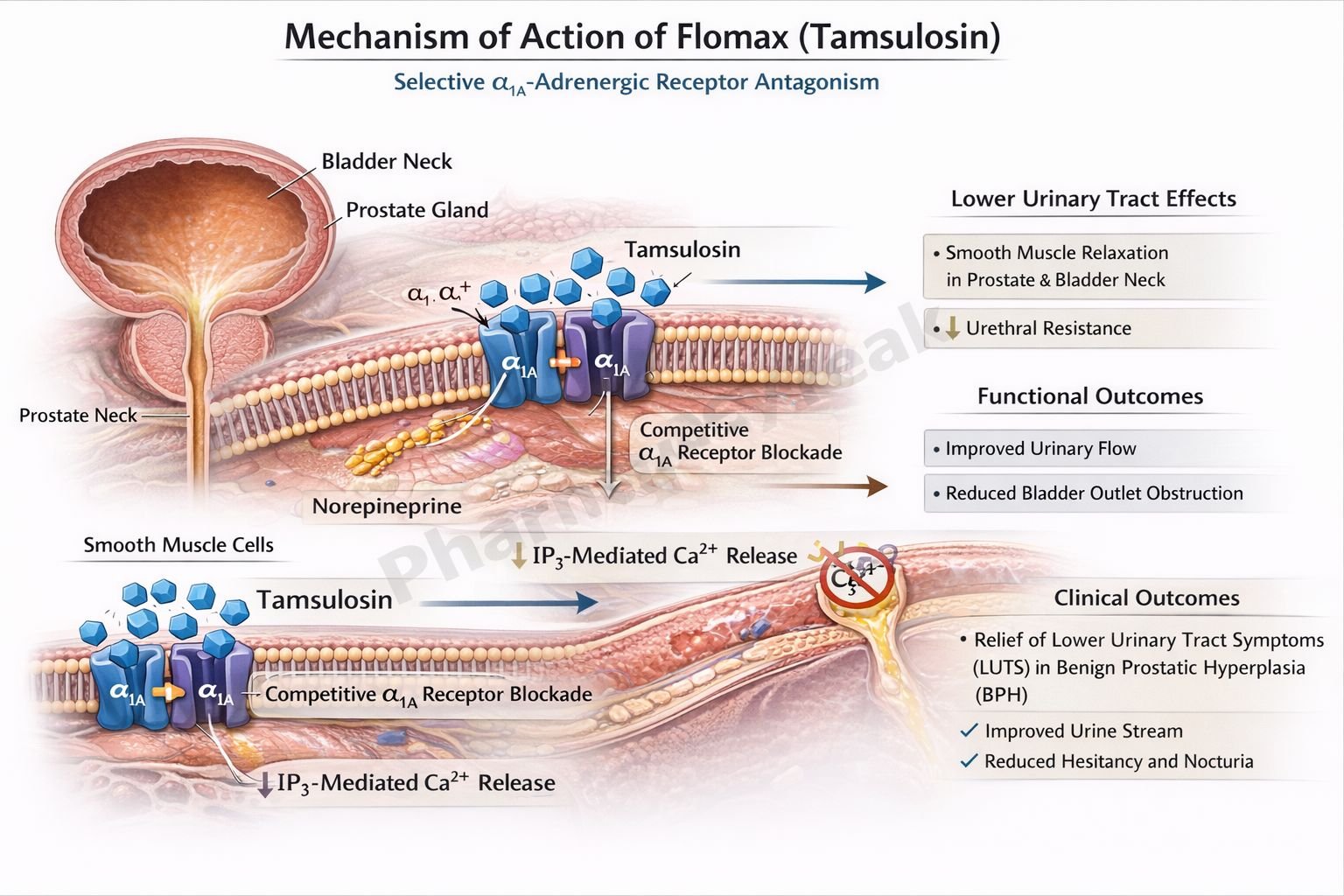
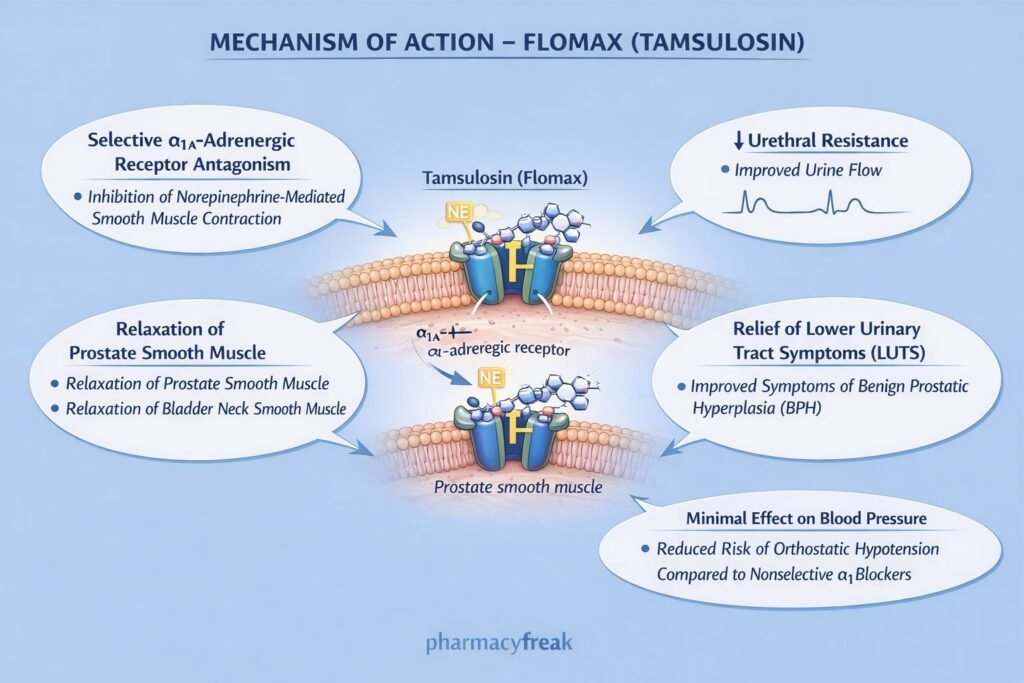
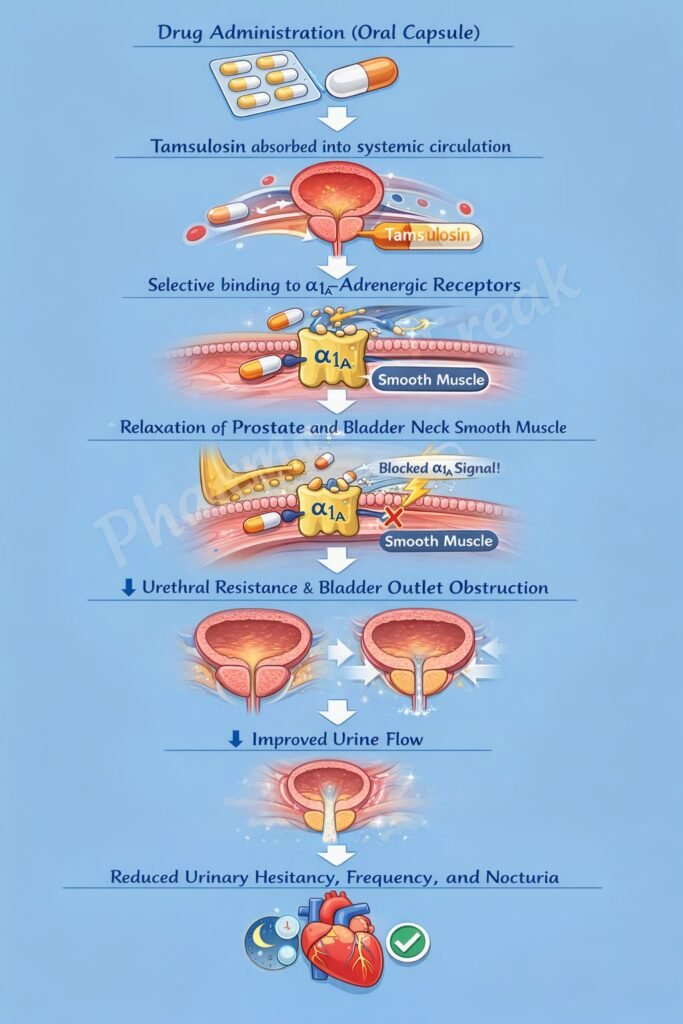
Flomax improves urinary flow by relaxing smooth muscle in the prostate and bladder neck.
Step 1: Targeting α₁-adrenergic receptors
Tamsulosin selectively binds to α₁-adrenergic receptors, particularly the α₁A subtype.
Step 2: Blockade of α₁A receptors in the prostate
α₁A receptors are predominantly located in the prostate, bladder neck, and prostatic urethra. Their blockade reduces smooth muscle tone.
Step 3: Inhibition of Gq-mediated signaling
α₁ receptor blockade inhibits the phospholipase C pathway, reducing IP₃-mediated intracellular calcium release.
Step 4: Smooth muscle relaxation
Decreased intracellular calcium leads to relaxation of smooth muscle in the prostate and bladder outlet.
Step 5: Improved urinary flow and symptom relief
Reduced urethral resistance improves urine flow and alleviates symptoms such as hesitancy, weak stream, and incomplete bladder emptying.
Exam pearl:
Flomax does not reduce prostate size—it provides symptomatic relief only.
Pharmacokinetics
- Route of administration: Oral
- Bioavailability: ~90%
- Protein binding: >95%
- Distribution: Extensive, including prostate tissue
- Metabolism: Hepatic (CYP3A4 and CYP2D6)
- Half-life: 9–15 hours
- Excretion: Urine (metabolites and unchanged drug)
- Dosing: Once daily
Clinical Uses
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Lower urinary tract symptoms (urgency, frequency, weak stream)
- Medical expulsive therapy for ureteric stones (off-label)
Flomax is preferred in elderly patients due to minimal blood pressure effects.
Adverse Effects
Common:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Rhinitis
- Fatigue
Genitourinary:
- Abnormal ejaculation
- Retrograde ejaculation
Cardiovascular:
- Orthostatic hypotension (less common than nonselective α-blockers)
Ophthalmic:
- Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome (important surgical warning)
Comparative Analysis
Tamsulosin (Flomax) vs Terazosin vs Finasteride
| Feature | Tamsulosin | Terazosin | Finasteride |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug class | α₁A blocker | Nonselective α₁ blocker | 5α-reductase inhibitor |
| Effect on prostate size | No | No | Yes |
| Onset of symptom relief | Rapid | Rapid | Slow (months) |
| Effect on BP | Minimal | Significant | None |
| Sexual side effects | Ejaculatory | Minimal | Decreased libido |
Explanation:
Flomax provides rapid symptomatic relief without significant hypotension due to α₁A selectivity. Finasteride reduces prostate size but has a delayed onset of action.
MCQs
- Flomax primarily blocks which receptor subtype?
a) α₁B
b) α₁D
c) α₁A
d) β₁
Answer: c) α₁A
- Primary site of action of Flomax is the:
a) Renal tubules
b) Prostate smooth muscle
c) Detrusor muscle
d) Adrenal medulla
Answer: b) Prostate smooth muscle
- Flomax improves urinary symptoms by:
a) Shrinking prostate size
b) Increasing bladder contraction
c) Relaxing smooth muscle
d) Increasing urine production
Answer: c) Relaxing smooth muscle
- Flomax has minimal hypotensive effect because it is:
a) Poorly absorbed
b) Short acting
c) α₁A selective
d) Renally excreted
Answer: c) α₁A selective
- A unique adverse effect associated with Flomax is:
a) Gynecomastia
b) Floppy iris syndrome
c) Hepatotoxicity
d) Hyperkalemia
Answer: b) Floppy iris syndrome
- Flomax is metabolized mainly by:
a) CYP1A2
b) CYP2C9
c) CYP3A4 and CYP2D6
d) MAO
Answer: c) CYP3A4 and CYP2D6
- Flomax does NOT affect:
a) Urinary flow rate
b) Prostate smooth muscle tone
c) Prostate gland size
d) Bladder outlet resistance
Answer: c) Prostate gland size
- Ejaculatory dysfunction with Flomax is due to:
a) Testosterone suppression
b) Smooth muscle relaxation
c) Estrogen excess
d) Dopamine blockade
Answer: b) Smooth muscle relaxation
- Flomax may be used off-label for:
a) Renal failure
b) Kidney stone expulsion
c) Overactive bladder
d) Prostate cancer
Answer: b) Kidney stone expulsion
- Best patient population for Flomax is:
a) Young men with hypotension
b) Elderly men with BPH
c) Women with stress incontinence
d) Children with enuresis
Answer: b) Elderly men with BPH
FAQs
1. Does Flomax reduce prostate size?
No, it provides symptomatic relief only.
2. Why is Flomax preferred over terazosin?
Due to fewer blood pressure effects.
3. Can Flomax cause erectile dysfunction?
It more commonly causes ejaculatory abnormalities.
4. What surgical warning is associated with Flomax?
Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome.
5. How soon does Flomax work?
Symptom relief usually begins within days.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com