Table of Contents
Introduction
Desmopressin (1-deamino-8-D-arginine vasopressin; DDAVP) is a synthetic analogue of the natural antidiuretic hormone vasopressin. It exhibits strong antidiuretic properties with minimal vasopressor activity, which makes it an effective and safer alternative in treating disorders involving water balance and bleeding diatheses. Its high affinity for V2 receptors and negligible action on V1 receptors differentiates it from native vasopressin, allowing selective therapeutic utility.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
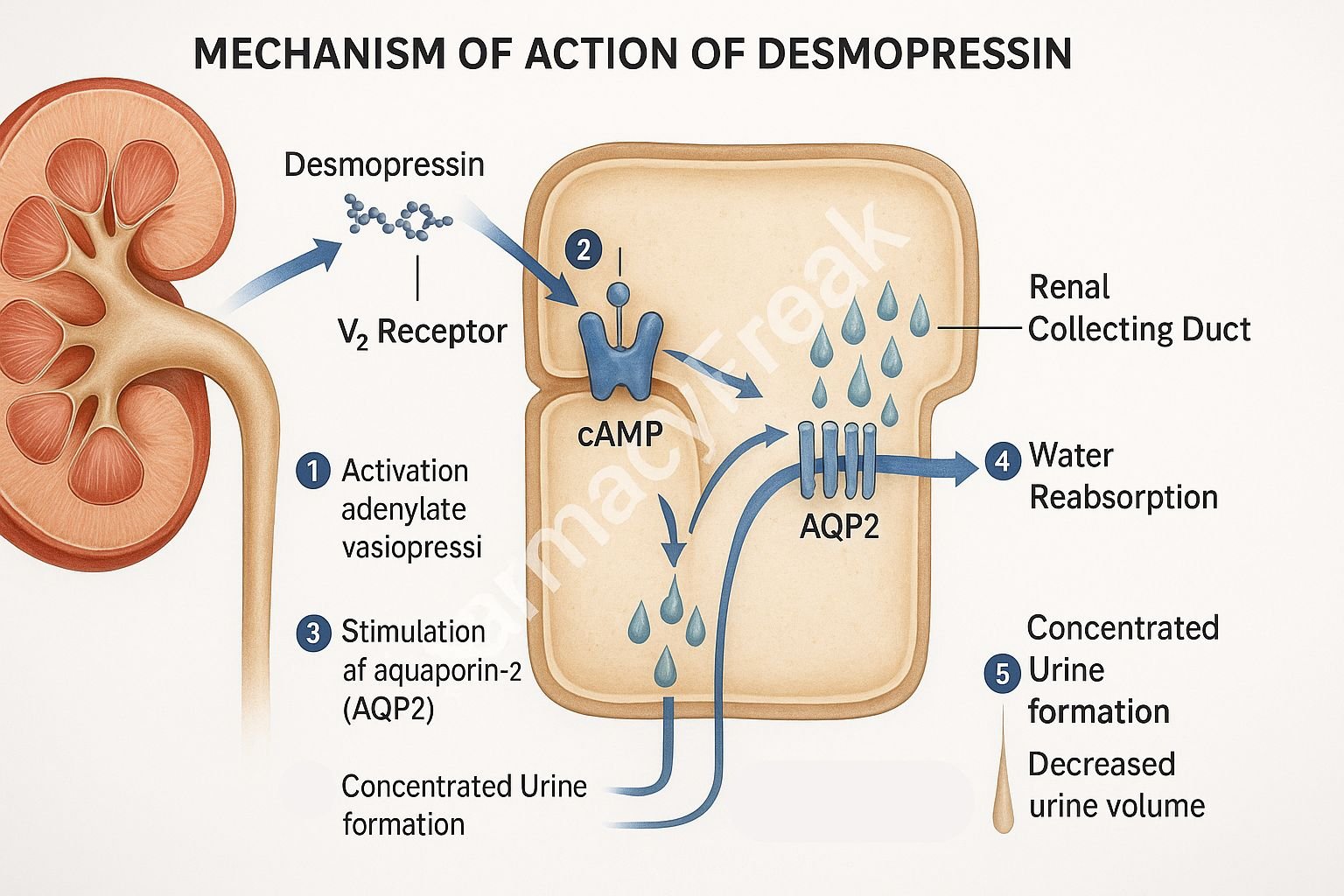
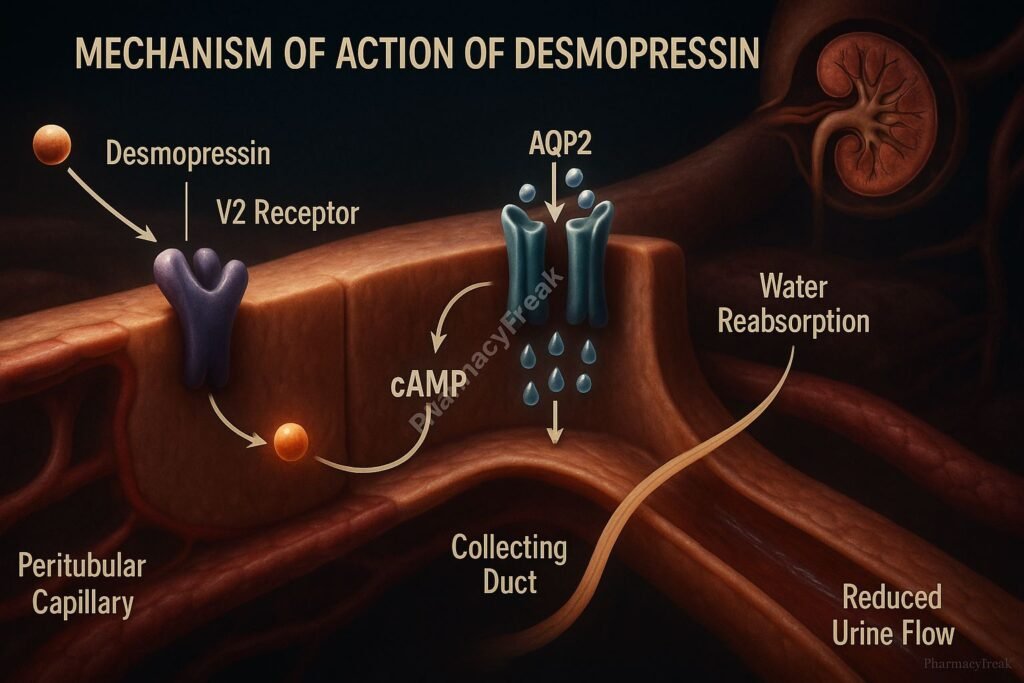
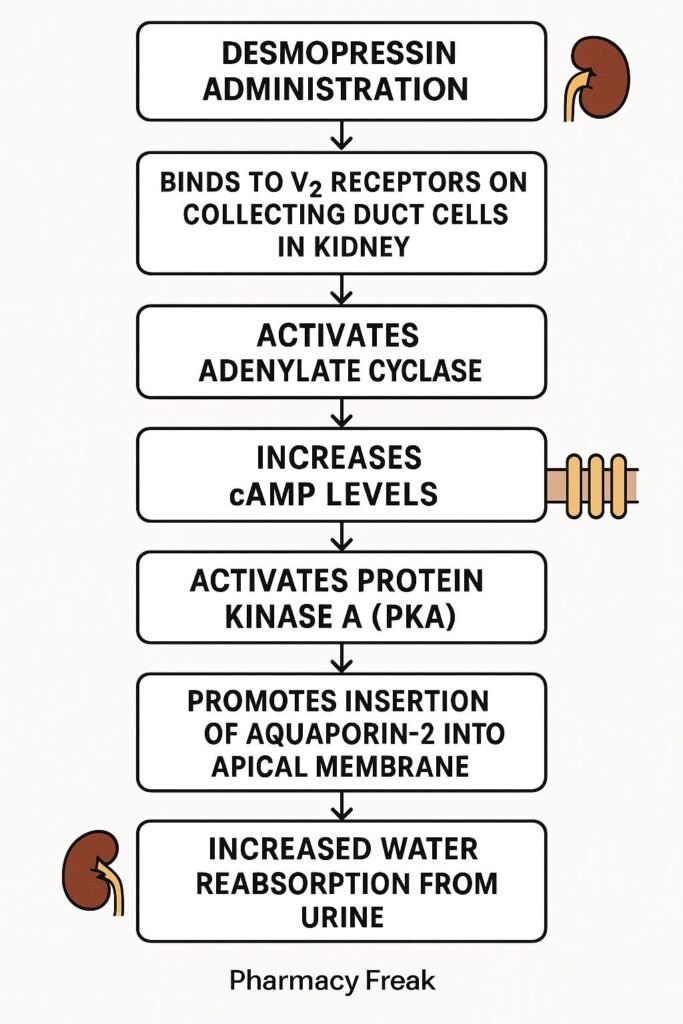
- Binding to V2 Receptors
Desmopressin selectively binds to vasopressin V2 receptors located in the renal collecting ducts. - Gs Protein Activation
V2 receptor activation engages Gs protein, stimulating adenylyl cyclase. - Increased cAMP Production
The intracellular rise in cyclic AMP (cAMP) leads to activation of protein kinase A (PKA). - Aquaporin-2 Phosphorylation
PKA phosphorylates aquaporin-2 (AQP2) water channel proteins. - Membrane Insertion of Aquaporins
Phosphorylated AQP2 channels are translocated and inserted into the apical membrane of renal epithelial cells. - Water Reabsorption Enhancement
Water is reabsorbed from tubular fluid back into the bloodstream, concentrating the urine and reducing diuresis. - Hemostatic Action
Desmopressin also stimulates endothelial release of von Willebrand factor (vWF), factor VIII, and tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), useful in patients with bleeding tendencies such as mild hemophilia A and type 1 von Willebrand disease.
Pharmacokinetics
- Routes: Oral, intranasal, intravenous, subcutaneous
- Oral Bioavailability: 0.1–0.2%
- Intranasal Bioavailability: 3–5%
- Peak Plasma Time: 1–2 hours (oral), 30–60 minutes (intranasal)
- Plasma Half-Life: 2–4 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic and renal
- Excretion: Primarily renal as inactive metabolites
Clinical Uses
- Central Diabetes Insipidus (CDI)
- Primary nocturnal enuresis
- Nocturia due to nocturnal polyuria
- Mild hemophilia A and von Willebrand disease (type 1)
- Platelet dysfunction in uremic patients
- Diagnostic test for differentiating CDI from nephrogenic DI
Adverse Effects
- Mild Effects: Headache, nausea, nasal irritation (intranasal route), flushing
- Severe Effects: Water intoxication, hyponatremia, seizures
- Precautions: Sodium monitoring in children and elderly
- Contraindications: Hyponatremia, moderate to severe renal impairment, SIADH
Comparative Analysis
| Parameter | Desmopressin | Vasopressin |
|---|---|---|
| Receptor Selectivity | V2 selective | V1 & V2 agonist |
| Antidiuretic Effect | Potent | Potent |
| Vasoconstrictive Effect | Minimal | Prominent |
| Duration of Action | Longer | Shorter |
| Hemostatic Action | Yes | No |
| Use in Bleeding Disorders | Yes | Rare |
Desmopressin’s improved receptor selectivity and prolonged duration make it a safer and more targeted therapy than vasopressin.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Desmopressin acts on which receptor?
A. V1a
B. V2
C. Alpha-1
D. Beta-1
Answer: B. V2 - A key adverse effect of desmopressin therapy:
A. Hyponatremia
B. Hyperkalemia
C. Tachycardia
D. Hypertension
Answer: A. Hyponatremia - Desmopressin enhances the release of all except:
A. Factor VIII
B. Tissue plasminogen activator
C. von Willebrand factor
D. ADH
Answer: D. ADH - Desmopressin is contraindicated in:
A. Type 1 VWD
B. Nocturnal enuresis
C. Severe renal impairment
D. Central diabetes insipidus
Answer: C. Severe renal impairment - Compared to vasopressin, desmopressin has:
A. Higher pressor activity
B. Shorter half-life
C. Greater V1 selectivity
D. Minimal vasoconstriction
Answer: D. Minimal vasoconstriction
FAQs
Q1. What makes desmopressin safer than vasopressin?
Desmopressin lacks vasoconstrictor effects, reducing the risk of cardiovascular side effects.
Q2. How is desmopressin administered for nocturnal enuresis?
Typically via oral tablets 1–2 hours before bedtime.
Q3. Why is sodium monitoring essential with desmopressin?
Because excessive water retention can lead to dilutional hyponatremia and seizures.
Q4. Can desmopressin be used for diagnostic purposes?
Yes, it helps differentiate central from nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
Q5. Is desmopressin effective in nephrogenic DI?
No, it is ineffective since the kidneys are unresponsive to ADH in nephrogenic DI.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- British National Formulary (BNF)
- FDA Drug Label for Desmopressin Acetate
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com