Table of Contents
Introduction
Buspirone is an anxiolytic medication primarily used for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Unlike benzodiazepines, it does not cause sedation, dependence, or withdrawal symptoms, making it a preferred long-term therapy option.
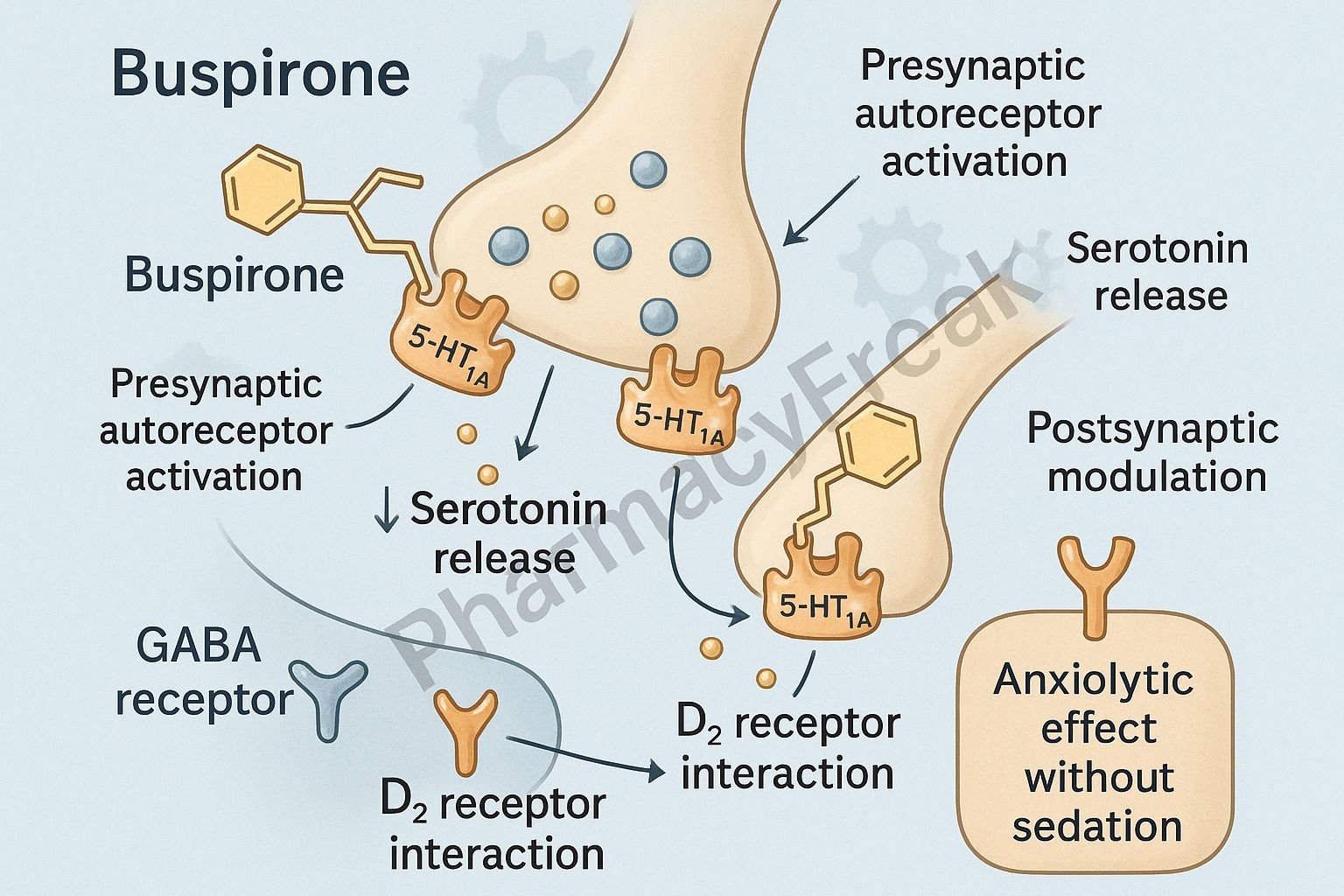
The Mechanism of Action of Buspirone is unique among anxiolytics. It acts mainly as a partial agonist at 5-HT1A serotonin receptors, along with mild dopamine D2 antagonism, which together reduce anxiety without CNS depression.



Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
1. Partial Agonist at 5-HT1A Receptors (Primary Mechanism)
Buspirone binds to presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in the brain.
Effects:
- ↓ Serotonin release (via presynaptic inhibition)
- Modulation of serotonergic neurotransmission
- ↓ Anxiety without sedation
This mechanism explains the delayed onset (2–4 weeks) similar to SSRIs.
2. Action on Dopamine D2 Receptors
Buspirone also acts as a:
- Weak D2 antagonist
- Weak D2 partial agonist
Effects:
- Mild dopaminergic modulation
- Contributes to anxiolytic action
- No antipsychotic effect
3. No Action on GABA Receptors (Major Distinction)
Unlike benzodiazepines, buspirone:
- Does NOT enhance GABAergic inhibition
- Does NOT cause sedation or muscle relaxation
- Does NOT cause dependence, tolerance, or withdrawal
Clinical relevance: Safe for long-term anxiety management.
4. No Effect on CNS Depression
Buspirone does not interact with:
- Alcohol
- CNS depressants
- Hypnotics
Effect: No respiratory depression.
5. Summary of Mechanism
| Mechanism | Effect |
|---|---|
| Partial 5-HT1A agonism | ↓ Serotonin release, anxiolysis |
| Weak D2 antagonism | Mild dopaminergic modulation |
| No GABA action | No sedation or dependence |
| Delayed onset | Improved long-term anxiety control |

Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Well absorbed orally
- Bioavailability: Low (first-pass metabolism)
- Onset: 2–4 weeks (not for acute anxiety)
- Metabolism: Hepatic (CYP3A4)
- Half-life: 2–3 hours
- Elimination: Renal + fecal
Clinical Uses
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Chronic anxiety states
- Patients needing a non-sedating, non-addictive anxiolytic
- Adjunct in depression (off-label)
Adverse Effects
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Nausea
- Nervousness
- Lightheadedness
- Restlessness
No sedation, no muscle relaxation, no dependence.
Contraindications
- Concomitant MAO inhibitor therapy
- Severe hepatic or renal impairment
- Hypersensitivity to buspirone
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Buspirone | Benzodiazepines | SSRIs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Onset | Slow (2–4 weeks) | Rapid | Slow (2–6 weeks) |
| Sedation | None | High | None |
| Dependence | None | High | None |
| Mechanism | 5-HT1A agonist | GABA-A modulation | 5-HT reuptake inhibition |
MCQs
1. Buspirone acts primarily on which receptor?
a) GABA-A
b) 5-HT2A
c) 5-HT1A
d) NMDA
Answer: c) 5-HT1A
2. A major advantage of buspirone over benzodiazepines:
a) Works immediately
b) No risk of dependence
c) Causes sedation
d) Depresses respiration
Answer: b) No risk of dependence
3. Buspirone exhibits mild antagonism at:
a) D2 receptors
b) M1 receptors
c) H1 receptors
d) GABA receptors
Answer: a) D2 receptors
4. Buspirone should NOT be combined with:
a) SSRIs
b) MAO inhibitors
c) Beta-blockers
d) Buspirone can be combined with all
Answer: b) MAO inhibitors
5. Buspirone is ineffective for:
a) Chronic anxiety
b) Generalized anxiety disorder
c) Acute panic attacks
d) Long-term anxiety
Answer: c) Acute panic attacks
FAQs
Q1. How long does buspirone take to work?
2–4 weeks—similar to antidepressants.
Q2. Can buspirone be used for panic attacks?
No—it is ineffective in acute anxiety.
Q3. Does buspirone cause sedation?
No—this is one of its biggest advantages.
Q4. Is buspirone addictive?
No dependency or withdrawal effects.
Q5. Can buspirone be taken with alcohol?
Yes—no CNS depression interactions.
References
Goodman & Gilman’s Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2189
Katzung: Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2464
Tripathi: Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://jaypeebrothers.com/
Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2129

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com