Table of Contents
Introduction
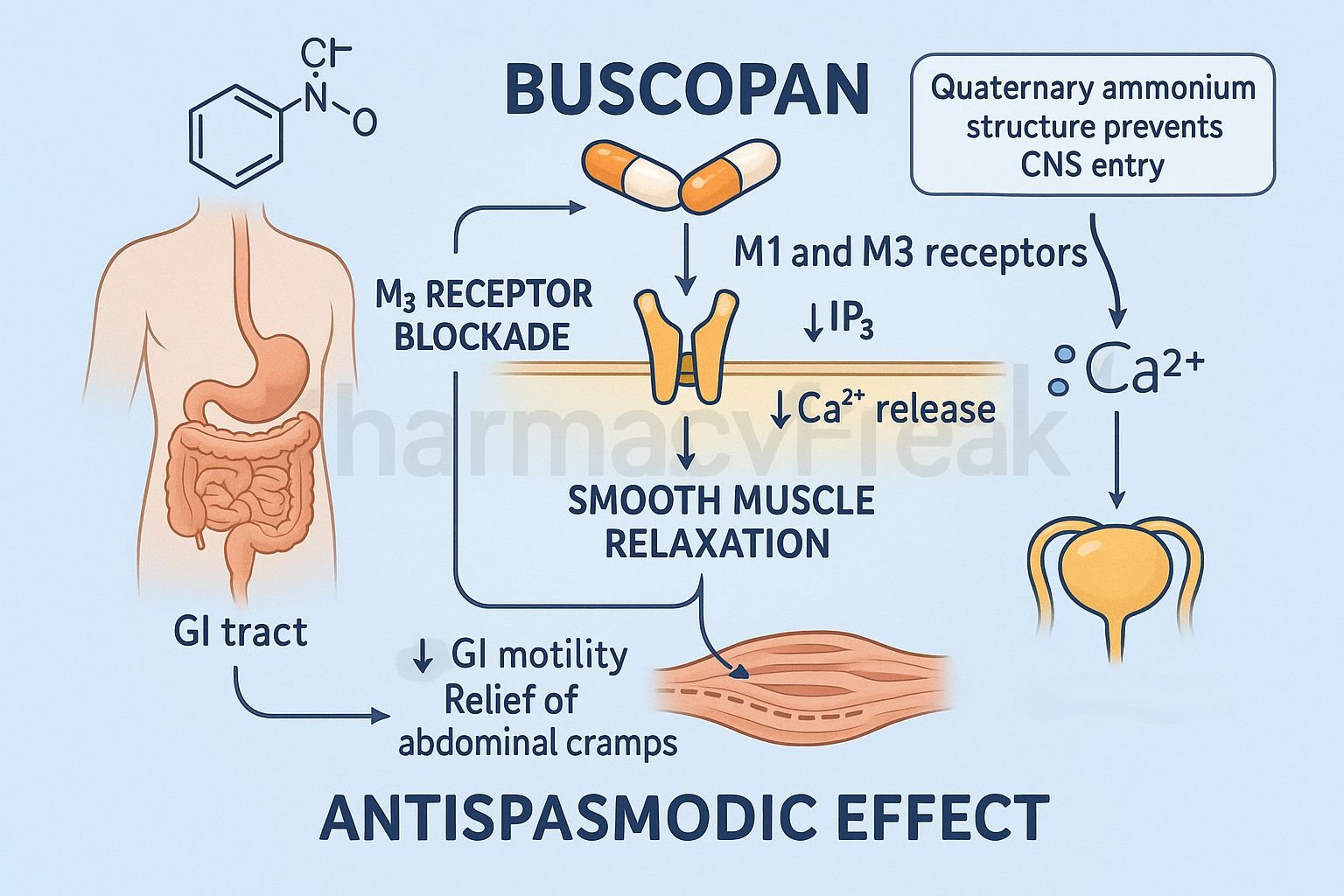
Buscopan (Hyoscine Butylbromide) is an antispasmodic drug widely used to relieve smooth muscle spasms in the gastrointestinal tract, biliary tract, urinary tract, and female reproductive system. It is commonly used for abdominal cramps, renal colic, biliary colic, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and dysmenorrhea.
The Mechanism of Action of Buscopan is primarily based on peripheral anticholinergic (muscarinic receptor–blocking) activity, which reduces smooth muscle contraction and alleviates spasms.


Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
1. Competitive Antagonism of Muscarinic (M1–M5) Receptors – Primary Mechanism
Buscopan blocks muscarinic receptors, mainly M3 receptors located on smooth muscle cells in:
- GI tract
- Biliary tract
- Urinary tract
- Uterus
By blocking acetylcholine at these receptors, it prevents:
- Smooth muscle contraction
- GI motility increases
- Spasmodic pain
Effect: Smooth muscle relaxation and spasm relief.
2. Poor CNS Penetration
Buscopan is a quaternary ammonium compound, meaning:
- Does not cross the blood–brain barrier
- Minimal central anticholinergic effects
- Mainly acts peripherally
This makes it safer than atropine-like drugs.
3. Reduced GI Motility and Secretions
Muscarinic antagonism leads to:
- ↓ Peristalsis
- ↓ Intestinal spasms
- ↓ GI secretions
- ↓ Colicky pain
Useful in conditions like IBS and spastic dysmenorrhea.
4. Relief of Smooth Muscle Spasm in Urinary and Biliary Tracts
M3 receptors regulate contraction in:
- Ureter
- Bladder
- Bile ducts
- Gallbladder
Blocking these receptors provides relief in:
- Renal colic
- Biliary colic
- Ureteric spasm
5. Summary of Mechanism
| Mechanism | Effect |
|---|---|
| M3 receptor blockade | Smooth muscle relaxation |
| ↓ Acetylcholine effects | Less spasm & pain |
| Peripheral-only action | No central effects |
| ↓ GI motility | Relief in IBS & cramps |
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Incomplete oral absorption
- CNS penetration: Minimal
- Onset: Within 20–30 minutes
- Duration: 4–6 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Excretion: Renal and fecal
Clinical Uses
- Abdominal cramps
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Biliary colic
- Renal colic (adjunct)
- Dysmenorrhea
- Spastic conditions of GI/urinary tracts
- Diagnostic procedures (endoscopy/colonoscopy) for smooth muscle relaxation
Adverse Effects
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Tachycardia
- Urinary retention
- Flushing
- Allergic reactions (rare)
Due to peripheral action, central effects like confusion or sedation are rare.
Contraindications
- Myasthenia gravis
- Megacolon
- Narrow-angle glaucoma
- Prostate hypertrophy (caution)
- Obstructive uropathy
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Buscopan | Atropine | Dicyclomine |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNS effects | Minimal | High | Moderate |
| GI spasm relief | Strong | Moderate | Strong |
| Use in colic | Very effective | Moderate | Limited |
| Duration | Moderate | Long | Moderate |
MCQs
1. Buscopan relieves abdominal cramps by blocking:
a) Beta receptors
b) Muscarinic M3 receptors
c) Histamine receptors
d) Serotonin receptors
Answer: b) Muscarinic M3 receptors
2. Buscopan causes minimal central side effects because it:
a) Is not metabolized
b) Is a quaternary ammonium compound
c) Has high lipid solubility
d) Stimulates dopamine receptors
Answer: b) Is a quaternary ammonium compound
3. One main therapeutic use of Buscopan is:
a) Asthma
b) Renal and biliary colic
c) Hypertension
d) Depression
Answer: b) Renal and biliary colic
4. Buscopan decreases abdominal spasm by:
a) Increasing peristalsis
b) Blocking acetylcholine effects
c) Stimulating GI secretion
d) Blocking H2 receptors
Answer: b) Blocking acetylcholine effects
5. A common adverse effect of Buscopan is:
a) Hyperhidrosis
b) Dry mouth
c) Bradycardia
d) Sedation
Answer: b) Dry mouth
FAQs
Q1. Does Buscopan cause drowsiness?
No—minimal CNS penetration prevents sedation.
Q2. Can Buscopan be used for IBS?
Yes—effective for crampy abdominal pain associated with IBS.
Q3. Is Buscopan addictive?
No—it has no dependence potential.
Q4. Can Buscopan help in kidney stone pain?
Yes—it relieves ureteric spasms, improving symptoms.
Q5. Is Buscopan safe in pregnancy?
Generally considered safe, but use only under medical advice.
References
Goodman & Gilman’s Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2189
Katzung: Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2464
Tripathi: Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://jaypeebrothers.com/
Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2129

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com