Table of Contents
Introduction
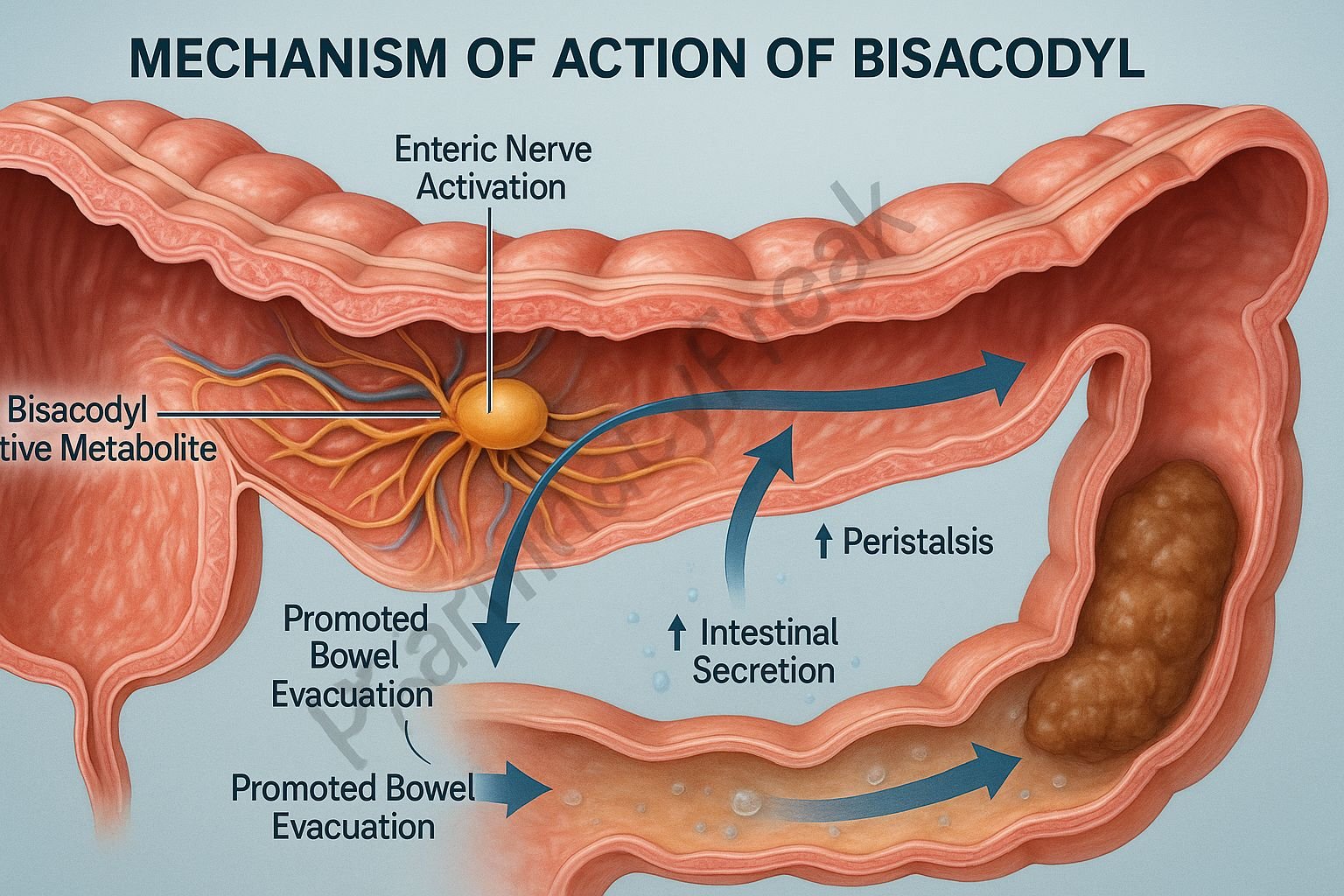
Bisacodyl is a stimulant laxative widely used for the short-term relief of constipation, for bowel preparation before procedures, and for evacuation in conditions requiring rapid colonic emptying. It works by directly stimulating the enteric nervous system, increasing intestinal motility, and promoting fluid accumulation in the colon. As a potent bowel stimulant, bisacodyl acts primarily on the large intestine, producing predictable and effective evacuation.


Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
1. Direct Stimulation of the Enteric Nervous System (Primary Mechanism)
Bisacodyl activates myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus neurons in the colon.
Effects:
- ↑ Peristaltic contractions
- ↑ Propulsive motility
- ↓ Colonic transit time
This is the hallmark feature of stimulant laxatives.
2. Increased Secretion of Water and Electrolytes
Bisacodyl enhances secretion of:
- Water
- Sodium
- Chloride
- Potassium
It also inhibits absorption of electrolytes from the colon.
Effect:
- Softer stool
- Increased stool volume
- Enhanced peristalsis through distension
3. Activation After Metabolic Conversion
Bisacodyl is a prodrug.
Steps:
- Oral or rectal administration
- Hydrolysis by intestinal and colonic enzymes
- Conversion to active metabolite (bisacodyl diphenol)
- Direct stimulation of colonic mucosa and enteric nerves
Effect: Targeted action in the colon with minimal small-intestinal involvement.
4. Colonic Irritation → Reflex Peristalsis
The active metabolite produces mild mucosal irritation, which reflexively increases motility.
5. Summary of Mechanism
| Mechanism | Effect |
|---|---|
| Stimulation of myenteric plexus | ↑ Peristalsis, ↑ motility |
| Fluid & electrolyte secretion | Softer stool, ↑ volume |
| Inhibition of absorption | Promotes water retention |
| Mild mucosal irritation | Reflex peristalsis |
| Prodrug activation | Colon-specific effect |
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Minimal
- Onset:
- Oral: 6–12 hours
- Rectal: 15–60 minutes
- Metabolism: Converted into active diphenol in colon
- Excretion: Fecal predominant
Clinical Uses
- Acute constipation
- Bowel evacuation prior to:
- Colonoscopy
- Radiologic bowel studies
- Surgery
- Chronic constipation (occasional use)
- Neurogenic bowel dysfunction
Adverse Effects
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea
- Electrolyte imbalance (with overuse)
- Nausea
- Rectal irritation (suppositories)
- Cathartic colon (long-term abuse)
Contraindications
- Intestinal obstruction
- Acute abdomen (appendicitis, peritonitis)
- Severe dehydration
- Rectal fissures (rectal form)
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Bisacodyl | Senna | Lactulose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Stimulant laxative | Stimulant laxative | Osmotic laxative |
| Onset | 6–12 hrs (oral) | 6–12 hrs | 24–48 hrs |
| Mechanism | ENS stimulation | ENS stimulation + anthraquinones | Draws water osmotically |
| Use | Rapid bowel emptying | Mild constipation | Chronic constipation |
MCQs
1. Bisacodyl acts primarily by stimulating:
a) Vagal nerve endings
b) Myenteric plexus
c) Parasympathetic ganglia
d) Skeletal muscle of colon
Answer: b) Myenteric plexus
2. Bisacodyl increases stool volume by:
a) Increasing fat absorption
b) Stimulating pancreatic enzymes
c) Increasing water and electrolyte secretion
d) Inhibiting bile salts
Answer: c) Increasing water and electrolyte secretion
3. Bisacodyl becomes active after:
a) Hepatic metabolism
b) Renal filtration
c) Hydrolysis in the colon
d) Gastric dissolution
Answer: c) Hydrolysis in the colon
4. Rectal bisacodyl has an onset of:
a) 6–12 hours
b) 24 hours
c) 15–60 minutes
d) 5 hours
Answer: c) 15–60 minutes
5. Long-term bisacodyl use may lead to:
a) Hyperthyroidism
b) Cathartic colon
c) Weight gain
d) Glaucoma
Answer: b) Cathartic colon
FAQs
Q1. Can bisacodyl be used daily?
No. Long-term daily use may cause dependence and electrolyte imbalance.
Q2. What is the fastest route for bisacodyl?
Rectal suppository (15–60 minutes).
Q3. Is bisacodyl safe in pregnancy?
Generally considered safe for short-term use, but always follow medical advice.
Q4. Why does bisacodyl cause cramping?
It strongly stimulates colonic contractions.
Q5. Can bisacodyl be taken at night?
Yes. Oral bisacodyl works overnight (6–12 hours).
References
Goodman and Gilman – Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
Katzung – Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
Tripathi – Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
Harrison – Principles of Internal Medicine

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com