Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Codeine is a naturally occurring phenanthrene (morphinan) opioid used as an analgesic and antitussive; a hepatic CYP2D6-dependent prodrug whose analgesic effect derives in part from conversion to morphine. Supplied mainly as phosphate, sulfate, or hydrochloride salts for oral solutions, tablets/capsules, and combination products.
Brand Names
Tylenol with Codeine, Co-codamol, Co-codydramol; numerous generics (region-dependent)
Name
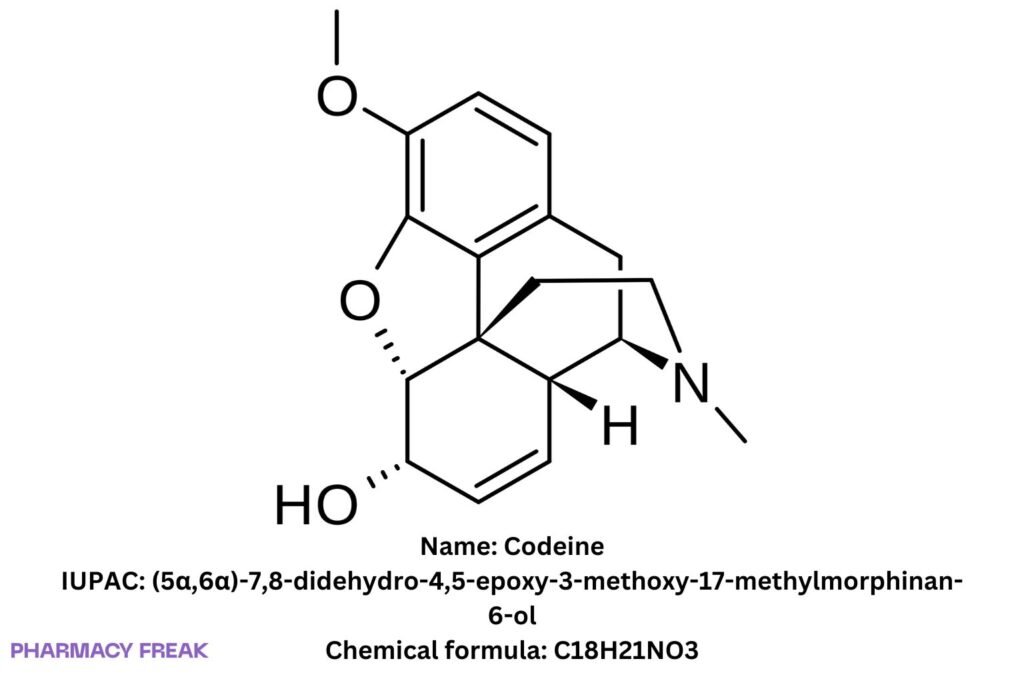
Codeine (3-methylmorphine)
Background
Opium alkaloid; Schedule/classification varies by jurisdiction. Often combined with paracetamol/acetaminophen, aspirin, or ibuprofen for pain; antitussive syrups remain in use where permitted.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription/controlled substance (jurisdiction-specific exemptions at low doses in combinations)
Structure
Weight
~299.36 g/mol (free base)
Chemical Formula
C₁₈H₂₁NO₃ (base)
Synonyms
3-Methylmorphine; methylmorphine
External IDs
CAS (base): 76-57-3; PubChem CID: 5284371; UNII (base/monohydrate): Q830PW7520; ATC: R05DA04 (antitussive), N02AJ06/07/08 (analgesic combos), N02AA59/N02AA79 (combinations)
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Mild–moderate pain (often in fixed combinations); cough suppression where approved; occasional use in diarrhea management.
Associated Conditions
Acute dental/musculoskeletal pain; cold/cough syndromes; palliative care protocols (jurisdiction-specific).
Associated Therapies
Fixed combinations with acetaminophen, aspirin, or ibuprofen; with promethazine (antitussive/antiemetic) in some markets.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Boxed warnings for addiction, abuse, misuse, life-threatening respiratory depression, accidental ingestion, neonatal opioid withdrawal, CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolism leading to high morphine exposure (especially in children), and risks with benzodiazepines/CNS depressants. Contraindicated with significant respiratory depression, acute/severe asthma without monitoring/resuscitative equipment, known hypersensitivity; avoid in children <12 years and post-tonsillectomy/adenoidectomy in <18 years where labeled.
Pharmacodynamics
μ-opioid receptor agonism (via morphine and codeine itself) → analgesia, antitussive effect, miosis, decreased GI motility; dose-dependent respiratory/CNS depression.
Mechanism of action
Prodrug O-demethylated by CYP2D6 → morphine; additional N-demethylation (CYP3A4) → norcodeine; extensive UGT2B7 conjugation to codeine-6-glucuronide (C6G).
Absorption
Well absorbed orally; tₘₐₓ ≈ ~1 h.
Volume of distribution
~3–6 L/kg (extensive tissue distribution).
Protein binding
~7–25% (low).
Metabolism
Hepatic: CYP2D6 (O-demethylation), CYP3A4 (N-demethylation); UGT2B7/2B4 glucuronidation (notably to C6G, 70–80% of dose).
Route of elimination
Primarily urinary within 24 h as codeine/C6G (~70%), norcodeine (~10%), morphine (~10%), normorphine (~4%), small hydrocodone (~1%); minor fecal excretion.
Half-life
~2.5–3 h (parent).
Clearance
Renal excretion of parent and metabolites; exposure rises in hepatic impairment and ultra-rapid CYP2D6 metabolizers; dose-adjust in renal impairment and monitor.
Adverse Effects
Dose-dependent sedation, dizziness, nausea/constipation, pruritus, urinary retention; serious: respiratory depression, hypotension, misuse/overdose; rare: anaphylactoid reactions.
Toxicity
Overdose → coma, miosis, respiratory depression; treat with airway support and naloxone with repeated dosing/infusion due to metabolite kinetics.
Pathways
CYP2D6/CYP3A4 biotransformation; UGT conjugation; renal elimination.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
CYP2D6 poor metabolizers: reduced analgesia. CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolizers: risk of morphine toxicity; major pediatric restrictions and post-operative contraindications in many labels/guidance.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
CNS depressants (benzodiazepines, alcohol, sedatives): additive respiratory/CNS depression.
CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., fluoxetine, paroxetine, bupropion, quinidine): ↓ morphine formation → reduced analgesia.
CYP3A4 inhibitors/inducers: shift metabolism (variable exposure).
MAOIs: avoid within recommended washouts (serotonergic/respiratory risks).
Mixed agonist–antagonist opioids (e.g., buprenorphine, nalbuphine): may precipitate withdrawal or blunt effect.
Food Interactions
No clinically meaningful food effect at usual doses.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
R05DA04 (antitussives, opium alkaloids & derivatives); N02AJ06/07/08 (analgesic combos); N02AA59/N02AA79 (combinations)
Drug Categories
Opioid analgesic; Antitussive; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Morphinan/phenanthrene alkaloid; 4,5-epoxy bridge; 3-O-methoxy derivative of morphine; secondary alcohol at C-6.
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
Q830PW7520 (codeine; base/monohydrate record)
CAS number
76-57-3 (base)
InChI Key
OROGSEYTTFOCAN-DNJOTXNNSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C18H21NO3/c1-19-8-7-18-11-4-5-13(20)17(18)22-16-14(21-2)6-3-10(15(16)18)9-12(11)19/h3-6,11-13,17,20H,7-9H2,1-2H3/t11-,12+,13-,17-,18-/m0/s1
IUPAC Name
(5α,6α)-7,8-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-ol
SMILES
COc1ccc2c3c1O[C@@H]1[C@@]43CCN(C@H[C@@H]4C=C[C@@H]1O)C
6. References
NIST Chemistry WebBook — formula C₁₈H₂₁NO₃, MW 299.364, Standard InChI for codeine base. NIST WebBook+1
IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology — InChIKey OROGSEYTTFOCAN-DNJOTXNNSA-N, canonical/isomeric SMILES, CAS 76-57-3. guidetopharmacology.org
DailyMed/FDA labels (codeine sulfate and APAP/codeine) — boxed warnings, t½ ~2.9–3 h, urinary excretion profile, protein binding 7–25%, Vd ~3–6 L/kg, CYP2D6/CYP3A4/UGT pathways. DailyMed+3FDA Access Data+3FDA Access Data+3
FDA Drug Safety Communication — restrictions in children due to ultra-rapid CYP2D6 metabolism. U.S. Food and Drug Administration
CPIC/NCBI Medical Genetics Summaries — CYP2D6 genotype impact on codeine response/toxicity. NCBI
ATC/DDD Index — R05DA04 (codeine); N02AJ06/07/08 and N02AA59/N02AA79 for combinations. FHI+2FHI+2

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com
