Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Cholesterol is an endogenous sterol (cholest-5-en-3β-ol) essential for mammalian cell membranes, precursor of bile acids, steroid hormones, and vitamin D, and a major cargo of lipoproteins (HDL, LDL, VLDL).
Brand Names
Not applicable (endogenous biomolecule; bulk chemical/excipient).
Name
Cholesterol
Background
Core membrane lipid that modulates fluidity and raft microdomains; central node of hepatic and intestinal sterol homeostasis (synthesis, dietary uptake, reverse transport). Widely used as an excipient and in liposomes.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Endogenous biomolecule; excipient
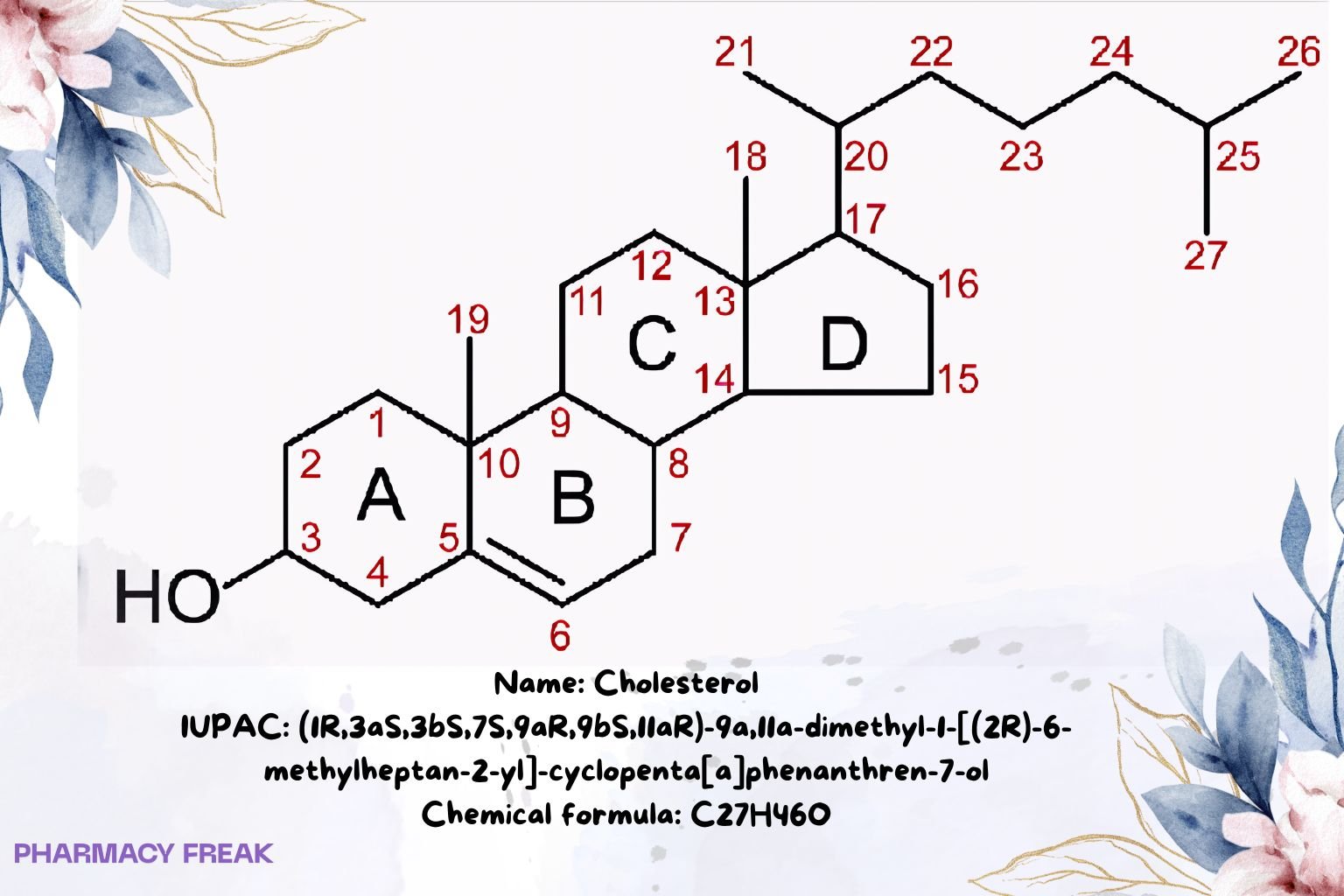
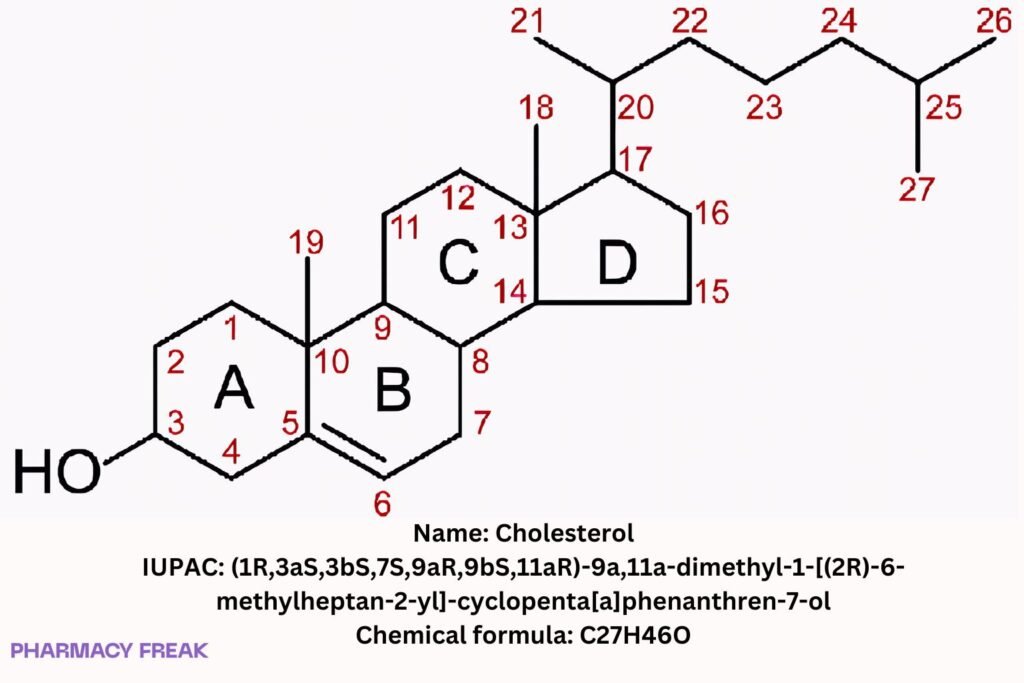
Structure
Weight
~386.65 g/mol
Chemical Formula
C₂₇H₄₆O
Synonyms
Cholest-5-en-3β-ol; 3β-hydroxycholest-5-ene; Cholesterin
External IDs
CAS: 57-88-5; PubChem CID: 5997; UNII: 97C5T2UQ7J
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Not an approved therapeutic active; roles as nutrient/excipient, and as a structural component in research lipid nanoparticles/liposomes.
Associated Conditions
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk relates to LDL-cholesterol burden; cholestasis and malabsorption affect sterol handling.
Associated Therapies
Targeted by statins (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors), ezetimibe (NPC1L1 inhibitor), PCSK9 inhibitors (↑ LDLR recycling), bile-acid sequestrants, bempedoic acid, fibrates (indirect effects).
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
None (molecule is endogenous; safety considerations pertain to dyslipidemia management rather than exogenous cholesterol per se).
Pharmacodynamics
Modulates membrane order and permeability; regulates SREBP2 feedback; substrates for LCAT (plasma esterification) and ACAT/SOAT (intracellular esterification).
Mechanism of action
Endogenous: integrates into phospholipid bilayers; serves as precursor for bile acids (CYP7A1 pathway) and steroidogenesis; governs lipoprotein assembly/clearance via LDLR–ApoB/ApoE interactions.
Absorption
Dietary sterol uptake via NPC1L1 in enterocytes; competition with plant sterols; packaged into chylomicrons.
Volume of distribution
Distributed across membranes and lipoproteins; major pools in hepatobiliary system, enterocytes, and tissues.
Protein binding
Carried predominantly within lipoprotein particles (ApoB/ApoA-I platforms), not classical plasma protein binding.
Metabolism
De novo synthesis via mevalonate pathway (HMG-CoA reductase rate-limiting); esterification by ACAT/LCAT; conversion to bile acids in liver.
Route of elimination
Fecal elimination as bile acids and neutral sterols; minimal urinary excretion.
Half-life
Pool- and compartment-dependent; turnover governed by synthesis, conversion to bile acids, and fecal loss.
Clearance
Physiologic clearance through hepatic uptake (LDLR), biliary secretion (ABCG5/ABCG8), and fecal excretion.
Adverse Effects
Not applicable to the molecule itself; pathologic elevation of atherogenic lipoproteins drives ASCVD risk.
Toxicity
No conventional overdose context for endogenous cholesterol; toxicology pertains to lipoprotein-mediated vascular disease.
Pathways
Mevalonate (cholesterol) biosynthesis, bile acid synthesis, reverse cholesterol transport (HDL–SR-B1), esterification (LCAT/ACAT), intestinal NPC1L1 uptake, hepatic LDLR clearance.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Variants in LDLR, PCSK9, APOB, APOE, ABCG5/8, NPC1L1 influence cholesterol levels and therapeutic response.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Not applicable as a therapeutic active; interactions concern lipid-lowering drugs acting on cholesterol pathways.
Food Interactions
Dietary cholesterol competes with phytosterols; overall impact on serum LDL-C is smaller than that of saturated/trans-fat intake.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
None assigned (not a drug active).
Drug Categories
Endogenous sterol; Excipient; Biomolecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Sterol (cholestanoid); tetracyclic cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene nucleus with Δ⁵ double bond; 3β-hydroxy substituent; isooctyl side chain.
Affected organisms
Humans and other animals
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
97C5T2UQ7J
CAS number
57-88-5
InChI Key
HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C27H46O/c1-18(2)7-6-8-19(3)23-11-12-24-22-10-9-20-17-21(28)13-15-26(20,4)25(22)14-16-27(23,24)5/h9,18-19,21-25,28H,6-8,10-17H2,1-5H3/t19-,21+,22+,23-,24+,25+,26+,27-/m1/s1
IUPAC Name
(1R,3aS,3bS,7S,9aR,9bS,11aR)-9a,11a-dimethyl-1-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-1H,2H,3H,3aH,3bH,4H,6H,7H,8H,9H,9aH,9bH,10H,11H,11aH-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-ol
SMILES
CC(C)CCCC(C)C1CCC2C3C(CC=C4C(C)(CCC(O)C24)C)C3CC1
6. References
PubChem Compound Summary: Cholesterol (CID 5997) — formula C₂₇H₄₆O, MW ~386.65, identifiers (InChI/InChIKey, SMILES). PubChem+1
CAS Common Chemistry — CAS RN 57-88-5, molecular formula, mass. Common Chemistry
FDA GSRS/UNII — Cholesterol UNII 97C5T2UQ7J entries in labeling databases. DailyMed+1
IUPAC/IARC Exposome-Explorer — IUPAC systematic name confirmation. Exposome Explorer
IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology — ligand page (cholesterol; PDB ligand CLR; cross-references). IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology
WHO/physiology texts — pathways: mevalonate biosynthesis, bile acid synthesis, lipoprotein transport; intestinal NPC1L1, hepatic LDLR, ABCG5/8 roles. Wikipedia

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com