Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Atorvastatin is an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) used for primary and secondary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and for treatment of dyslipidemias; clinical effect reflects LDL-C reduction via hepatic HMG-CoA reductase blockade and upregulation of LDL receptors.
Brand Names
Lipitor; numerous generics (region-dependent)
Name
Atorvastatin
Background
Synthetic, lipophilic statin introduced in the 1990s; supplied clinically as atorvastatin calcium (anhydrous or trihydrate) for oral use.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
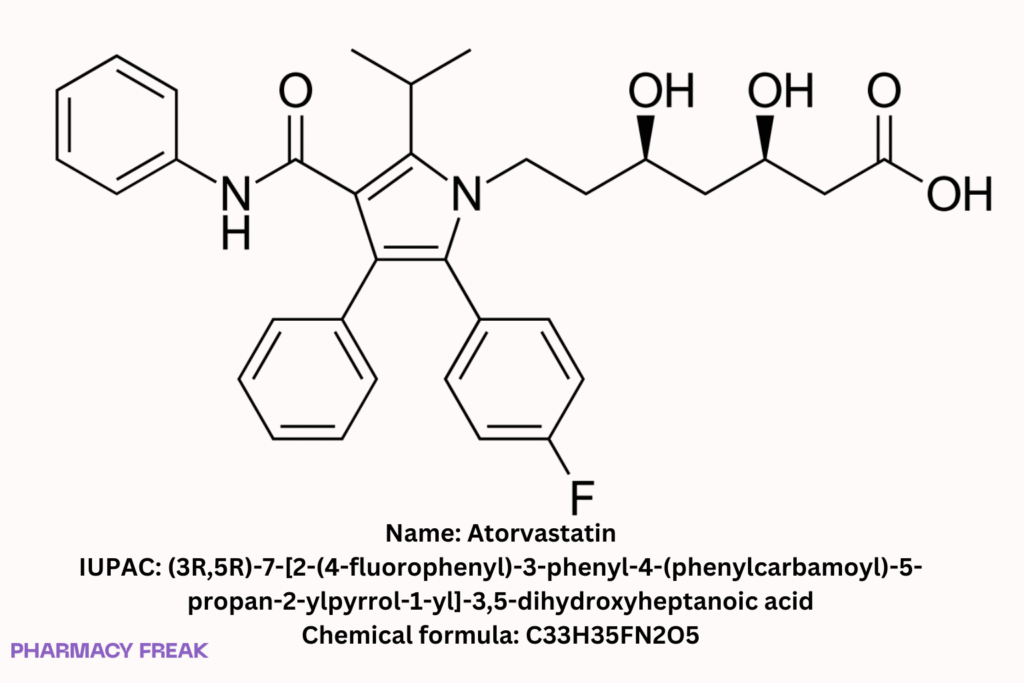
Structure
Weight
~558.65 g/mol (free base)
Chemical Formula
C₃₃H₃₅FN₂O₅ (free base)
Synonyms
(3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid; atorvastatin free acid; atorvastatin calcium (salt)
External IDs
CAS (base): 134523-00-5; PubChem CID: 60823; UNII (base): A0JWA85V8F; ATC: C10AA05 (plain); KEGG: D07474; ChEMBL: 1487; ChEBI: 39548
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Primary hypercholesterolemia, mixed dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, homozygous/heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia; ASCVD risk reduction (MI, stroke, revascularization) per labeling and guidelines.
Associated Conditions
Dyslipidemias requiring LDL-C lowering; diabetes with elevated ASCVD risk; post-ACS secondary prevention as part of high-intensity statin therapy.
Associated Therapies
Combination with ezetimibe or PCSK9 inhibitors when additional LDL-C lowering is needed; fixed combinations exist in some regions (e.g., atorvastatin/amlodipine; atorvastatin/ezetimibe—ATC combo codes).
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Contraindicated in active liver disease, pregnancy, and breastfeeding; avoid with serious hypersensitivity. Statins carry class warnings for myopathy/rhabdomyolysis and potential liver enzyme elevations; monitor per label.
Pharmacodynamics
Competitive HMG-CoA reductase inhibition → ↓ hepatic cholesterol synthesis → ↑ LDL-receptor expression → LDL-C reduction; modest ↓ TG and ↑ HDL-C. Onset in days; near-max effect within ~2 weeks; effect outlasts plasma half-life due to active metabolites.
Mechanism of action
Inhibits conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate; downstream lipid effects drive ASCVD risk reduction.
Absorption
Rapid; tₘₐₓ 1–2 h. Absolute bioavailability ≈14% (parent) and ≈30% for total inhibitory activity due to first-pass metabolism; food reduces Cmax/AUC modestly without altering LDL-C effect. FDA Access Data+1
Volume of distribution
~380–381 L. DailyMed+1
Protein binding
≥98%. DailyMed
Metabolism
Extensive hepatic metabolism, mainly CYP3A4 to active ortho-/para-hydroxy metabolites; substrates of OATP1B1 hepatic uptake transporters. FDA Access Data+1
Route of elimination
Primarily biliary/fecal as metabolites; <2% in urine unchanged; no meaningful enterohepatic recirculation reported. DailyMed
Half-life
Parent ~14 h; HMG-CoA inhibitory activity ~20–30 h (active metabolites). DailyMed+1
Clearance
High hepatic clearance via CYP3A4 and transporters; minimal renal clearance; exposure increased by CYP3A4/OATP1B1 inhibition. FDA Access Data+1
Adverse Effects
Common: myalgia, diarrhea, dyspepsia, nasopharyngitis, headache. Serious: myopathy/rhabdomyolysis, hepatotoxicity, rare immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy; hyperglycemia/diabetes risk signal in class labeling. FDA Access Data
Toxicity
Overdose: supportive care; monitor CK, LFTs, renal function if myopathy suspected.
Pathways
Cholesterol biosynthesis (mevalonate pathway) inhibition; LDL-receptor upregulation; hepatic uptake via OATP1B1.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
SLCO1B1 variants (↓ OATP1B1 function) can raise exposure; routine PGx not universally required; adjust based on clinical tolerability and interacting drugs. FDA Access Data
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors/transport inhibitors (clarithromycin, itraconazole, HIV protease inhibitors, cobicistat, cyclosporine) → ↑ AUC and myopathy/rhabdomyolysis risk; avoid or limit dose per label. Gemfibrozil and cyclosporine increase risk of myopathy; not recommended together. Grapefruit juice (excess, >1.2 L/day) increases exposure via intestinal CYP3A4 inhibition. OATP1B1 inhibitors (e.g., cyclosporine) increase bioavailability. FDA Access Data+3FDA Access Data+3FDA Access Data+3
Food Interactions
Food delays/lowers absorption slightly without altering LDL-C response; avoid excessive grapefruit juice due to exposure increase. FDA Access Data+1
4. Categories
ATC Codes
C10AA05 (atorvastatin, plain); combinations include C10BA05 (with ezetimibe) and C10BX03 (with amlodipine). atcddd.fhi.no+2atcddd.fhi.no+2
Drug Categories
Statin; Antihyperlipidemic; HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Fluorophenyl-substituted, dihydroxyheptanoic-acid side chain; pyrrole core; administered as calcium salt.
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
A0JWA85V8F (atorvastatin, base) Wikipedia
CAS number
134523-00-5 (atorvastatin, base) Wikipedia
InChI Key
XUKUURHRXDUEBC-KAYWLYCHSA-N Wikipedia
InChI
InChI=1S/C33H35FN2O5/c1-21(2)31-30(33(41)35-25-11-7-4-8-12-25)29(22-9-5-3-6-10-22)32(23-13-15-24(34)16-14-23)36(31)18-17-26(37)19-27(38)20-28(39)40/h3-16,21,26-27,37-38H,17-20H2,1-2H3,(H,35,41)(H,39,40)/t26-,27-/m1/s1 Wikipedia
IUPAC Name
(3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid Wikipedia
SMILES
O=C(O)CC@HCC@HCCn2c(c(c(c2c1ccc(F)cc1)c3ccccc3)C(=O)Nc4ccccc4)C(C)C Wikipedia
6. References
- DailyMed / FDA labels — absorption and bioavailability (14% parent; tₘₐₓ 1–2 h); distribution (Vd ≈381 L); protein binding ≥98%; elimination primarily biliary; half-life 14 h; inhibitory activity 20–30 h; interaction cautions. DailyMed+3DailyMed+3DailyMed+3
- Pfizer Labeling (2024 LIPITOR) — PK (bioavailability), food effect language; interaction tables for CYP3A4/transport inhibitors and gemfibrozil/cyclosporine. FDA Access Data+1
- FDA labeling PDFs (historical updates) — grapefruit juice (>1.2 L/day) interaction; OATP1B1 substrate note; co-administration restrictions. FDA Access Data+1
- ATC/DDD Index (FHI/WHOCC) — C10AA05; related combination codes. atcddd.fhi.no+2atcddd.fhi.no+2
- PubChem / Wikipedia identifiers — formula C₃₃H₃₅FN₂O₅; InChI, InChIKey XUKUURHRXDUEBC-KAYWLYCHSA-N; SMILES; CAS 134523-00-5; CID 60823. PubChem+1
- StatPearls — summary PK (bioavailability 14%, Vd ~380 L, half-life ~14 h) and class cautions. NCBI

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com