Table of Contents
Introduction
Fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid analgesic belonging to the phenylpiperidine class. It is approximately 50–100 times more potent than morphine and is widely used in anesthesia, perioperative pain control, intensive care, and chronic cancer pain management. Fentanyl is high-yield for pharmacology examinations because of its receptor selectivity, strong analgesic efficacy, rapid onset, and characteristic respiratory depressant effects.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
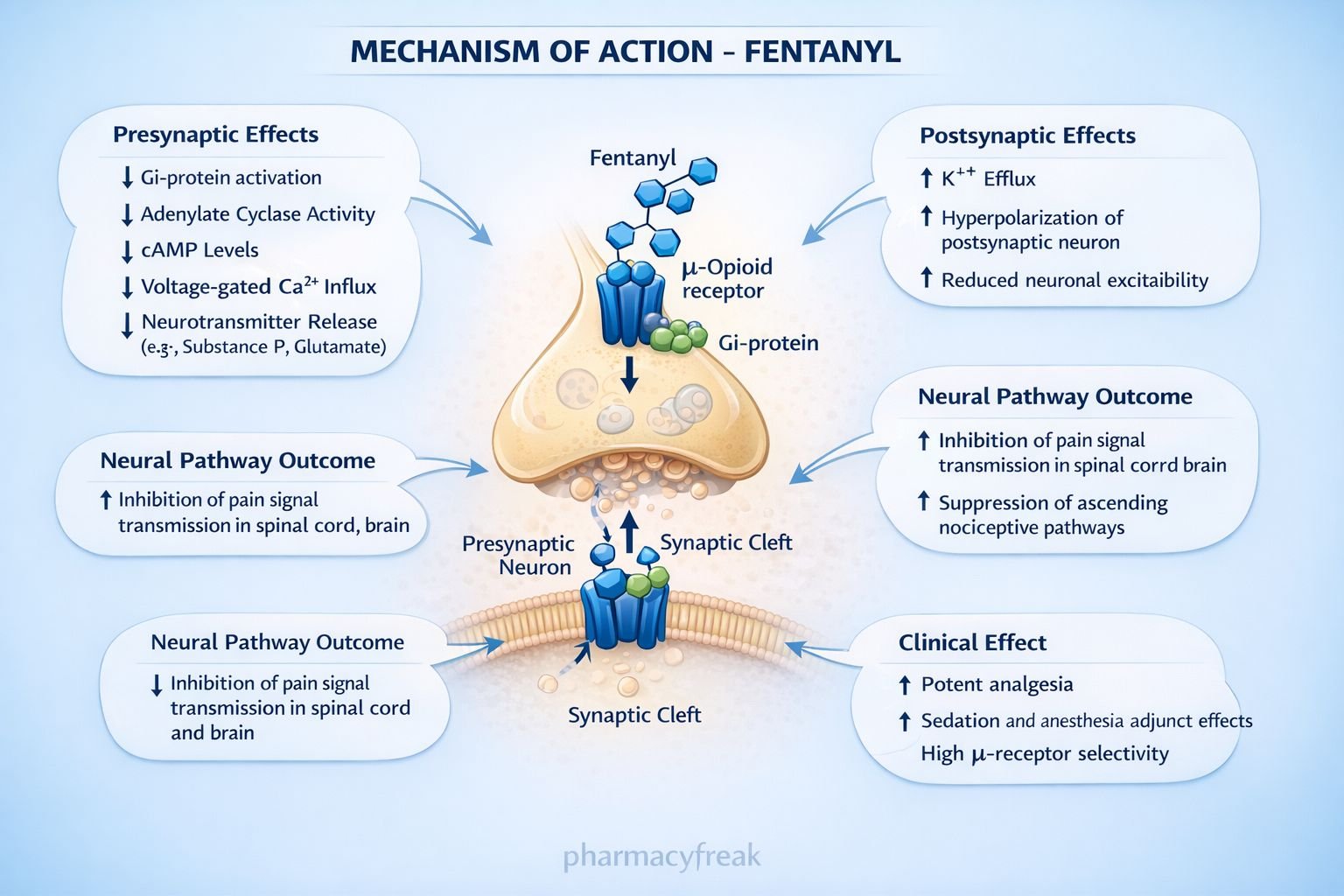
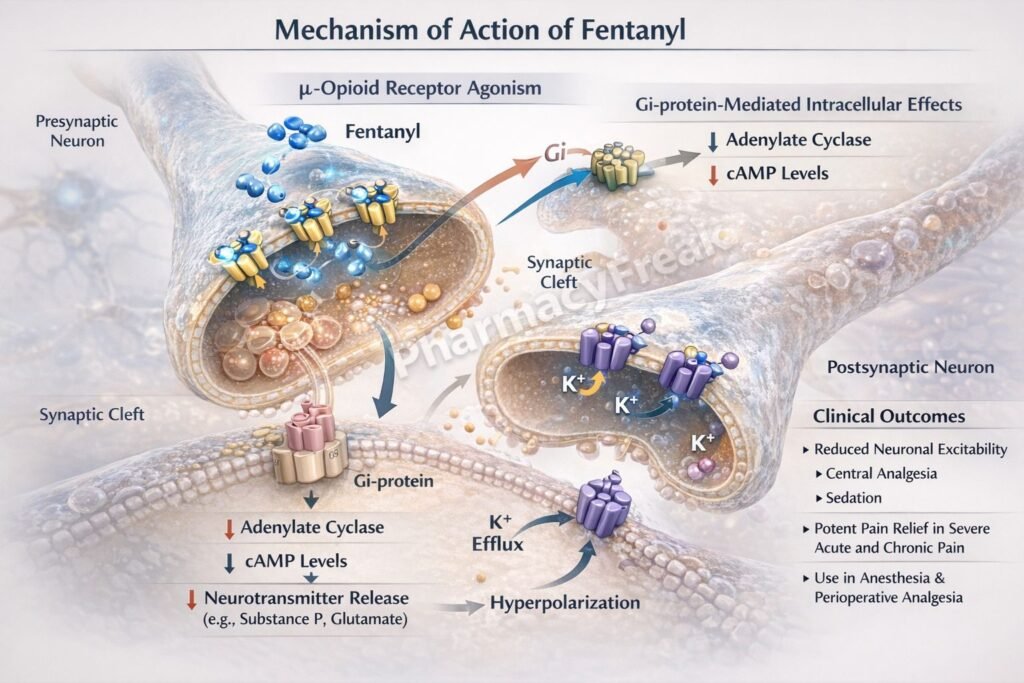
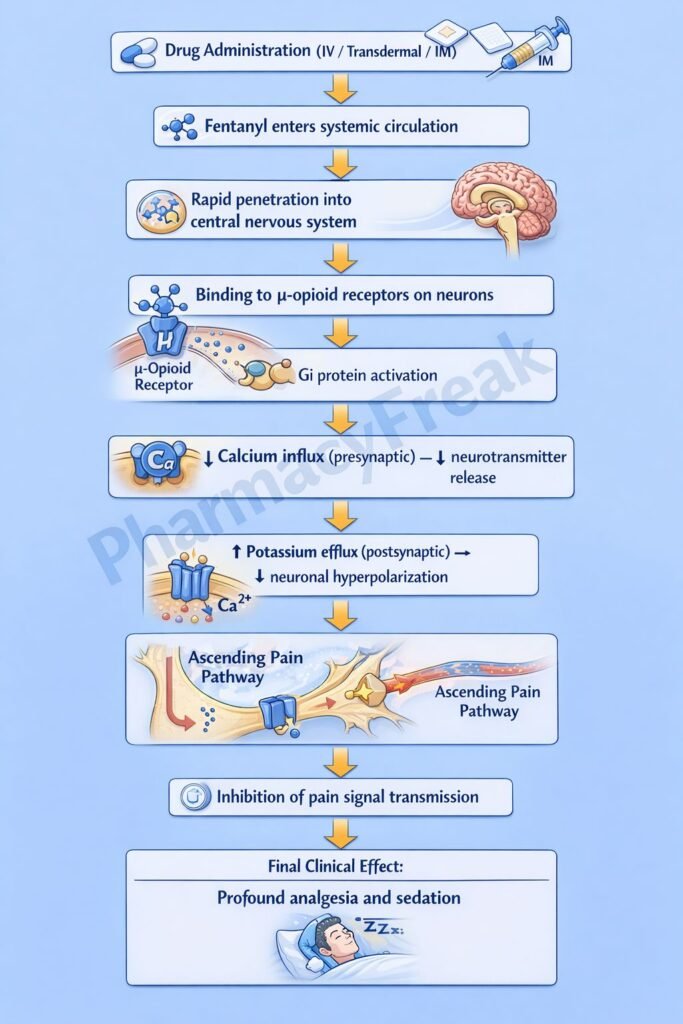
Fentanyl produces analgesia and sedation by activating opioid receptors in the central nervous system.
Step 1: Binding to μ-opioid receptors
Fentanyl selectively binds to μ (mu) opioid receptors located in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral tissues.
Step 2: G-protein–coupled receptor activation
μ-opioid receptors are Gi/o protein–coupled receptors. Receptor activation inhibits adenylate cyclase.
Step 3: Decrease in intracellular cAMP
Inhibition of adenylate cyclase leads to reduced cAMP levels within neurons.
Step 4: Modulation of ion channels
- Presynaptic: Inhibition of voltage-gated Ca²⁺ channels → reduced neurotransmitter release (substance P, glutamate)
- Postsynaptic: Opening of K⁺ channels → neuronal hyperpolarization
Step 5: Suppression of pain transmission
Reduced neurotransmitter release and neuronal hyperpolarization decrease nociceptive signal transmission, producing profound analgesia and sedation.
Exam pearl:
Fentanyl has minimal histamine release compared to morphine.
Pharmacokinetics
- Route of administration: IV, transdermal, transmucosal, intranasal, epidural
- Lipid solubility: Very high
- Onset of action: Rapid (especially IV)
- Protein binding: High
- Distribution: Extensive CNS penetration
- Metabolism: Hepatic (CYP3A4)
- Half-life: 3–12 hours (context-sensitive half-time increases with infusion)
- Excretion: Urine as inactive metabolites
Clinical Uses
- Severe acute pain (postoperative, trauma)
- Adjunct to general anesthesia
- Chronic cancer pain (transdermal patches)
- Procedural sedation
- Analgesia in intensive care units
Fentanyl is preferred in hemodynamically unstable patients due to minimal cardiovascular depression.
Adverse Effects
Respiratory:
- Respiratory depression (dose-limiting)
- Chest wall rigidity (rapid IV administration)
Central nervous system:
- Sedation
- Euphoria
- Dizziness
Gastrointestinal:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
Cardiovascular:
- Bradycardia
- Minimal hypotension (less histamine release)
Others:
- Tolerance
- Physical dependence
Comparative Analysis
Fentanyl vs Morphine vs Methadone
| Feature | Fentanyl | Morphine | Methadone |
|---|---|---|---|
| μ-receptor activity | Very strong | Strong | Strong |
| Potency | Very high | Moderate | High |
| Histamine release | Minimal | Significant | Minimal |
| Onset | Rapid | Slower | Slow |
| Duration | Short–moderate | Moderate | Long |
| QT prolongation | No | No | Yes |
Explanation:
Fentanyl’s high lipid solubility explains its rapid onset and potent analgesic effect. Unlike morphine, it causes minimal histamine release, reducing hypotension. Methadone’s long duration and QT-prolonging potential limit its routine use.
MCQs
- Fentanyl primarily acts on which receptor?
a) κ-opioid receptor
b) δ-opioid receptor
c) μ-opioid receptor
d) NMDA receptor
Answer: c) μ-opioid receptor
- μ-opioid receptors are coupled to which G protein?
a) Gs
b) Gq
c) Gi
d) G12
Answer: c) Gi
- Fentanyl reduces neurotransmitter release by inhibiting:
a) Sodium channels
b) Potassium channels
c) Calcium channels
d) Chloride channels
Answer: c) Calcium channels
- Opening of which channel causes neuronal hyperpolarization with fentanyl?
a) Na⁺ channel
b) Ca²⁺ channel
c) K⁺ channel
d) Cl⁻ channel
Answer: c) K⁺ channel
- Most serious adverse effect of fentanyl is:
a) Constipation
b) Bradycardia
c) Respiratory depression
d) Nausea
Answer: c) Respiratory depression
- Fentanyl differs from morphine because it causes:
a) More histamine release
b) Less histamine release
c) More hypotension
d) Less analgesia
Answer: b) Less histamine release
- Chest wall rigidity with fentanyl occurs due to:
a) Slow infusion
b) Rapid IV administration
c) Oral dosing
d) Transdermal use
Answer: b) Rapid IV administration
- Fentanyl metabolism primarily involves:
a) CYP2D6
b) CYP2C9
c) CYP3A4
d) MAO
Answer: c) CYP3A4
- Transdermal fentanyl is mainly used for:
a) Acute postoperative pain
b) Mild pain
c) Chronic cancer pain
d) Neuropathic pain
Answer: c) Chronic cancer pain
- Fentanyl produces analgesia mainly at the level of the:
a) Peripheral nerves
b) Spinal cord and brain
c) Neuromuscular junction
d) Autonomic ganglia
Answer: b) Spinal cord and brain
FAQs
1. Why is fentanyl more potent than morphine?
Due to higher lipid solubility and stronger μ-receptor affinity.
2. Does fentanyl cause histamine release?
Minimal, compared to morphine.
3. Why is fentanyl preferred in anesthesia?
Rapid onset, potent analgesia, and cardiovascular stability.
4. Can fentanyl cause dependence?
Yes, with prolonged use.
5. Why is respiratory monitoring essential?
Because respiratory depression is dose-limiting and potentially fatal.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com