Table of Contents
Introduction
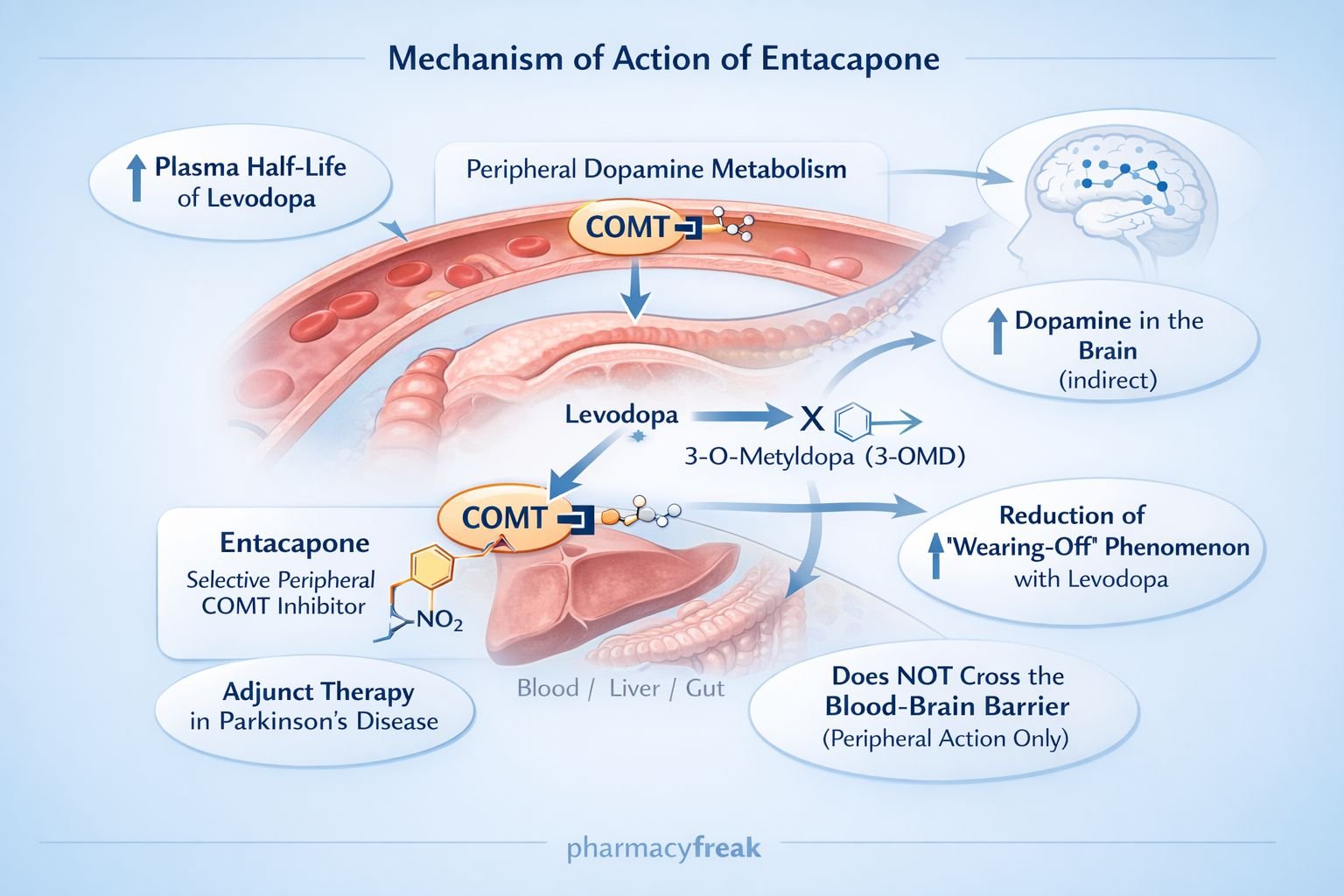
Entacapone is a catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor used as an adjunct therapy in Parkinson’s disease, particularly in patients experiencing end-of-dose “wearing-off” phenomena with levodopa. It enhances and prolongs the effect of levodopa by reducing its peripheral metabolism. Entacapone is a high-yield drug in pharmacology and neurology examinations because of its enzyme inhibition–based mechanism and its role in optimizing dopaminergic therapy.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
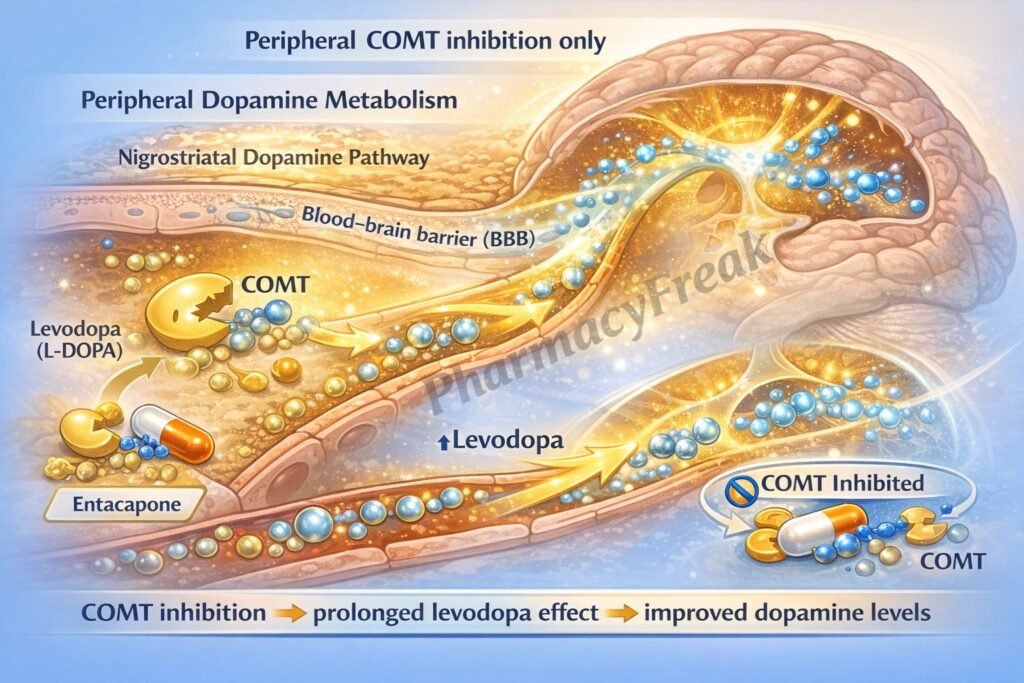
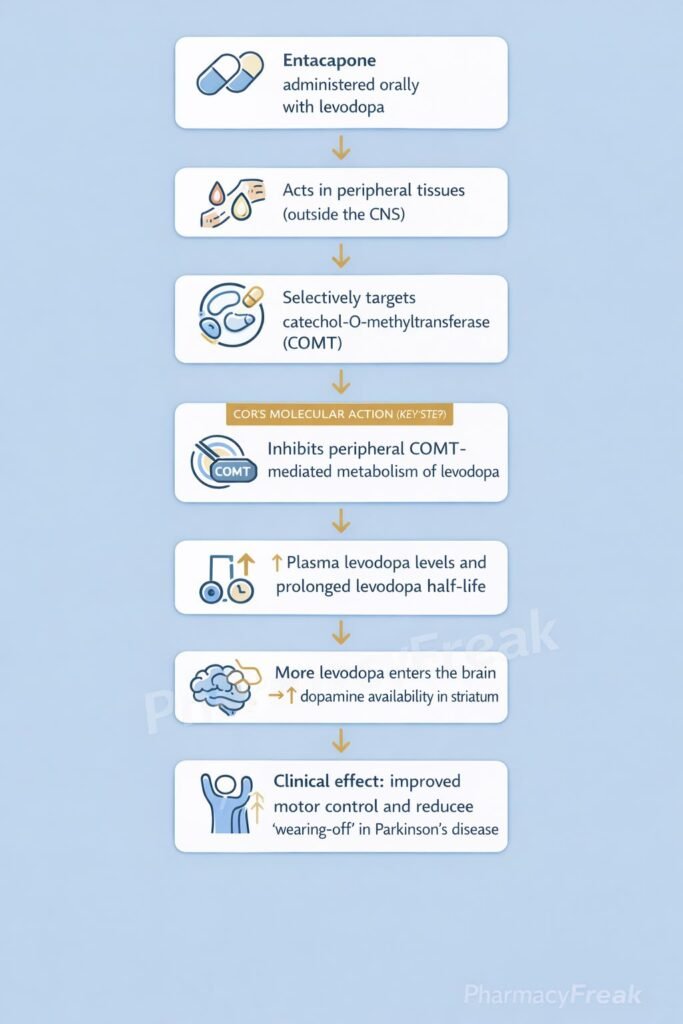
Entacapone acts by inhibiting peripheral metabolism of levodopa, increasing its bioavailability to the brain.
- Dopamine Deficiency in Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. - Role of Levodopa Therapy
Levodopa is a dopamine precursor that crosses the blood–brain barrier and is converted to dopamine in the CNS. - Peripheral Metabolism of Levodopa
In the periphery, levodopa is metabolized by:- Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)
- Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT)
- Action of COMT Enzyme
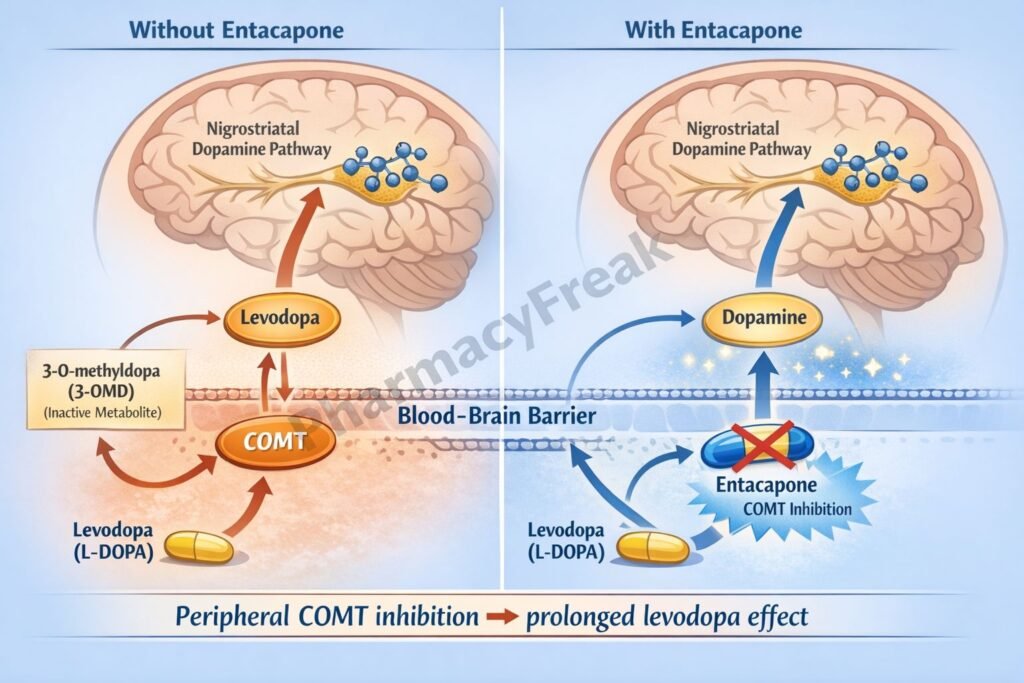
COMT converts levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa (3-OMD), an inactive metabolite that competes with levodopa for transport across the blood–brain barrier. - Selective Peripheral COMT Inhibition
Entacapone selectively inhibits peripheral COMT (does not significantly cross the BBB). - Reduced Formation of 3-O-Methyldopa
Inhibition of COMT decreases levodopa degradation in the periphery. - Increased Plasma Half-life of Levodopa
Higher and more sustained levodopa levels are available for CNS uptake. - Enhanced Central Dopamine Availability
More levodopa reaches the brain and is converted to dopamine, improving motor control. - Reduction of “Wearing-Off” Effect
Prolonged dopaminergic stimulation reduces motor fluctuations.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Rapid oral absorption
- Bioavailability: Moderate
- Distribution: Limited CNS penetration
- Metabolism: Extensive hepatic metabolism
- Elimination: Fecal excretion
- Half-life: Short (~0.5–2 hours)
- Special note: Always administered with levodopa–carbidopa
Clinical Uses
Entacapone is used exclusively as adjunct therapy in Parkinson’s disease:
- Parkinson’s disease with motor fluctuations
- End-of-dose “wearing-off” phenomenon
- To enhance and prolong levodopa response
Entacapone has no antiparkinsonian effect when used alone.
Adverse Effects
Adverse effects are mainly related to increased dopaminergic activity:
- Dyskinesia
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea (common)
- Abdominal pain
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Harmless brownish-orange discoloration of urine
Rare but important:
- Hepatotoxicity (much less than tolcapone)
Comparative Analysis (must include a table + explanation)
Comparison of COMT Inhibitors
| Feature | Entacapone | Tolcapone |
|---|---|---|
| Site of action | Peripheral COMT | Central + peripheral COMT |
| BBB penetration | No | Yes |
| Hepatotoxicity risk | Low | High |
| Monitoring required | No | Yes (LFTs) |
| Clinical use | Commonly used | Restricted use |
Explanation:
Entacapone is preferred over tolcapone due to its safer profile and lack of significant hepatotoxicity. Tolcapone is more potent but requires strict liver function monitoring.
MCQs (10–15)
- Entacapone inhibits which enzyme?
a) MAO-B
b) DOPA decarboxylase
c) COMT
d) Tyrosine hydroxylase
Answer: c) COMT
- Entacapone primarily acts in the:
a) Brain
b) Spinal cord
c) Peripheral tissues
d) Basal ganglia
Answer: c) Peripheral tissues
- Entacapone is always given with:
a) Bromocriptine
b) Selegiline
c) Levodopa
d) Amantadine
Answer: c) Levodopa
- Entacapone reduces formation of:
a) Dopamine
b) DOPAC
c) 3-O-methyldopa
d) Homovanillic acid
Answer: c) 3-O-methyldopa
- Entacapone improves Parkinson’s symptoms by:
a) Increasing dopamine synthesis
b) Blocking dopamine receptors
c) Prolonging levodopa action
d) Inhibiting acetylcholine
Answer: c) Prolonging levodopa action
- A common adverse effect of entacapone is:
a) Hepatitis
b) Diarrhea
c) Nephrotoxicity
d) Agranulocytosis
Answer: b) Diarrhea
- Entacapone does NOT:
a) Cross the blood–brain barrier
b) Inhibit COMT
c) Increase levodopa bioavailability
d) Reduce peripheral levodopa metabolism
Answer: a) Cross the blood–brain barrier
- Entacapone is useful mainly for:
a) Early Parkinson’s disease monotherapy
b) Tremor-dominant Parkinson’s disease
c) Wearing-off phenomenon
d) Parkinson’s psychosis
Answer: c) Wearing-off phenomenon
- Urine discoloration with entacapone is:
a) Dangerous
b) Due to hematuria
c) Benign
d) Due to renal damage
Answer: c) Benign
- Which COMT inhibitor has higher hepatotoxic risk?
a) Entacapone
b) Tolcapone
c) Both equally
d) Neither
Answer: b) Tolcapone
FAQs (minimum 5)
- What is the primary mechanism of entacapone?
Inhibition of peripheral COMT, reducing levodopa metabolism. - Does entacapone cross the blood–brain barrier?
No, it acts only peripherally. - Why is entacapone combined with levodopa?
To prolong levodopa’s effect and reduce motor fluctuations. - Is entacapone effective alone?
No, it has no effect without levodopa. - Why does entacapone cause urine discoloration?
Due to colored metabolites; it is harmless. - Is liver monitoring required with entacapone?
No, unlike tolcapone.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://www.jaypeebrothers.com - Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com