Table of Contents
Introduction
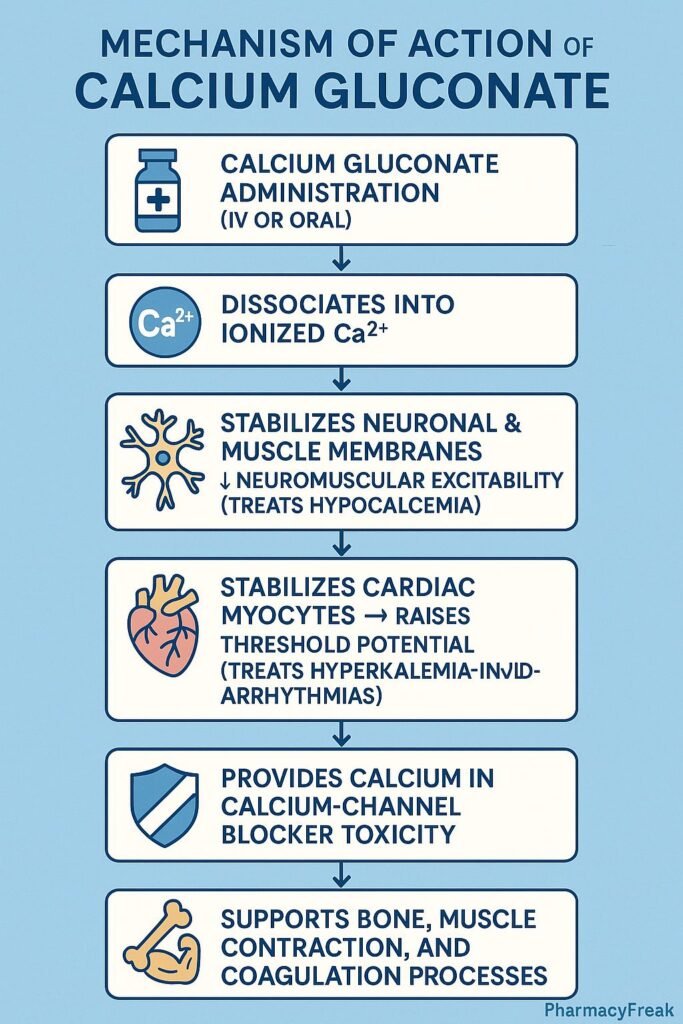
Calcium gluconate is an intravenous and oral calcium supplement widely used for the management of hypocalcemia, cardiac membrane stabilization during hyperkalemia, calcium channel blocker toxicity, magnesium sulfate overdose, and neonatal hypocalcemic tetany.
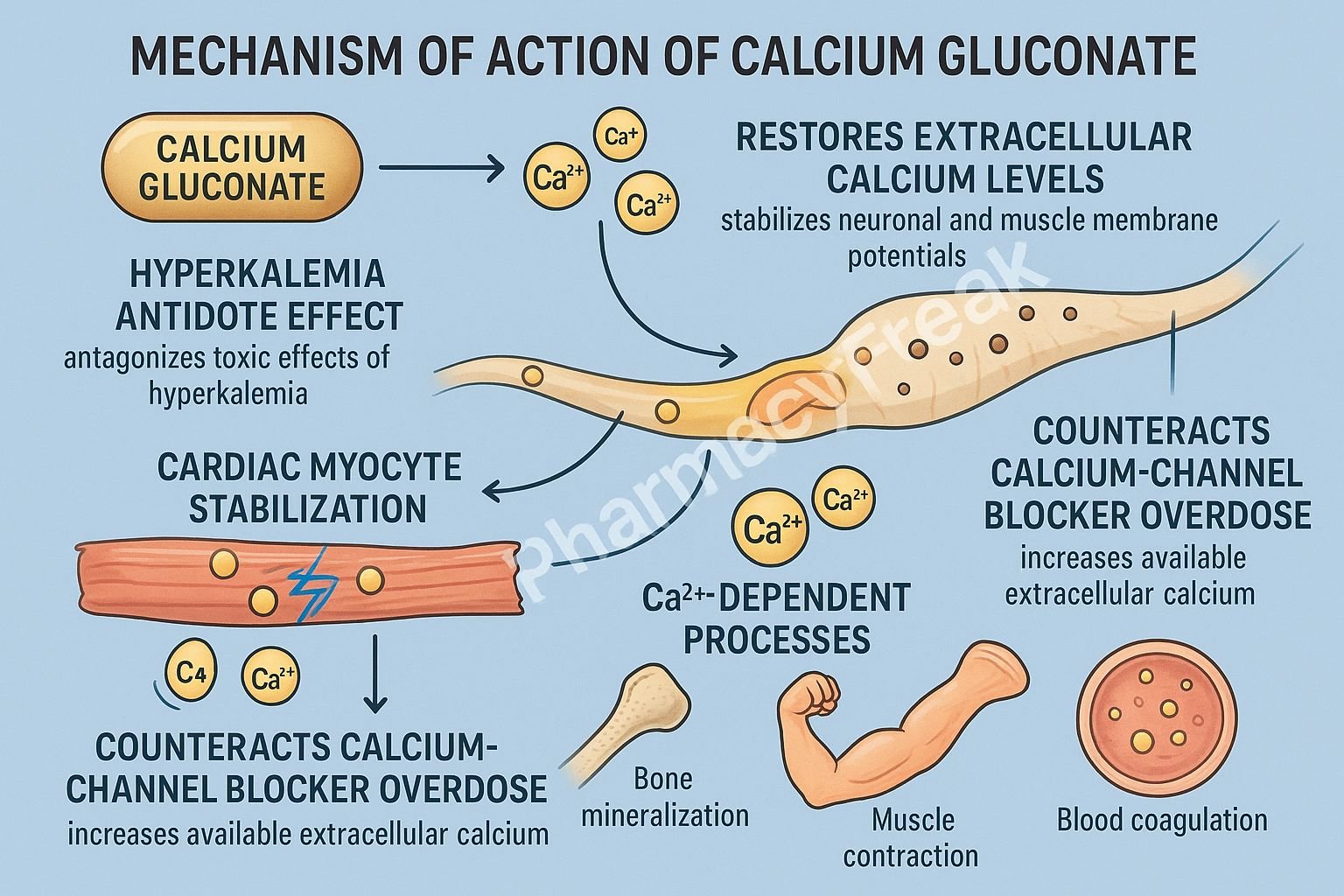
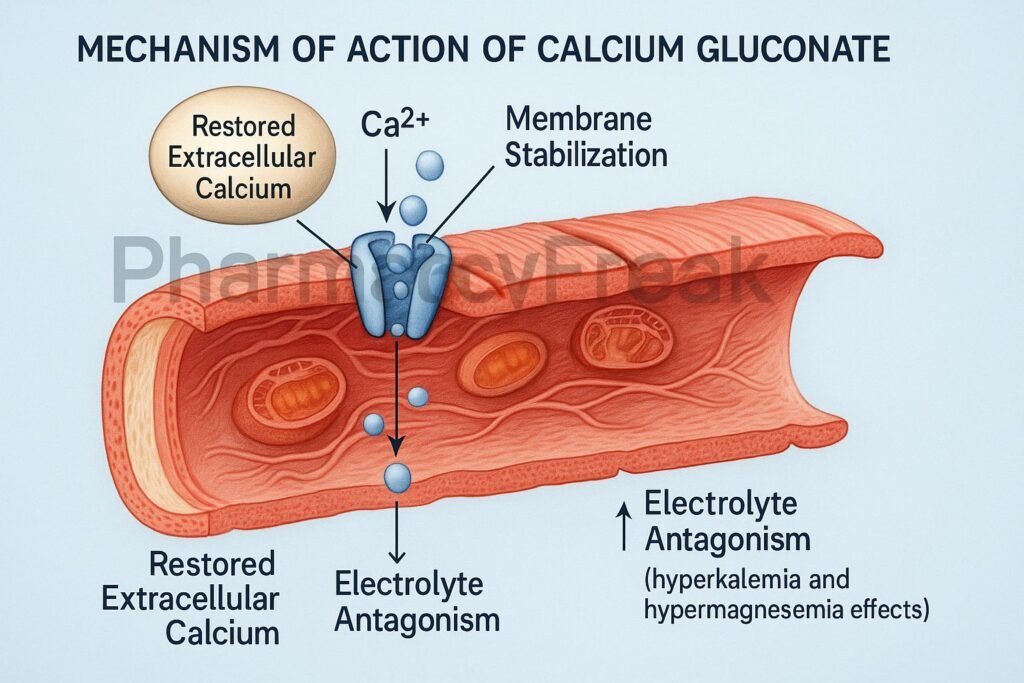
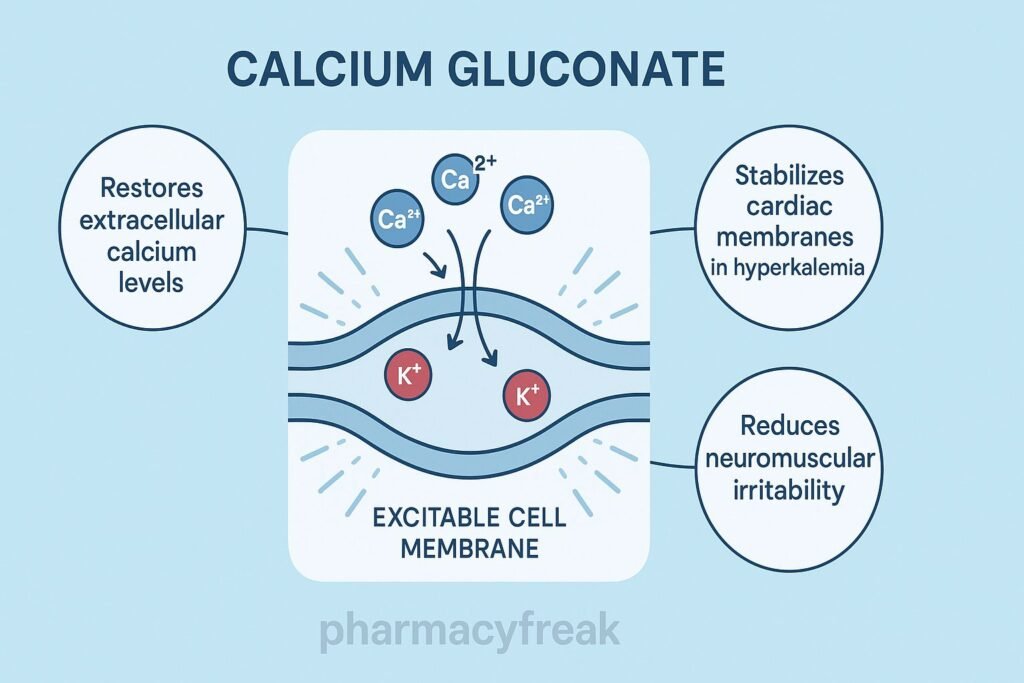
The Mechanism of Action of Calcium Gluconate primarily involves rapid elevation of extracellular calcium levels, leading to stabilization of neuronal and cardiac membrane potentials, restoration of normal neuromuscular function, and correction of calcium deficiency.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
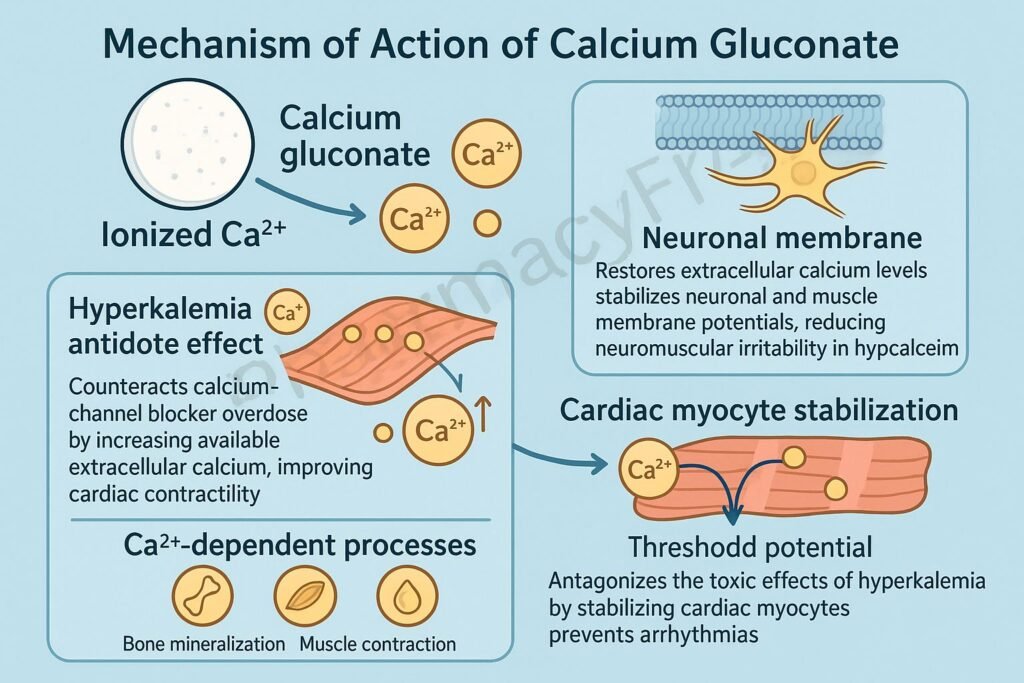
1. Increases Extracellular Ionized Calcium – Primary Mechanism
Calcium gluconate dissociates to release free calcium ions (Ca²⁺) into the blood.
Effects:
- Restores low serum calcium
- Normalizes neuromuscular excitability
- Reverses symptoms of hypocalcemia (tetany, paresthesias, spasms)
2. Stabilization of Cardiac Myocyte Membranes
In hyperkalemia and calcium channel blocker overdose, calcium gluconate:
- Raises the threshold potential of cardiac myocytes
- Stabilizes cardiac membranes
- Reduces the risk of arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation
Important: It does not lower potassium, but prevents fatal cardiac effects.
3. Reduces Neuromuscular Excitability
Low calcium increases neuronal excitability due to decreased threshold potential.
Calcium gluconate:
- ↑ Threshold potential
- ↓ Spontaneous neuronal firing
- ↓ Muscle cramps, tetany, laryngospasm
4. Antagonizes the Effects of Hypermagnesemia
Magnesium toxicity depresses neuromuscular and cardiac conduction.
Calcium gluconate competitively reverses this by:
- Restoring calcium–magnesium balance
- Reversing hypotension and respiratory depression
- Restoring deep tendon reflexes
5. Counteracts Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB) Toxicity
Calcium gluconate increases extracellular calcium, which:
- Overcomes CCB-induced blockade of L-type calcium channels
- Improves cardiac contractility
- Increases blood pressure
- Improves myocardial conduction
6. Provides a Calcium Source for Physiological Functions
Calcium is essential for:
- Muscle contraction
- Neurotransmitter release
- Blood coagulation
- Hormone secretion
- Cardiac pacemaker activity
Calcium gluconate replenishes body stores to support these processes.
7. Summary of Mechanism
| Mechanism | Effect |
|---|---|
| ↑ Extracellular calcium | Corrects hypocalcemia |
| Membrane stabilization | Protects heart during hyperkalemia |
| Antagonizes hypermagnesemia | Reverses toxicity |
| Counters CCB overdose | Improves contractility and BP |
| ↓ Neuronal excitability | Reduces tetany |
Pharmacokinetics
- Route: IV preferred; oral absorption is limited
- Onset:
- IV: Immediate (minutes)
- Oral: Slow
- Distribution: Rapidly enters extracellular space
- Metabolism: Not metabolized
- Elimination: Renal and fecal
Clinical Uses
- Acute symptomatic hypocalcemia
- Hyperkalemia (cardiac protection)
- Calcium channel blocker overdose
- Hypermagnesemia
- Neonatal hypocalcemia
- Adjunct in cardiac resuscitation
- Prevention of hypocalcemia in massive transfusion
Adverse Effects
- Local irritation or extravasation injury
- Bradycardia with rapid infusion
- Arrhythmias (rare; with too rapid IV push)
- Hypercalcemia (with repeated dosing)
- Nausea, metallic taste
Contraindications
- Hypercalcemia
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Concurrent digoxin therapy (caution — risk of arrhythmia)
- Severe renal impairment (caution)
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Calcium Gluconate | Calcium Chloride | IV Calcium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elemental calcium | 9% | 27% | Variable |
| Irritation risk | Low | High | Moderate |
| Use in codes | Good | Strong | Moderate |
| Line requirement | Peripheral safe | Central line preferred | — |
| Hyperkalemia stabilization | Effective | More potent | Effective |
MCQs
1. Calcium gluconate stabilizes the myocardium in hyperkalemia by:
a) Lowering serum potassium
b) Raising cardiac threshold potential
c) Blocking sodium channels
d) Increasing potassium excretion
Answer: b) Raising cardiac threshold potential
2. Which condition is treated by antagonizing magnesium toxicity?
a) Hypokalemia
b) Hypermagnesemia
c) Hypercalcemia
d) Hyponatremia
Answer: b) Hypermagnesemia
3. In CCB overdose, calcium gluconate:
a) Decreases heart rate
b) Increases ionized calcium to overcome channel block
c) Blocks adrenergic receptors
d) Lowers serum calcium
Answer: b) Increases ionized calcium to overcome channel block
4. Calcium gluconate infusion can cause:
a) Hyperkalemia
b) Hypercalcemia
c) Hypomagnesemia
d) Hypoglycemia
Answer: b) Hypercalcemia
5. Oral calcium gluconate is less preferred because:
a) Poor stability
b) Low absorption
c) High risk of toxicity
d) High magnesium content
Answer: b) Low absorption
FAQs
Q1. Does calcium gluconate lower potassium in hyperkalemia?
No—it stabilizes the myocardium but does not change serum potassium.
Q2. Which form is safer for peripheral IV administration?
Calcium gluconate (less irritating than calcium chloride).
Q3. How fast does IV calcium gluconate work?
Within minutes, especially in cardiac emergencies.
Q4. Can it be used with digoxin?
Caution is required due to risk of arrhythmias.
Q5. Is calcium gluconate useful in massive blood transfusion?
Yes—prevents citrate-induced hypocalcemia.
References
Goodman & Gilman’s Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2189
Katzung: Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2464
Tripathi: Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://jaypeebrothers.com/
Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookid=2129

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com