Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
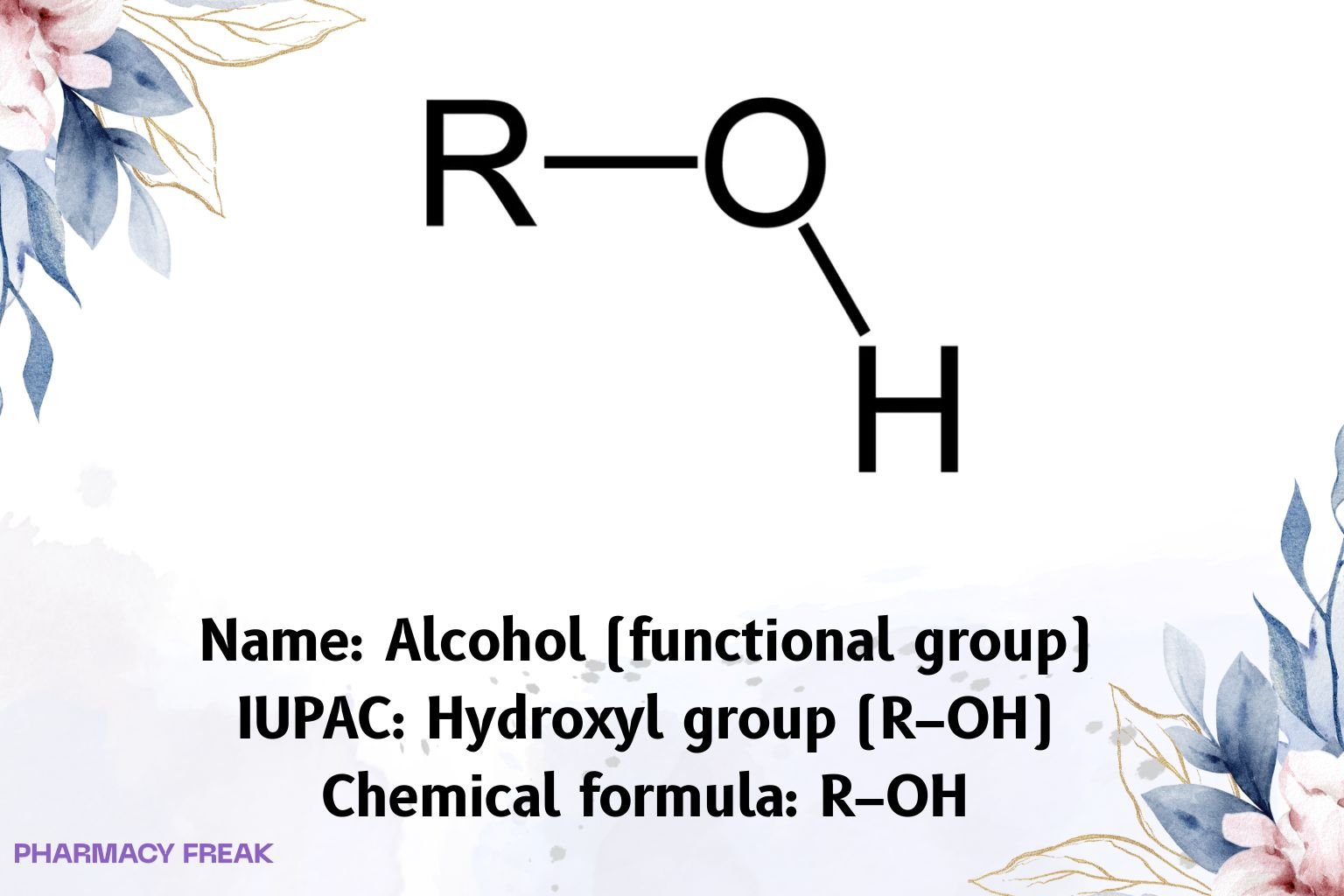
Alcohol (functional group) denotes an sp³ carbon bearing a hydroxyl (–OH) substituent: general formula R–OH. Hallmarks: hydrogen bonding, moderate nucleophilicity of the oxygen lone pairs, weak Brønsted acidity (pKₐ ~15–19), and formation of derivatives (ethers, esters, sulfonates).
Brand Names
Not applicable.
Name
Alcohol (hydroxyl functional group)
Background
Classified by substitution at the α-carbon (primary, secondary, tertiary). Physical trends: higher boiling points vs hydrocarbons due to H-bonding; miscibility with water decreases with increasing hydrophobic R. Spectroscopy: IR O–H stretch ~3200–3600 cm⁻¹ (broad), C–O stretch ~1000–1200 cm⁻¹; ¹H NMR O–H often broad/variable; ¹³C NMR C–O at 50–80 ppm.
Modality
Functional group (class of small molecules)
Groups
Endogenous metabolites and exogenous chemicals
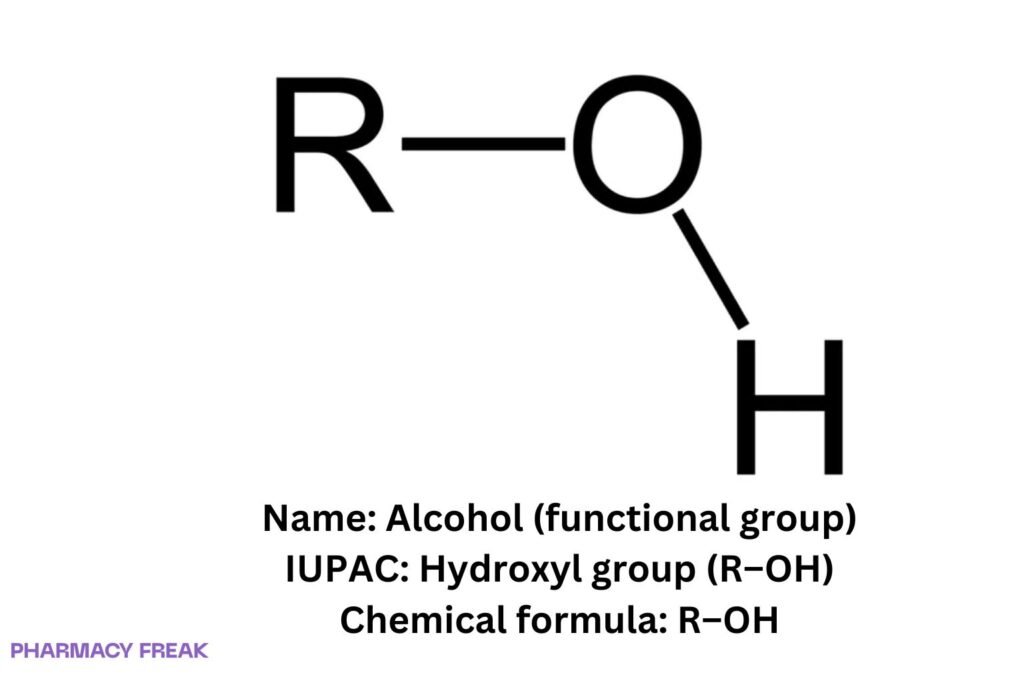
Structure
Weight
Not applicable (class-dependent)
Chemical Formula
R–OH
Synonyms
Hydroxyl group; alkanol; –OH
External IDs
Not applicable (generic functional group)
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Not a therapeutic agent (group descriptor).
Associated Conditions
Occurs in biomolecules (sugars, steroids, amino-acid side chains) and countless APIs; often masked as esters/ethers to tune ADME.
Associated Therapies
Medicinal chemistry prodrug strategies (e.g., ester prodrugs to enhance permeability).
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Not applicable at the group level.
Pharmacodynamics
Chemical behavior: nucleophilic substitution at the α-carbon (after activation), esterification with acids/acid derivatives, oxidation (primary→aldehyde/acid; secondary→ketone; tertiary: resistant), dehydration to alkenes (E1/E2), and formation of sulfonate leaving groups (tosylate/mesylate).
Mechanism of action
Reactivity arises from the polar O–H and σ C–O bonds; lone pairs on oxygen participate in Lewis basic interactions and metal coordination; H-bond donor/acceptor behavior governs solvation, binding, and boiling point elevation.
Absorption
Ionization rare (weak acid), but extensive H-bonding increases aqueous solubility vs hydrocarbons of similar size.
Volume of distribution / Protein binding / Metabolism / Elimination / Half-life / Clearance
Not applicable at the class level; scaffold-dependent.
Adverse Effects / Toxicity / Pharmacogenomics
Not applicable to the functional group per se.
Pathways
Conversions: ROH → RCl/RBr (PX₃, SOCl₂), ROH → ROTs/OMs (leaving-group install) → SN2; Fischer esterification (ROH + R′CO₂H ⇄ R′CO₂R); oxidations (PCC/Swern/DMP; catalytic O₂); Williamson ether synthesis (RO⁻ + R′X).
3. Interactions
Chemical Interactions
Acid–base with strong bases (RO⁻ formation), metal alkoxides with Na/K, acetal/ketal formation via carbonyl chemistry (after oxidation/derivatization), and coordination to Lewis acids/cations.
Food/Drug Interactions
Not applicable to the group.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
None (functional group)
Drug Categories
Functional group; Polar protic motif
Chemical Taxonomy
sp³ carbon–oxygen single bond with terminal hydroxyl; generic notation R–OH; hydrogen-bond donor/acceptor; IR O–H ~3200–3600 cm⁻¹.
Affected organisms
Not applicable
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII / CAS / InChI / InChIKey
Not applicable (class).
Generic SMILES: R–O
IUPAC Name
Alcohol functional group (hydroxyl group)
6. References
IUPAC Gold Book — definitions of alcohols and hydroxyl group; spectroscopic conventions.
Clayden, Greeves, Warren. Organic Chemistry — alcohol reactivity (oxidation, substitution, dehydration), physical properties.
March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry — mechanisms of esterification, sulfonate formation, and redox of alcohols.
Silverstein et al. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds — IR/NMR signatures of alcohols.

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com