Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Beta blockers (β-adrenergic receptor antagonists) are small-molecule agents that reduce heart rate, contractility, AV-node conduction, and renin release via competitive antagonism at β₁/β₂ receptors; clinical subclasses include non-selective, β₁-selective (cardioselective), and α₁/β blockers. ISA (partial agonist) and vasodilatory properties vary by drug.
Brand Names
Not applicable at class level.
Name
Beta blocker (β-adrenergic receptor antagonist class)
Background
Generations by pharmacology:
• 1st: non-selective (e.g., propranolol, nadolol)
• 2nd: β₁-selective (e.g., metoprolol, atenolol, bisoprolol, esmolol)
• 3rd: vasodilating or α₁/β (carvedilol, labetalol) and NO-mediated (nebivolol).
Formulations: oral, IV; ophthalmic for glaucoma (e.g., timolol).
Modality
Small molecules
Groups
Approved; prescription
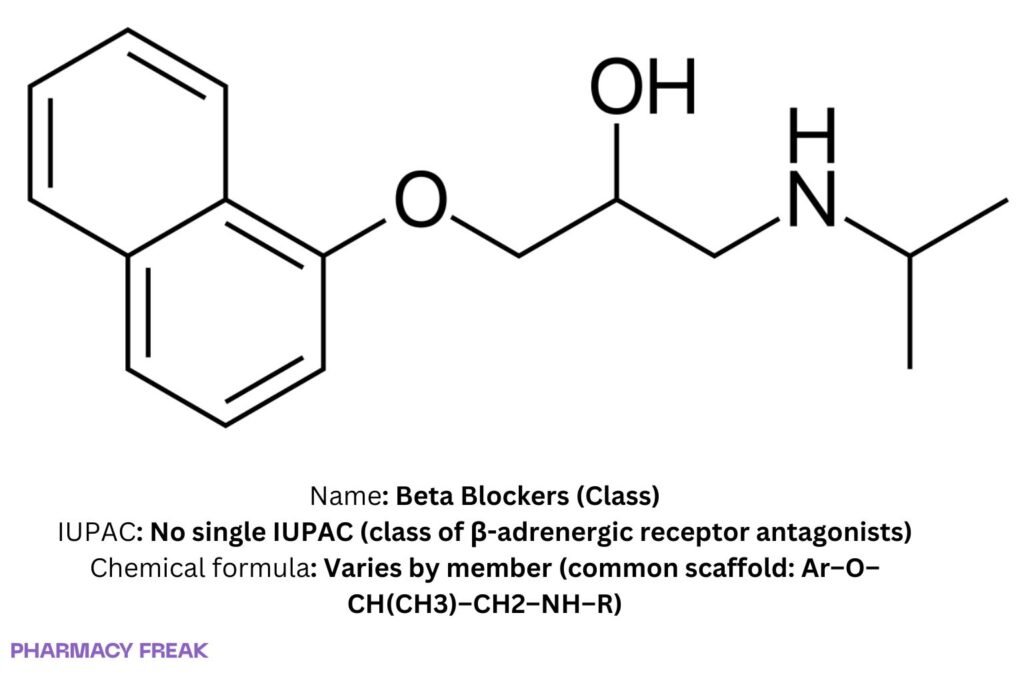
Structure
Weight
Varies by member
Chemical Formula
Varies by member
Synonyms
β-blockers; beta-adrenergic antagonists; β-AR antagonists
External IDs
ATC family: C07 (subgroups below)
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Hypertension; chronic stable angina; post-MI secondary prevention; heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (evidence-based: bisoprolol, metoprolol succinate, carvedilol); supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias (rate control/antiarrhythmic use); hyperthyroidism/thyrotoxicosis (symptom control); migraine prophylaxis; essential tremor; portal hypertension (non-selective); glaucoma (topical timolol); selected peri-operative uses (e.g., esmolol).
Associated Conditions
CAD, atrial fibrillation/flutter, SVT, HFrEF, pheochromocytoma (only with prior α-blockade), anxiety tachycardia, aortic dissection protocols (with vasodilator).
Associated Therapies
With ACEI/ARB/ARNI, MRA, SGLT2i in HFrEF; with nitrates/CCBs in angina; with diuretics/RAAS blockers in hypertension.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Class: severe bradycardia, 2nd/3rd-degree AV block without pacing, cardiogenic shock, acute decompensated HF (until stabilized), severe bronchospasm/asthma for non-selective agents, untreated pheochromocytoma without α-blockade.
Cautions: diabetes (hypoglycemia masking), peripheral vascular disease, depression (drug-specific), abrupt withdrawal (rebound ischemia/tachycardia)—taper.
Pharmacodynamics
β₁ blockade → ↓ HR, ↓ contractility, ↓ AV conduction, ↓ renin.
β₂ blockade (non-selective) → bronchoconstriction, peripheral vasoconstriction, ↓ glycogenolysis.
Mechanism of action
Reversible competitive antagonism (often inverse agonism) at β-adrenergic GPCRs. Some agents have additional actions: α₁ antagonism (carvedilol, labetalol) and endothelium-NO release (nebivolol).
Absorption
Oral absorption generally good; first-pass metabolism is drug-dependent (high for propranolol, moderate for metoprolol; low for atenolol/nadolol). IV agents include esmolol for rapid titration.
Volume of distribution
Lipophilic (e.g., propranolol) → large Vd/CNS penetration; hydrophilic (atenolol, nadolol) → smaller Vd/CNS sparing.
Protein binding
Drug-dependent (low to high).
Metabolism
Pathways differ: CYP2D6 (metoprolol, carvedilol), CYP1A2/2D6 (propranolol); esterase hydrolysis (esmolol); minimal metabolism with predominant renal excretion (atenolol, nadolol).
Route of elimination
Hepatic metabolism with biliary/renal excretion (many); primarily renal unchanged for atenolol/nadolol.
Half-life
Wide range: esmolol ~9 min (IV), metoprolol ~3–7 h, atenolol ~6–9 h, nadolol ~20–24 h.
Clearance
Hepatic (high-extraction drugs) vs renal (hydrophilic agents); genotype and drug interactions alter exposure for CYP-metabolized members.
Adverse Effects
Bradycardia, hypotension, fatigue, dizziness, cold extremities, sexual dysfunction; bronchospasm (non-selective), sleep disturbance/vivid dreams (more lipophilic), depression (signal varies), masking of hypoglycemia; rare: AV block, HF worsening, severe bronchospasm.
Toxicity
Overdose → profound bradycardia, hypotension, shock, hypoglycemia; management: airway/fluids/vasopressors, glucagon, high-dose insulin euglycemia therapy; lipid emulsion for lipophilic agents in select cases.
Pathways
β-receptor signaling antagonism; downstream ↓ cAMP/PKA in heart/kidney.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
CYP2D6 phenotype significantly affects metoprolol exposure/response; monitor for exaggerated bradycardia in poor metabolizers or with strong CYP2D6 inhibitors.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Additive AV-node depression with non-DHP CCBs (verapamil/diltiazem), digoxin, and antiarrhythmics (amiodarone, sotalol).
CYP2D6 inhibitors (fluoxetine, paroxetine, bupropion, quinidine) ↑ metoprolol levels.
Clonidine: risk of rebound hypertension if clonidine stopped first—taper β-blocker last.
Insulin/sulfonylureas: masking of hypoglycemia; monitor.
Bronchodilators may be antagonized by non-selective agents.
PDE5 inhibitors: additive hypotension (patient-specific).
Food Interactions
Mostly minor and drug-specific; dose consistently per label.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
C07 Beta blocking agents; key subgroups: C07AA non-selective, C07AB selective (β₁), C07AG alpha- and beta-blocking; fixed-dose diuretic combinations C07BA/C07BB/C07BG.
Drug Categories
Antihypertensive; Antianginal; Antiarrhythmic/rate control; HF therapy (selected agents); Antimigraine prophylaxis; Antitremor; Antiglaucoma (topical)
Chemical Taxonomy
Predominant aryloxypropanolamine scaffold; heteroaryl variants; third-generation additions (α₁ blockade; NO-mediated vasodilation).
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
Not applicable (class)
CAS number
Not applicable (class)
InChI Key
Not applicable (class)
InChI
Not applicable (class)
IUPAC Name
No single IUPAC (class)
SMILES
No single SMILES (class)
6. References
StatPearls: Beta Blockers — classification (non-selective vs β₁-selective), indications, contraindications, adverse effects. NCBI
ATC/DDD Index (WHOCC): C07 Beta blocking agents and subgroup definitions (C07AA, C07AB, C07AG, combinations). atcddd.fhi.no+2atcddd.fhi.no+2
Esmolol labeling (FDA): IV use, elimination half-life ~9 minutes, rapid titration facts. FDA Access Data
StatPearls: Esmolol monograph — PK confirmation (t½ ~9 min). NCBI
PubMed review: Nebivolol promotes NO-mediated vasodilation (β₃-linked endothelial pathway). PubMed
Drug class summaries (clinical overviews): selectivity lists and practice notes. Wikipedia+1

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com