Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Rifampicin (USAN: rifampin) is an ansamycin antibiotic that inhibits bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase; first-line for tuberculosis (in combinations), used for meningococcal carriage eradication, and other susceptible infections; hallmark potent enzyme/transporter inducer; orange-red discoloration of body fluids is characteristic.
Brand Names
Rifadin, Rimactane; numerous generics
Name
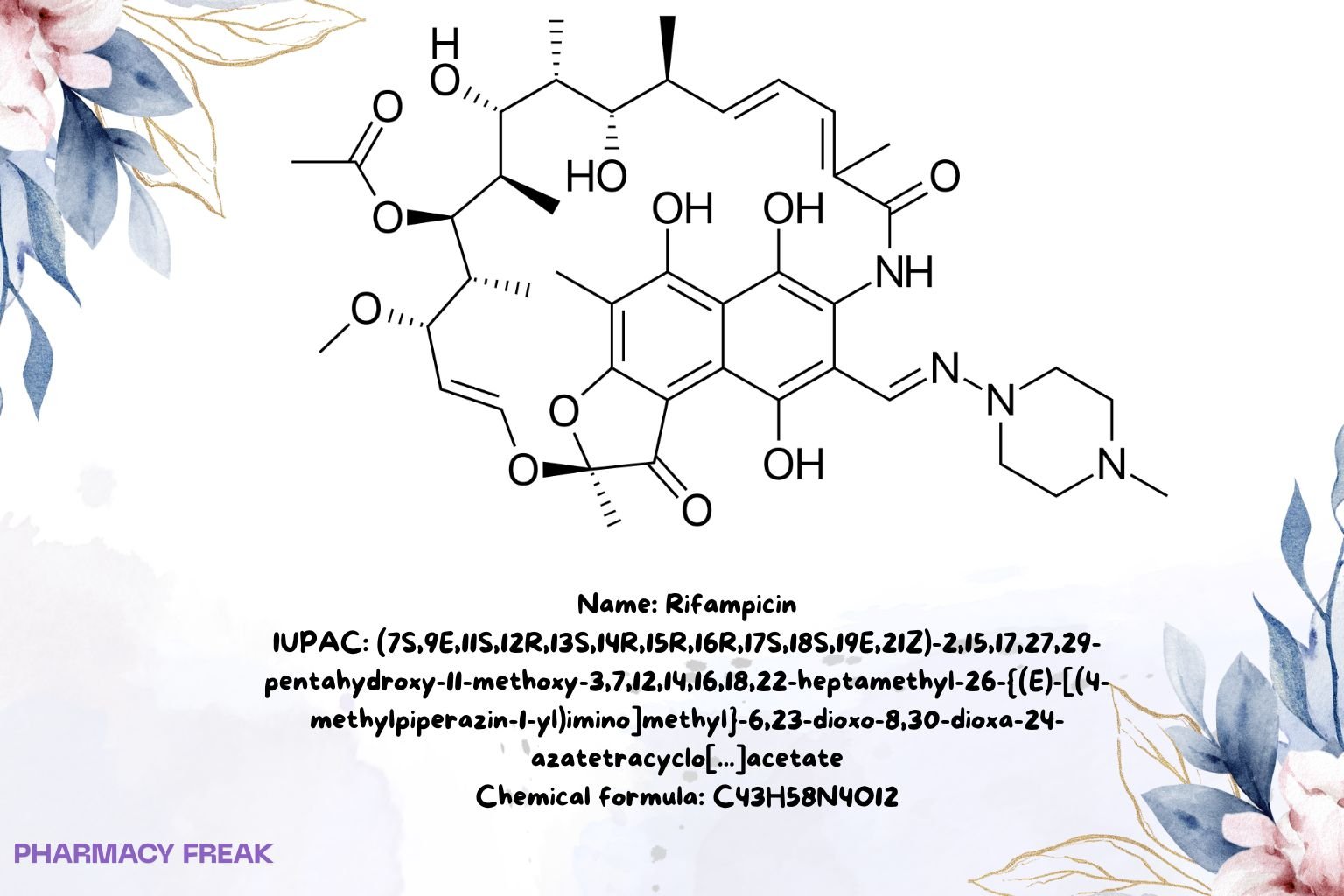
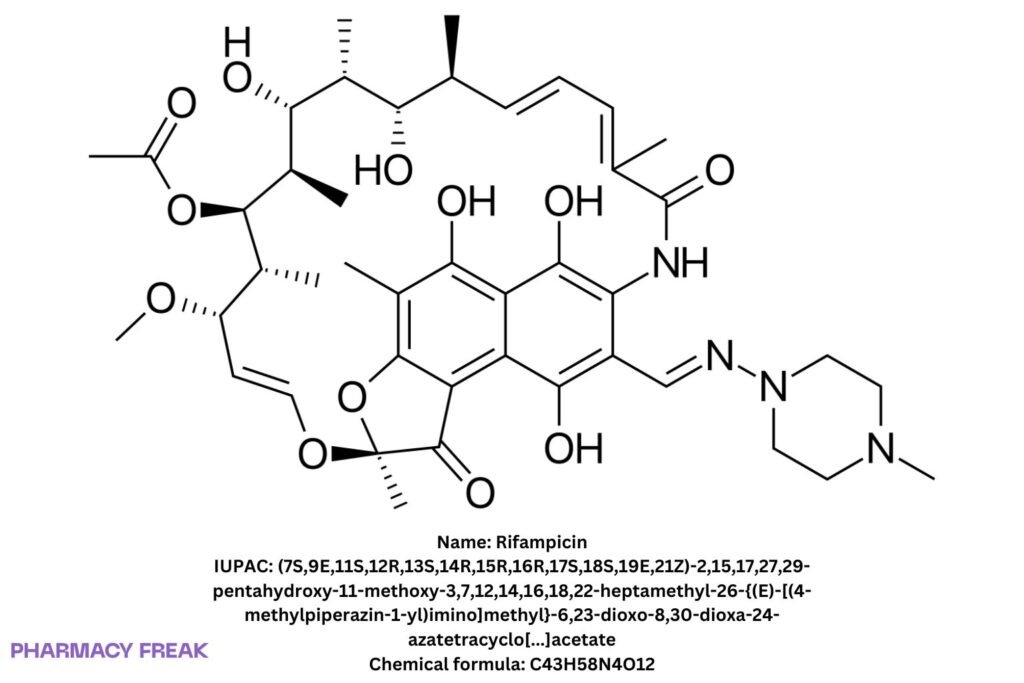
Rifampicin
Background
Semisynthetic derivative of rifamycin SV; oral and IV formulations; strong inducer of CYP3A/CYP2C/CYP2B6, UGT1A1, and P-gp affecting many co-medications.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
Structure
Weight
~822.94 g/mol (base)
Chemical Formula
C₄₃H₅₈N₄O₁₂
Synonyms
Rifampin; 3-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)iminomethyl]rifamycin SV acetate (systematic variant)
External IDs
CAS: 13292-46-1; PubChem CID: 5381226; UNII: VJT6J7R4TR; ATC: J04AB02; KEGG: D00211; ChEBI: 28077
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Combination therapy for pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB; eradication of Neisseria meningitidis carriage; adjunctive/off-label in select staphylococcal device infections and cholestatic pruritus per guidelines.
Associated Conditions
TB (drug-susceptible regimens), latent TB infection (LTBI), meningococcal prophylaxis, leprosy programs (regimen-dependent).
Associated Therapies
Standard TB regimens with isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol; combinations vary by phase and resistance profile.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Contraindicated with ritonavir-boosted saquinavir (severe hepatotoxicity) and with several HIV protease inhibitors/NNRTIs per labeling; hypersensitivity to rifamycins. Major warnings: hepatotoxicity, severe cutaneous ADRs (e.g., SJS/TEN), drug interactions due to enzyme induction.
Pharmacodynamics
Rapid bactericidal activity against M. tuberculosis, including slowly/intermittently replicating populations; post-antibiotic effect present.
Mechanism of action
Binds the β-subunit pocket of bacterial RNA polymerase, blocking transcription elongation (steric occlusion).
Absorption
Well absorbed orally; food reduces absorption ~30%—dose on an empty stomach when feasible.
Volume of distribution
High; representative adult Vd ~1.6 L/kg; penetrates CSF (especially with meningeal inflammation); stains body fluids orange-red.
Protein binding
~80% (concentration-independent)
Metabolism
Hepatic deacetylation to active 25-desacetyl-rifampin; strong induction of CYP3A4/2C9/2C19/2C8/2B6, UGT1A1, and P-gp.
Route of elimination
Predominantly biliary/fecal via enterohepatic cycling; urine <30% (parent + metabolites).
Half-life
Typical ~2–4 h (shortens with auto-induction on repeated dosing).
Clearance
Total body clearance ~0.14–0.19 L/h/kg IV (dose-dependent in label data); no routine adjustment in renal impairment at usual doses; use caution in hepatic disease.
Adverse Effects
GI upset, rash, pruritus, flu-like syndrome (more with intermittent dosing), transaminitis/hepatitis, thrombocytopenia/hemolysis (rare), orange discoloration of tears/urine/sweat (contact lens staining).
Toxicity
Overdose: nausea, vomiting, confusion, cholestasis, “red man-like” discoloration; supportive care.
Pathways
RNA polymerase inhibition → bacterial death; enterohepatic recirculation; deacetylation to active metabolite.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
No required PGx; interaction burden driven by induction of metabolic enzymes/transporters.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Potent inducer → ↓ exposure/efficacy of many drugs: warfarin, DOACs (apixaban, rivaroxaban, dabigatran via P-gp), oral contraceptives, calcineurin inhibitors (cyclosporine, tacrolimus), azoles (itraconazole/ketoconazole), macrolides (clarithromycin), antiarrhythmics, statins, opioids (methadone, oxycodone), antiplatelets (ticagrelor ↓; clopidogrel active metabolite ↑), many antiretrovirals (contraindicated/not recommended per agent). Increased hepatotoxicity with other hepatotoxins (e.g., isoniazid, halothane).
Food Interactions
Food ↓ absorption (~30%); administer 1 h before or 2 h after meals when possible.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
J04AB02 (antimycobacterials—antibiotics for TB)
Drug Categories
Antimycobacterial; Rifamycin/ansamycin; RNA-polymerase inhibitor; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Ansamycin macrocycle bridging a naphthoquinone core; acetate ester; tertiary amine side chain
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use); targets Mycobacterium spp. and select bacteria
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
VJT6J7R4TR
CAS number
13292-46-1
InChI Key
JQXXHWHPUNPDRT-WLSIYKJHSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C43H58N4O12/c1-21-12-11-13-22(2)42(55)45-33-28(20-44-47-17-15-46(9)16-18-47)37(52)30-31(38(33)53)36(51)26(6)40-32(30)41(54)43(8,59-40)57-19-14-29(56-10)23(3)39(58-27(7)48)25(5)35(50)24(4)34(21)49/h11-14,19-21,23-25,29,34-35,39,49-53H,15-18H2,1-10H3,(H,45,55)/b12-11+,19-14+,22-13-,44-20+/t21-,23+,24+,25+,29-,34-,35+,39+,43-/m0/s1
IUPAC Name
(7S,9E,11S,12R,13S,14R,15R,16R,17S,18S,19E,21Z)-2,15,17,27,29-pentahydroxy-11-methoxy-3,7,12,14,16,18,22-heptamethyl-26-{(E)-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)imino]methyl}-6,23-dioxo-8,30-dioxa-24-azatetracyclo[23.3.1.1^4,7.0^5,28]triaconta-1(28),2,4,9,19,21,25(29),26-octaen-13-yl acetate
SMILES
CN1CCN(CC1)/N=C/c2c(O)c3c5C(=O)[C@@]4(C)O/C=C/C@HC@@HC@@HC@HC@HC@HC@@HC@@H\C=C\C=C(\C)C(=O)Nc2c(O)c3c(O)c(C)c5O4
6. References
DailyMed label (RIFAMPIN capsules/injection): food ↓ absorption ~30%, protein binding ~80%, half-life ~2–3 h (range ~1–5 h), biliary elimination with desacetyl-rifampin, urine <30%, contraindication with ritonavir-boosted saquinavir. FDA Access Data
FDA GSRS/UNII: UNII VJT6J7R4TR, InChIKey JQXXHWHPUNPDRT-WLSIYKJHSA-N, formula C43H58N4O12. precisionFDA
PubChem: CID 5381226, formula, mass, SMILES/InChI records. PubChem
KEGG DRUG: D00211 (rifampin/rifampicin names and products). KEGG
StatPearls: Vd ~1.6 L/kg adults, strong inducer (CYP3A/2C/2B6, UGT1A1, P-gp), interaction exemplars; distribution notes. NCBI
ATC/DDD Index: J04AB02 classification and DDD context. FHI
Wikipedia (cross-checked identifiers/values; not primary): CAS 13292-46-1, general bioavailability/PK ranges, IUPAC string. Wikipedia

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com