Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) for hypertension, diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes with proteinuria, and risk reduction of stroke in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy.
Brand Names
Cozaar; numerous generics
Name
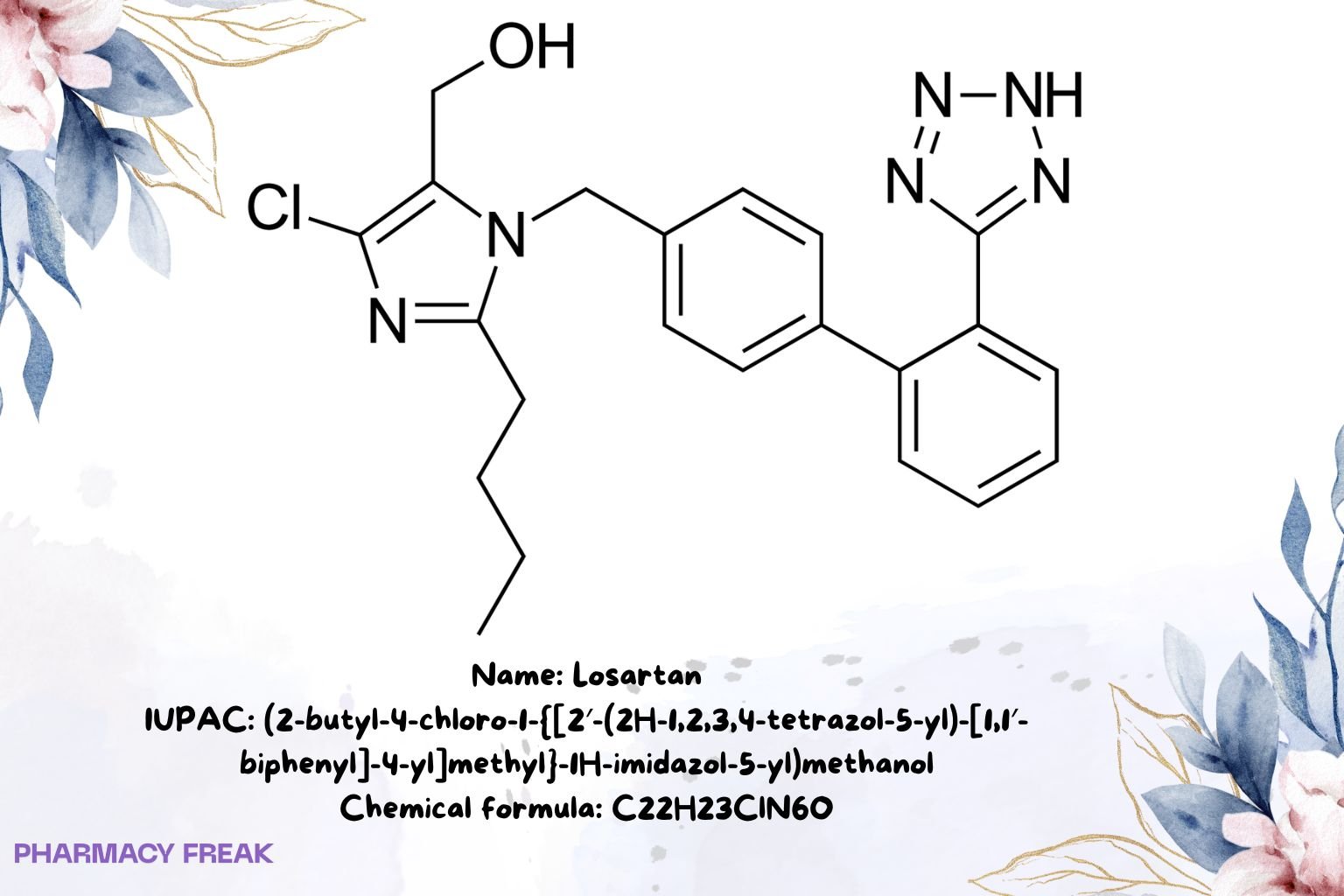
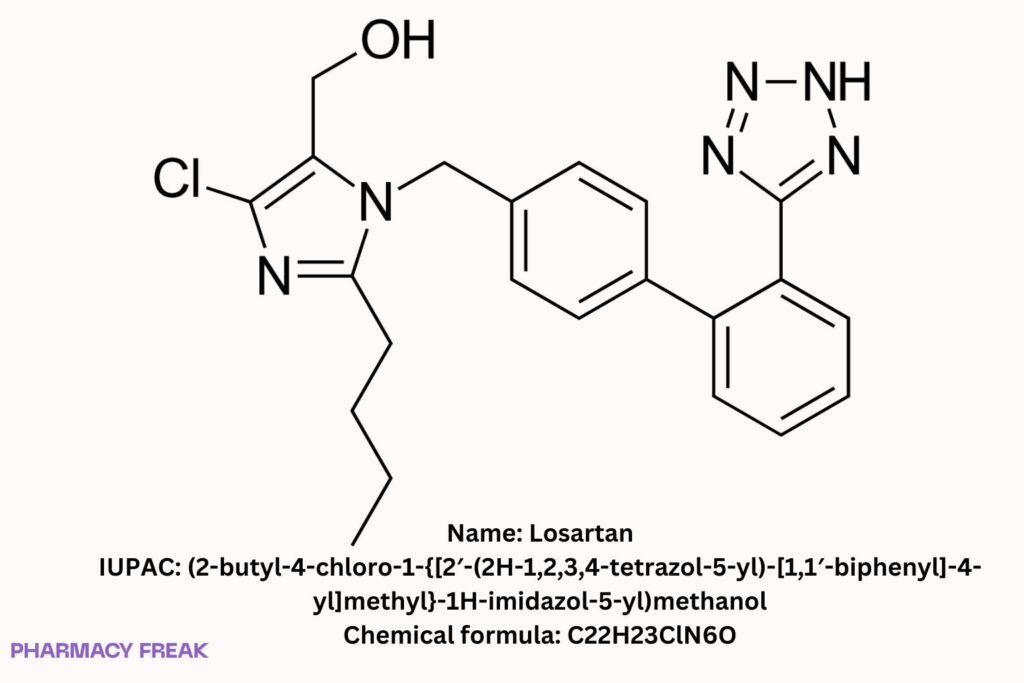
Losartan
Background
First-in-class ARB; marketed commonly as the potassium salt for oral tablets and fixed-dose combinations with hydrochlorothiazide.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
Structure
Weight
~422.91 g/mol (free base)
Chemical Formula
C₂₂H₂₃ClN₆O (free base)
Synonyms
(2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2′-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanol; losartan free base; losartan potassium (salt form)
External IDs
CAS (base): 114798-26-4; PubChem CID: 3961; UNII (base): JMS50MPO89; ATC: C09CA01; KEGG: D08146
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Hypertension; diabetic nephropathy in T2DM with elevated urinary albumin; reduction of stroke risk in hypertensive patients with LVH.
Associated Conditions
Hypertension with compelling indications; proteinuric kidney disease; LVH.
Associated Therapies
Monotherapy or combined with thiazide diuretics; combinations with other antihypertensives per guidelines.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Boxed warning (pregnancy): drugs acting on the renin–angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus. Contraindicated in pregnancy.
Pharmacodynamics
Selective antagonism of AT₁ receptors reduces vasoconstriction and aldosterone effects; active carboxylic acid metabolite EXP3174 contributes substantially to effect.
Mechanism of action
Competitive AT₁ receptor blockade; feedback increases plasma renin activity and angiotensin II, but receptor antagonism prevents downstream vasoconstriction and aldosterone release.
Absorption
Oral absorption with ~33% systemic bioavailability; peak tₘₐₓ ≈1 h for losartan and 3–4 h for EXP3174.
Volume of distribution
Approx. ~34 L for losartan; ~12 L for EXP3174.
Protein binding
High: ~98–99% (albumin-dominant).
Metabolism
Hepatic CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 form active EXP3174 and other metabolites.
Route of elimination
Renal and biliary/fecal elimination, mostly as metabolites.
Half-life
Losartan ~2 h; active metabolite ~6–9 h.
Clearance
Hepatic metabolism and biliary/renal routes; exposure increased in hepatic impairment.
Adverse Effects
Dizziness, upper respiratory infection, back pain; class risks include hyperkalemia, symptomatic hypotension, renal function changes, and rare angioedema.
Toxicity
Overdose management is supportive with monitoring of BP, renal function, and electrolytes.
Pathways
Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system blockade at AT₁; downstream reduction in vasoconstriction and aldosterone-mediated sodium retention.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
No required PGx; CYP2C9 variability may influence metabolite formation; monitor when strong enzyme modulators are present.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Potassium-sparing diuretics, potassium supplements, or salt substitutes containing potassium → hyperkalemia risk.
Lithium → increased lithium exposure and toxicity risk.
NSAIDs → reduced antihypertensive effect; renal risk, especially with dehydration or CKD.
Aliskiren → avoid with diabetes; monitor if combined otherwise.
Dual RAAS blockade with ACE inhibitors or other ARBs → not recommended due to renal and hyperkalemia risk.
Food Interactions
Food has minimal effect on overall exposure; administer consistently.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
C09CA01 (ARB, plain)
Drug Categories
Angiotensin II receptor blocker; Antihypertensive; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Biphenyl tetrazole bioisostere of carboxylate; imidazole core; administered commonly as potassium salt
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
JMS50MPO89 (losartan, base)
CAS number
114798-26-4 (losartan, base)
InChI Key
PSIFNNKUMBGKDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C22H23ClN6O/c1-2-3-8-20-24-21(23)19(14-30)29(20)13-15-9-11-16(12-10-15)17-6-4-5-7-18(17)22-25-27-28-26-22/h4-7,9-12,30H,2-3,8,13-14H2,1H3,(H,25,26,27,28)
IUPAC Name
(2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2′-(2H-1,2,3,4-tetrazol-5-yl)-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl}-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanol
SMILES
CCCCc1nc(Cl)c(CO)n1Cc1ccc(-c2ccccc2-c2nn[nH]n2)cc1
6. References
DailyMed — Losartan potassium tablets: PK (bioavailability ~33%, tₘₐₓ 1 h/3–4 h), distribution (~34 L/12 L), protein binding (~98–99%), mechanism, warnings. DailyMed+3DailyMed+3DailyMed+3
PubChem / Merck Index — identifiers (formula C₂₂H₂₃ClN₆O, MW ~422.91), IUPAC, InChI, InChIKey. Merck Index+1
precision.fda (UNII) — losartan base JMS50MPO89; losartan potassium 3ST302B24A. precisionFDA+1
ATC/KEGG — C09CA01 classification and cross-references. Genome
StatPearls — interaction themes (hyperkalemia with K⁺-raising agents), general clinical use overview. NCBI
MedicalNewsToday/GoodRx — practical interaction details (aliskiren in diabetes, lithium, NSAIDs, potassium). Medical News Today+1

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com