Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Ciprofloxacin is a second-generation fluoroquinolone antibiotic used for a wide range of susceptible infections (e.g., urinary tract, GI, bone/joint, some lower respiratory infections) and available as oral, IV, ophthalmic, and otic products. Class labeling carries serious safety warnings (e.g., tendon rupture, neuropathy, CNS effects), so use is guided by risk–benefit and local stewardship.
Brand Names
Cipro, Cipro XR, Ciloxan (ophthalmic), Cetraxal (otic), and many generics (region-dependent)
Name
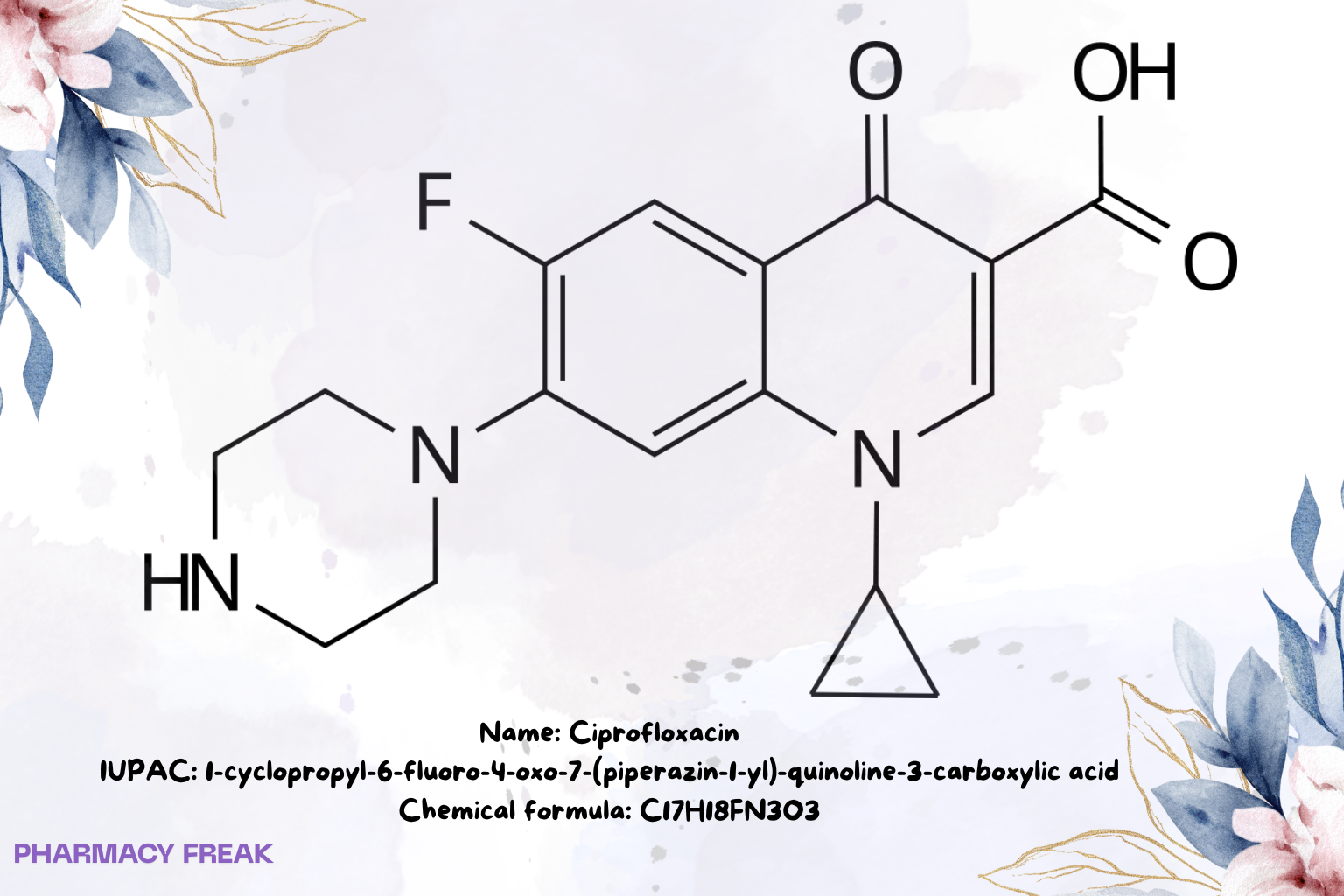
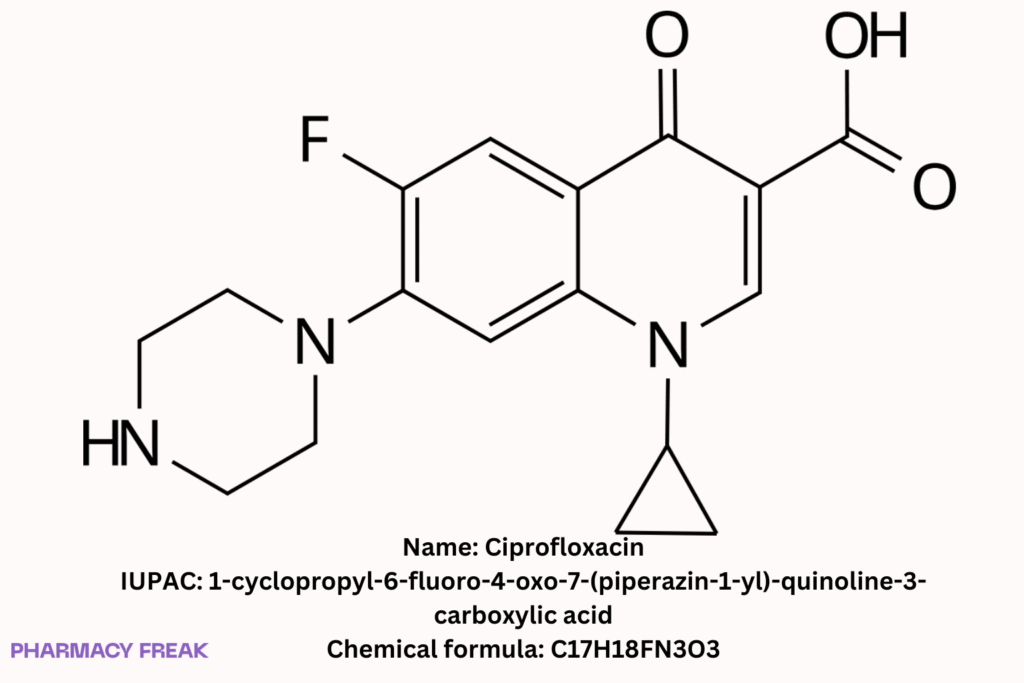
Ciprofloxacin
Background
A synthetic quinolone introduced in the 1980s; the hydrochloride salt is common for oral tablets/suspensions, while topical products use hydrochloride solutions. It inhibits bacterial DNA processes via topoisomerase targets (see Pharmacology).
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; prescription
Structure
Weight
≈ 331.35 g/mol (free base)
Chemical Formula
C₁₇H₁₈FN₃O₃ (free base)
Synonyms
1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; ciprofloxacin free base; ciprofloxacin HCl (salt form)
External IDs
CAS (base): 85721-33-1; PubChem CID: 2764; UNII (base): 5E8K9I0O4U; KEGG: D00186; ChEMBL: 8; ChEBI: 100241; ATC (systemic): J01MA02
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Treatment of susceptible infections (e.g., UTI/pyelonephritis, infectious diarrhea/typhoid, certain bone/joint infections, prostatitis, post-exposure inhalational anthrax, plague); ophthalmic/otic forms for bacterial conjunctivitis/corneal ulcer and otitis indications per label.
Associated Conditions
Complicated/acute uncomplicated UTI, traveler’s diarrhea, intra-abdominal infections (with adjuncts), osteomyelitis, selected lower respiratory infections (pathogen-specific), ocular/otic infections (topical).
Associated Therapies
Often combined with metronidazole (intra-abdominal), or dexamethasone/hydrocortisone in otic combos; avoid routine co-use with other QT-prolonging or strong CYP1A2 substrates without assessment.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Fluoroquinolone boxed warnings: tendinitis/tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, CNS effects; may exacerbate myasthenia gravis. Additional FDA warnings highlight aortic aneurysm/dissection risk in susceptible patients; restrict use for uncomplicated infections when risks outweigh benefits. Tizanidine is contraindicated with ciprofloxacin (CYP1A2 inhibition). DailyMed+2U.S. Food and Drug Administration+2
Pharmacodynamics
Bactericidal, concentration-dependent killing via inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) and topoisomerase IV, blocking DNA replication, transcription, and repair.
Mechanism of action
Fluorinated quinolone core binds gyrase/topo IV–DNA complexes, stabilizing double-strand breaks and leading to rapid bacterial cell death.
Absorption
Oral bioavailability ~70%; food may delay tₘₐₓ but not overall exposure. Avoid co-administration with polyvalent cations (e.g., Al/Mg antacids, iron, zinc, sucralfate): they markedly reduce absorption; separate doses (e.g., ≥2 h before or ≥6 h after). DailyMed
Volume of distribution
Large; typically ~2–3 L/kg, reflecting extensive tissue penetration (e.g., urine, prostate, lungs, skin, bone). NCBI+1
Protein binding
~20–40%. DailyMed
Metabolism
Hepatic biotransformation to several metabolites; ciprofloxacin is a CYP1A2 inhibitor (interaction relevance—see Interactions). DailyMed
Route of elimination
Primarily renal as unchanged drug (≈40–50% oral dose) with additional fecal/biliary excretion and minor active metabolites. DailyMed
Half-life
About ~4 hours in normal renal function (slightly prolonged with impairment). DailyMed
Clearance
Renal clearance ~300 mL/min (active tubular secretion contributes); reduced by probenecid. DailyMed
Adverse Effects
GI upset, headache, dizziness, photosensitivity; serious class effects include tendinopathy/rupture, peripheral neuropathy, CNS effects (seizures, psychosis), QT prolongation, dysglycemia, aortic aneurysm risk, and C. difficile–associated diarrhea. DailyMed
Toxicity
Overdose: supportive management; crystalluria risk mitigated by hydration. Hemodialysis removes little drug. DailyMed
Pathways
Topoisomerase targeting (DNA gyrase/topo IV); distribution via passive/active transport; renal tubular secretion.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
No routine PGx testing; CYP1A2 interactions are clinically significant; tendon risk increased with age and concurrent corticosteroids. DailyMed
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
- Contraindicated: Tizanidine (↑ exposure via CYP1A2 inhibition, severe hypotension/sedation). DailyMed
- Chelation/complexation: Al/Mg antacids, sucralfate, iron, zinc, calcium—marked ↓ absorption; separate dosing. DailyMed
- CYP1A2 substrates: Theophylline, caffeine, ropinirole, clozapine, tizanidine, sildenafil—↑ levels; monitor/avoid as labeled. DailyMed
- Probenecid: ↓ renal clearance → ↑ ciprofloxacin exposure. DailyMed
Food Interactions
May take with food; avoid dairy/calcium-fortified juices alone (reduce exposure). Take with a mixed meal if needed. DailyMed
4. Categories
ATC Codes
J01MA02 (systemic fluoroquinolone), S01AE03 (ophthalmic), S02AA15 (otic antiinfective); combination otic codes exist (e.g., S02CA05/06 with corticosteroids). atcddd.fhi.no+2atcddd.fhi.no+2
Drug Categories
Fluoroquinolone; Antibacterial; Small molecule; Topoisomerase inhibitor (bacterial)
Chemical Taxonomy
Quinolone carboxylic acid with piperazinyl and cyclopropyl substituents; fluorinated at C-6.
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use); target bacteria susceptible to fluoroquinolones
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
5E8K9I0O4U (ciprofloxacin, base) precisionFDA
CAS number
85721-33-1 (base) precisionFDA
InChI Key
MYSWGUAQZAJSOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N PubChem
InChI
InChI=1S/C17H18FN3O3/c18-13-7-11-14(8-15(13)20-5-3-19-4-6-20)21(10-1-2-10)9-12(16(11)22)17(23)24/h7-10,19H,1-6H2,(H,23,24) Wikipedia
IUPAC Name
1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid Wikipedia
SMILES
C1CNCCN1c(c2)c(F)cc3c2N(C4CC4)C=C(C3=O)C(=O)O Wikipedia
6. References
- DailyMed: Ciprofloxacin tablets—PK (bioavailability ~70%, protein binding 20–40%, t½ ~4 h), interactions (antacids/cations), tizanidine contraindication, renal clearance details. DailyMed
- PubChem (CID 2764): Molecular formula C₁₇H₁₈FN₃O₃, MW ≈331.35 g/mol; identifiers. PubChem
- FDA GSRS / precision.fda (UNII): Ciprofloxacin UNII 5E8K9I0O4U, CAS 85721-33-1. precisionFDA+1
- ATC/DDD Index (FHI): J01MA02; topical codes S01AE03, S02AA15 listings. atcddd.fhi.no+2atcddd.fhi.no+2
- StatPearls (NCBI Bookshelf): Distribution ~2–3 L/kg and clinical use overview. NCBI
- FDA Drug Safety Communications: Fluoroquinolone warnings including aortic aneurysm/dissection risk; reinforce boxed warnings. U.S. Food and Drug Administration+1

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com