Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
Omeprazole is a proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) used to reduce gastric acid secretion, treating GERD, peptic ulcer disease, erosive esophagitis, and hypersecretory states; it is supplied as a racemic mixture and often dosed before meals.
Brand Names
Prilosec, Losec, Zegerid (omeprazole/sodium bicarbonate); numerous generics (region-dependent)
Name
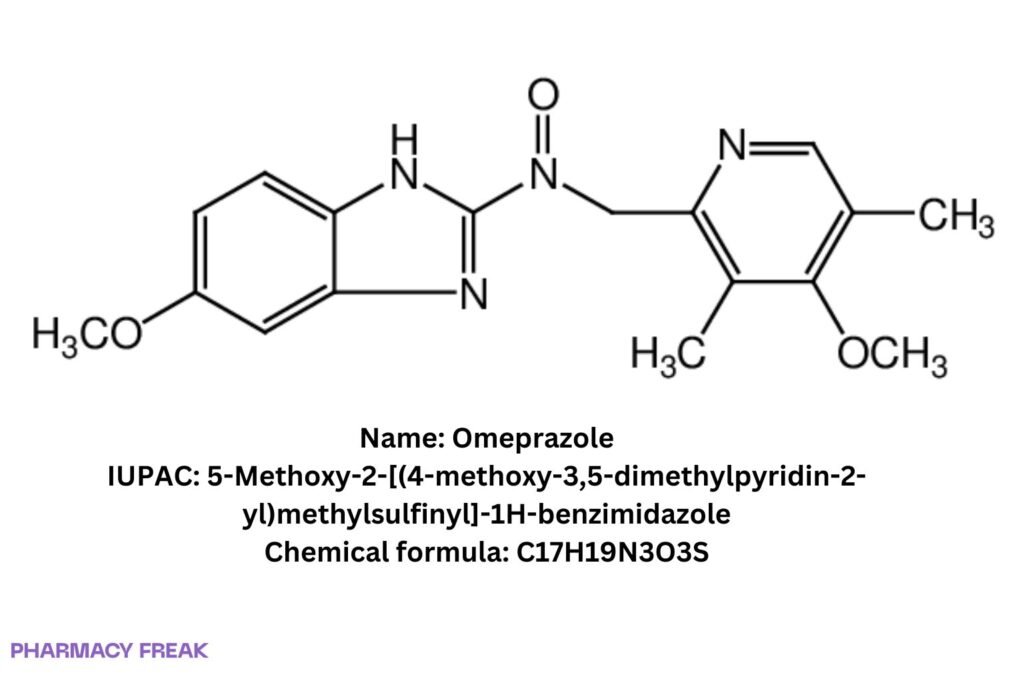
Omeprazole
Background
A benzimidazole sulfoxide first approved in the late 1980s; acid-activated in parietal cells to a reactive sulfenamide that irreversibly inhibits the gastric H⁺/K⁺-ATPase. Available as delayed-release capsules/tablets, suspensions/granules, and certain IV/lyophilized products (jurisdiction-dependent).
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Approved; OTC/Rx (region-dependent)
Structure
Weight
≈ 345.42 g/mol
Chemical Formula
C₁₇H₁₉N₃O₃S
Synonyms
5-Methoxy-2-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole; Prilosec (trade)
External IDs
CAS: 73590-58-6; PubChem CID: 4594; UNII: KG60484QX9; ATC: A02BC01; KEGG: D00455; ChEMBL: 1503; ChEBI: 7772
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Short- and long-term management of GERD, erosive esophagitis, peptic/duodenal ulcers (including H. pylori eradication regimens), and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome; maintenance of healing where indicated.
Associated Conditions
Heartburn/acid reflux, NSAID-associated ulcer prevention (per label), hypersecretory states.
Associated Therapies
Triple therapy for H. pylori (e.g., omeprazole + amoxicillin + clarithromycin or bismuth-based regimens). Combination with sodium bicarbonate to expedite absorption (Zegerid).
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Hypersensitivity to omeprazole/PPIs or formulation components. (Class has no boxed warning; labels include precautions such as bone fracture risk with long-term/high-dose use, acute interstitial nephritis, C. difficile–associated diarrhea, lupus erythematosus, B₁₂ deficiency, hypomagnesemia, and masking of gastric malignancy—evaluate alarm symptoms.)
Pharmacodynamics
Marked and sustained suppression of basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion; duration exceeds plasma half-life due to irreversible pump inhibition.
Mechanism of action
A prodrug that accumulates in the acidic canaliculi of parietal cells and converts to a sulfenamide that forms covalent bonds with cysteine residues on the H⁺/K⁺-ATPase, irreversibly blocking acid secretion until new pumps are synthesized.
Absorption
Delayed-release forms protect against acid degradation; food can delay absorption. Oral bioavailability varies and may increase on repeated dosing.
Volume of distribution
Approx. ~0.4 L/kg (literature values vary by source/formulation).
Protein binding
High (~95%).
Metabolism
Extensively hepatic via CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 to inactive metabolites; CYP2C19 phenotype influences exposure.
Route of elimination
Metabolites excreted predominantly in urine (major fraction) and in feces (biliary).
Half-life
Typically ~0.5–1 hour in healthy adults (prolonged in hepatic impairment); pharmacodynamic effect lasts much longer.
Clearance
Apparent oral clearance influenced by CYP2C19 activity and drug interactions (inducers/inhibitors).
Adverse Effects
Common: headache, abdominal pain, nausea/diarrhea, flatulence. Serious but uncommon: C. difficile infection, fractures (long-term/high dose), hypomagnesemia, B₁₂ deficiency, AIN, cutaneous/systemic lupus, and rare severe skin reactions.
Toxicity
Overdose is uncommon; management is supportive. Chronic over-suppression risks are addressed in labeling (e.g., infections, micronutrient effects).
Pathways
Acid-activation → covalent H⁺/K⁺-ATPase inhibition; downstream suppression of gastric acid.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
CYP2C19 poor metabolizers show increased exposure and effect; potent enzyme inducers (e.g., rifampin, St. John’s wort) may reduce efficacy.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
- Clopidogrel: avoid co-administration—omeprazole inhibits CYP2C19, reducing clopidogrel activation and antiplatelet effect (label caution).
- Drugs needing acidic pH for absorption (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, erlotinib, some HIV protease inhibitors/atazanavir): decreased exposure—consider alternatives/timing per label.
- CYP inducers/inhibitors: rifampin/St. John’s wort (↓ levels/efficacy); strong inhibitors may ↑ exposure.
- High-dose methotrexate: PPIs may reduce clearance—consider temporary interruption (per institutional/label guidance where applicable).
Food Interactions
Administer before meals (commonly 30–60 minutes) to optimize effect; food may slow absorption but not necessarily reduce total exposure.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
A02BC01 (proton-pump inhibitors)
Drug Categories
Proton-pump inhibitor; Anti-ulcer agent; Small molecule
Chemical Taxonomy
Benzimidazole sulfoxide; weak base; racemate (R/S-omeprazole)
Affected organisms
Humans (therapeutic use)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
KG60484QX9
CAS number
73590-58-6
InChI Key
SUBDBMMJDZJVOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C17H19N3O3S/c1-10-8-18-15(11(2)16(10)23-4)9-24(21)17-19-13-6-5-12(22-3)7-14(13)20-17/h5-8H,9H2,1-4H3,(H,19,20)
IUPAC Name
5-Methoxy-2-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methylsulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole
SMILES
COc1ccc2nc(Nc2c1)S(=O)Cc1ncc(c(c1C)OC)C (canonical forms vary across sources; confirm per chosen database.)
6. References
- FDA/GSRS UNII — Omeprazole: UNII KG60484QX9, formula C17H19N3O3S, InChIKey SUBDBMMJDZJVOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N. precisionFDA+1
- ATC/DDD Index (WHO/NCMP, Norway/FHI) — A02BC01 omeprazole; DDD routes. atcddd.fhi.no+1
- DailyMed — Omeprazole labels: clopidogrel interaction warning; precautions (fracture, C. difficile, AIN, lupus). DailyMed+2DailyMed+2
- StatPearls (NCBI Bookshelf) — PK/PD overview: short plasma half-life (~0.5–1 h), metabolism via CYP2C19/3A4, urinary excretion of metabolites. NCBI+1
- KEGG DRUG — Entry D00455 (omeprazole), cross-refs and classification. genome.jp+1
- PubChem — Omeprazole/Prilosec pages (CID 4594): identifiers and chemical data. PubChem+1
- Tocris / Fisher — CAS 73590-58-6, molecular weight 345.42 g/mol, and identifier confirmations. Tocris Bioscience+1
- IUPHAR Guide to Pharmacology — Ligand entry notes (PPI class; racemic mixture). guidetopharmacology.org

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com
