Table of Contents
Introduction
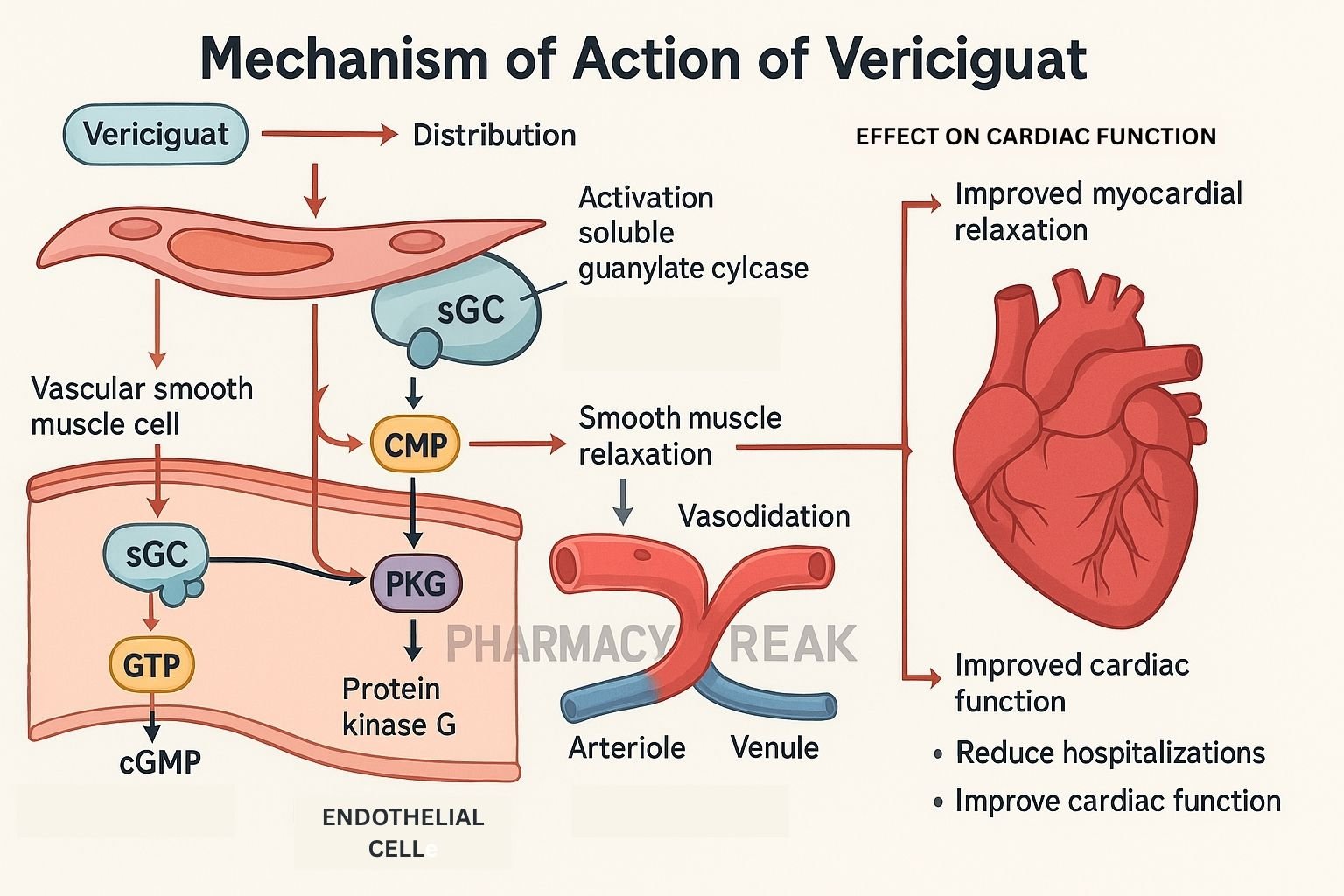
Vericiguat is a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulator used in patients with chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) following hospitalization or intravenous diuretics. It enhances the nitric oxide (NO)–sGC–cGMP pathway to support cardiovascular function.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Direct stimulation of sGC
Vericiguat binds directly to the β-subunit of sGC, increasing enzyme activity even when NO levels are low youtube.com+10pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+10thecvc.ca+10go.drugbank.com+1en.wikipedia.org+1. - Sensitization to nitric oxide
It enhances sGC’s responsiveness to any remaining endogenous NO, facilitating more robust cGMP production . - Elevation of cGMP levels
Increased cGMP leads to smooth muscle relaxation, vasodilation, and lowered vascular resistance youtube.com+10mdpi.com+10thecvc.ca+10go.drugbank.com+1merckconnect.com+1. - Cardioprotective effects
Enhanced cGMP supports reduced myocardial remodeling, decreased inflammation, and improved endothelial function .
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
- Route: Oral, once daily with food
- Bioavailability: ~93% when taken with meals thecvc.ca+4pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+4en.wikipedia.org+4
- Time to Peak (Tmax): ~4 hours with food
- Half-life: ~30 hours allowing once-daily dosing en.wikipedia.org+2pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+2go.drugbank.com+2
- Metabolism: Primarily glucuronidated via UGT1A9/UGT1A1; <5% CYP involvement en.wikipedia.org+3pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+3mdpi.com+3
- Elimination: High protein binding (~98%); excreted via urine and feces en.wikipedia.org+2go.drugbank.com+2mdpi.com+2
Clinical Uses
- To reduce risk of cardiovascular death or heart failure hospitalization in adults with symptomatic chronic HFrEF after a worsening event (hospitalization or IV diuretics) merckconnect.com+7pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+7go.drugbank.com+7.
Adverse Effects
- Mild decrease in blood pressure
- Anemia
- Low risk of symptomatic hypotension or syncope youtube.compmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Vericiguat (sGC Stimulator) | Nitrates | PDE5 Inhibitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO-dependent action | NO-independent + sensitizing | NO-dependent | Requires NO; blocks breakdown of cGMP |
| Tolerance development | None reported with daily use | Common with nitrates | Not significant |
| Target | cGMP production | cGMP production | cGMP accumulation |
MCQs
- Vericiguat primarily stimulates which enzyme?
a) PDE5 b) sGC c) NO synthase d) Guanylate kinase
Answer: b) sGC - It increases production of which second messenger?
a) cAMP b) cGMP c) IP3 d) DAG
Answer: b) cGMP - Vericiguat enhances responsiveness to:
a) Endothelin b) NO c) Angiotensin II d) Vasopressin
Answer: b) NO - Main metabolic pathway is:
a) CYP3A4 b) UGT1A9/1A1 c) CYP2D6 d) Renal filtration
Answer: b) UGT1A9/1A1 - Typical elimination half-life allows:
a) Once-daily dosing b) Twice-daily dosing c) Weekly dosing d) PRN dosing
Answer: a) Once-daily dosing - Vericiguat reduces hospitalization in patients with:
a) Stable HFpEF b) Worsened HFrEF c) Acute MI d) Stable angina
Answer: b) Worsened HFrEF - Food intake affects bioavailability by:
a) Decreasing it significantly b) Increasing it to ~93% c) No effect d) Doubling it
Answer: b) Increasing it to ~93% - Protein binding is approximately:
a) 50% b) 70% c) 98% d) 10%
Answer: c) 98% - Adverse effect seen in clinical trials:
a) Severe hypotension b) Anemia c) Arrhythmias d) Hyperkalemia
Answer: b) Anemia - Compared to nitrates, vericiguat does NOT cause:
a) Vasodilation b) Tolerance c) Hypotension d) cGMP increase
Answer: b) Tolerance
FAQs
1. When should vericiguat be given?
To patients with HFrEF who remain symptomatic after hospitalization or IV diuretics.
2. Can it be taken without food?
No—must be taken with food to ensure proper absorption.
3. Is it safe with nitrates or PDE5 inhibitors?
Avoid concurrent PDE5 inhibitors. Short‑acting nitrates tolerated but avoid combined vasodilation.
4. Does vericiguat cause reflex tachycardia?
No significant reflex tachycardia has been reported.
5. What follow-up is needed?
Monitor blood pressure and hematocrit for anemia, especially after dosage titration.
References
- Mechanism of Action of Vericiguat (Verquvo)
- DrugBank: Vericiguat pharmacology summary
- MDPI: Vericiguat in heart failure review
- Clinical FAQ on VICTORIA trial (sGC stimulation)
- Wikipedia: Vericiguat
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com