Table of Contents
Introduction
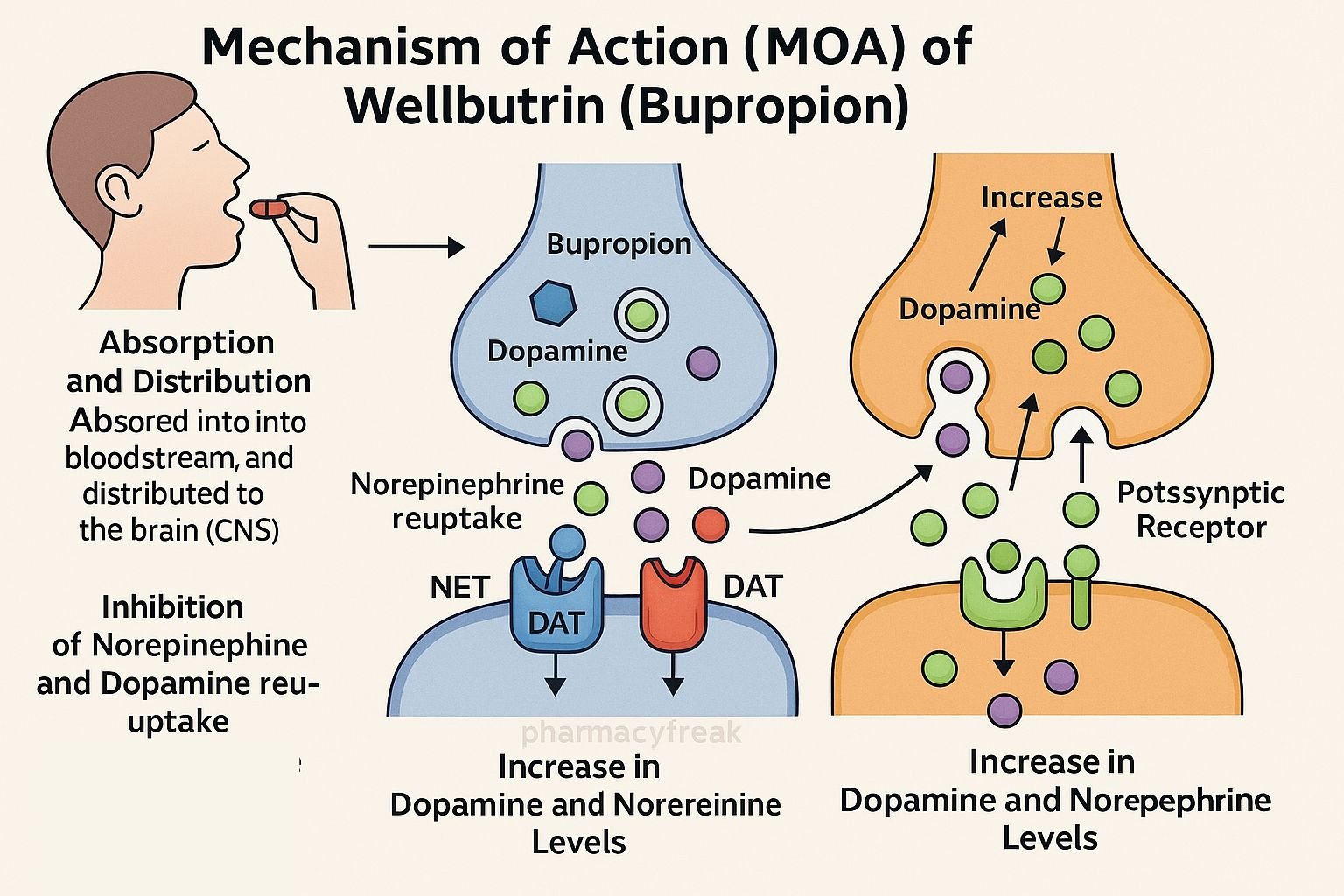
Wellbutrin (bupropion) is an atypical antidepressant and smoking cessation aid. It primarily works by inhibiting reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine, without affecting serotonin. Additionally, it acts as a nicotinic receptor antagonist, reducing nicotine cravings.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Inhibits norepinephrine reuptake
Bupropion blocks the norepinephrine transporter (NET), increasing norepinephrine in synaptic clefts. - Inhibits dopamine reuptake
It also inhibits the dopamine transporter (DAT), previously known to enhance mood and motivation. - No significant effect on serotonin
Lack of SERT inhibition results in lower risk of sexual side effects and weight gain. - Antagonizes nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
This action helps reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms in smoking cessation. - Promotes neurotrophic effects
Increased dopamine and norepinephrine may elevate BDNF levels, supporting neuronal resilience.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Oral (IR, SR, XL formulations) |
| Bioavailability | ~5–20% |
| Time to Peak (Tmax) | ~2 hours (IR); 5 hours (SR/XL) |
| Protein Binding | ~84% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic via CYP2B6 to active metabolites |
| Half-life | ~21 hours (parent); ~20–37 hours (metabolites) |
| Excretion | Renal (~87%), fecal (~10%) |
Clinical Uses
- Major depressive disorder
- Seasonal affective disorder
- Smoking cessation aid (as Zyban)
- Off-label: ADHD, neuropathic pain adjunct, weight management
Adverse Effects
- Stimulating effects: insomnia, dry mouth, headache
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate
- Dose-dependent seizure risk (>450 mg/day or in seizure-prone individuals)
- Rare GI symptoms, diaphoresis, tremors
- Low risk of sexual dysfunction or sedation
Comparative Analysis
| Drug Type | NE & DA Reuptake | Serotonin Effect | Seizure Risk | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bupropion | Moderate | None | Moderate–High | Depression, smoking cessation |
| SSRIs | None | High | Low | Depression, anxiety |
| Venlafaxine | High (NE), moderate (5‑HT) | Moderate | Moderate | Depression, neuropathic pain |
MCQs
1. Which transporters does bupropion inhibit?
a) SERT & NET b) DAT & NET c) DAT & SERT d) VMAT
Answer: b) DAT & NET
2. A key advantage over SSRIs is:
a) Weight gain b) Sexual dysfunction c) Sedation d) Lower sexual side effects
Answer: d) Lower sexual side effects
3. What is the main seizure-related risk factor?
a) High dose b) Hypoglycemia c) Hepatic impairment d) Hypertension
Answer: a) High dose
4. Which enzyme metabolizes bupropion?
a) CYP2B6 b) CYP3A4 c) CYP2D6 d) CYP1A2
Answer: a) CYP2B6
5. Bupropion aids smoking cessation by:
a) Increasing nicotine effect b) Blocking nicotine receptors c) Mimicking nicotine d) Enhancing dopamine only
Answer: b) Blocking nicotine receptors
6. Protein binding is approximately:
a) 84% b) 50% c) 10% d) 99%
Answer: a) 84%
7. Tmax for SR/XL formulations is about:
a) 2 hrs b) 5 hrs c) 10 hrs d) 24 hrs
Answer: b) 5 hrs
8. Off‑label use includes:
a) ADHD b) Asthma c) Rheumatoid arthritis d) Migraine
Answer: a) ADHD
9. Bupropion does NOT affect:
a) Dopamine b) Serotonin c) Norepinephrine d) Nicotinic receptors
Answer: b) Serotonin
10. Half-life of the parent drug is:
a) 6 hours b) 21 hours c) 48 hours d) 72 hours
Answer: b) 21 hours
11. Common side effect is:
a) Sedation b) Weight gain c) Dry mouth d) Bradycardia
Answer: c) Dry mouth
12. Metabolites have half-lives of:
a) 5–10 hrs b) 10–20 hrs c) 20–37 hrs d) >48 hrs
Answer: c) 20–37 hrs
13. Bupropion may increase levels of:
a) BDNF b) Morphine c) Cortisol d) Insulin
Answer: a) BDNF
14. Maximum recommended daily dose to minimize seizure risk is:
a) 300 mg b) 450 mg c) 600 mg d) 150 mg
Answer: b) 450 mg
15. Drug class of bupropion is:
a) SSRI b) NDRI c) MAOI d) SNRI
Answer: b) NDRI
FAQs
1. Does Wellbutrin cause sexual dysfunction?
No—sexual side effects are rare compared to SSRIs.
2. When should dosing exceed 450 mg/day?
It generally shouldn’t, due to increased seizure risk.
3. How quickly does it improve mood?
May take 4–6 weeks to see full antidepressant effect.
4. Can it be combined with nicotine patches?
Yes—but monitor for combined side effects.
5. Is it suitable for adolescents?
Only approved for adults; caution is advised for younger patients.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th Edition
- KD Tripathi. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 8th Edition
- DrugBank: Bupropion pharmacology summary
- StatPearls: Bupropion pharmacology
- PubMed review: Dopamine–norepinephrine role in depression
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com