Table of Contents
Introduction
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are among the most widely used medications globally. They are primarily prescribed for their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. Whether it’s managing acute pain, chronic arthritis, or postoperative inflammation, NSAIDs are essential tools in clinical practice. Understanding their classification is critical for pharmacy students and healthcare professionals to ensure rational and safe use.
What are NSAIDs?
NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2), which are essential for prostaglandin synthesis. Prostaglandins play a role in pain, fever, and inflammation, as well as in protecting the gastric mucosa and regulating renal blood flow. By blocking COX enzymes, NSAIDs reduce inflammation and pain but can also lead to adverse effects like gastric ulcers and renal dysfunction.
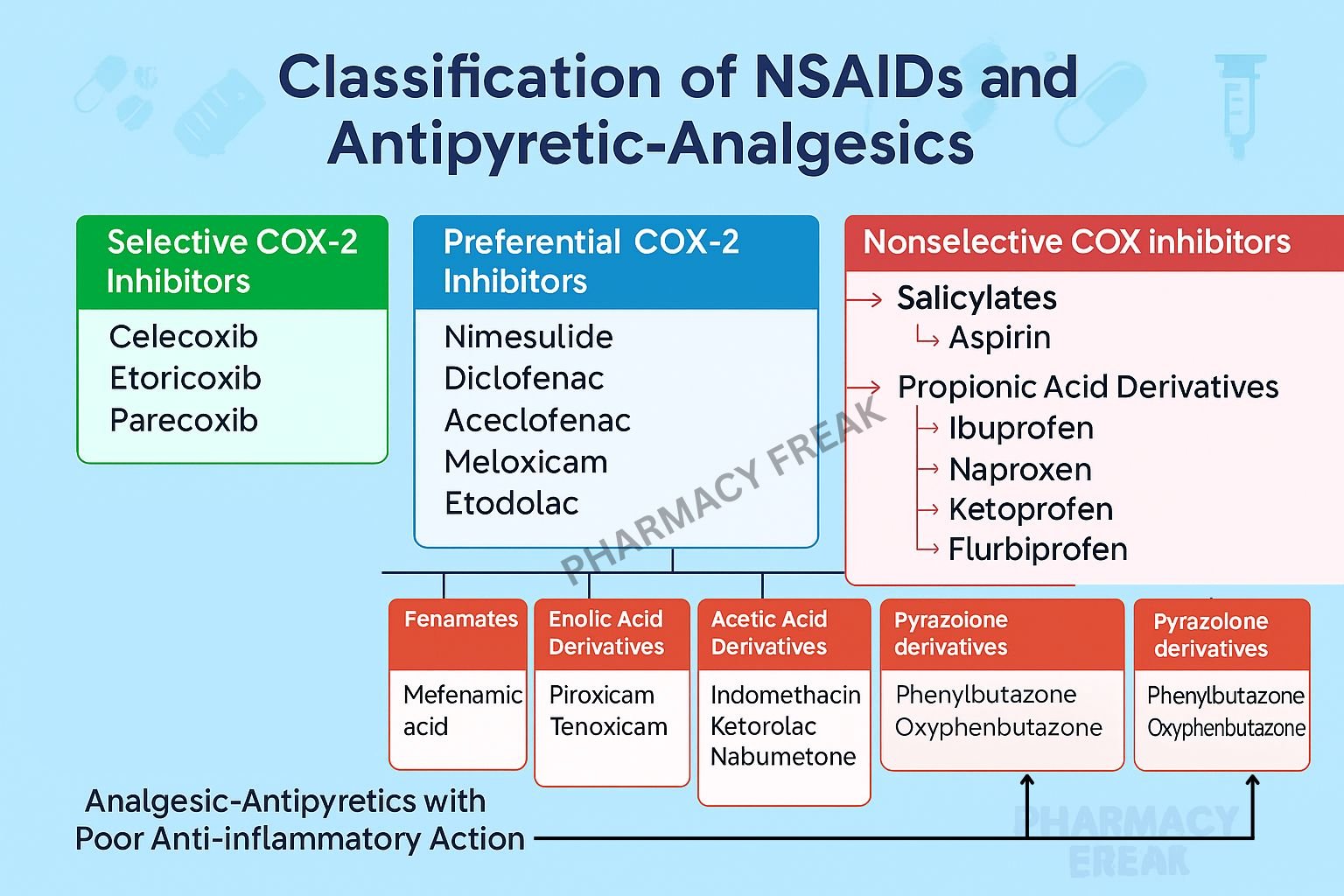
Classification of NSAIDs
NSAIDs can be classified based on various parameters such as selectivity, chemical structure, and duration of action.
1. Based on COX Selectivity
| Category | Example Drugs | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Non-selective COX inhibitors | Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Naproxen, Indomethacin | Inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 |
| Preferential COX-2 inhibitors | Nimesulide, Meloxicam, Etodolac | Higher affinity for COX-2, safer for GI |
| Selective COX-2 inhibitors (Coxibs) | Celecoxib, Etoricoxib, Parecoxib | Least GI toxicity, but cardiovascular risks |
2. Based on Chemical Structure
| Class | Examples |
|---|---|
| Salicylates | Aspirin, Diflunisal |
| Propionic acid derivatives | Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Ketoprofen |
| Acetic acid derivatives | Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Etodolac |
| Oxicams | Piroxicam, Meloxicam, Tenoxicam |
| Fenamates (Anthranilic acid derivatives) | Mefenamic acid, Flufenamic acid |
| Pyrazolones | Metamizole (Dipyrone), Phenylbutazone |
| Coxibs | Celecoxib, Etoricoxib, Parecoxib |
3. Based on Duration of Action
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Short-acting NSAIDs | Ibuprofen, Diclofenac |
| Long-acting NSAIDs | Piroxicam, Naproxen, Meloxicam |
Pharmacological Actions of NSAIDs
- Anti-inflammatory – reduces inflammation by decreasing prostaglandin synthesis.
- Analgesic – relieves mild-to-moderate pain.
- Antipyretic – lowers fever via hypothalamic thermoregulatory center.
- Antiplatelet (e.g., Aspirin) – used in cardiovascular prophylaxis.
Common Clinical Uses
- Rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis
- Dysmenorrhea
- Fever
- Postoperative pain
- Gout (acute attack)
- Cardiovascular prophylaxis (low-dose aspirin)
Adverse Effects of NSAIDs
- Gastrointestinal: Gastritis, ulcers, bleeding
- Renal: Acute kidney injury, fluid retention
- Cardiovascular: Hypertension, myocardial infarction (especially with selective COX-2 inhibitors)
- Hematologic: Bleeding risk (due to platelet inhibition)
- Hypersensitivity reactions
Conclusion
NSAIDs are indispensable but must be used cautiously. Knowing their classification helps in choosing the most appropriate drug based on therapeutic need and patient safety. As future pharmacists, mastering NSAID classification is key to optimizing therapy and preventing adverse effects.
References
- KD Tripathi – Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 8th Edition
- Chapter: Anti-inflammatory Drugs
- Details on NSAID classification, COX enzymes, pharmacological actions, and adverse effects.
- Sparsh Gupta – Review of Pharmacology, 10th Edition
- Quick reference for classification and therapeutic uses of NSAIDs.
- Goodman & Gilman – The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 13th Edition
- In-depth details on the mechanism of COX inhibition, pharmacokinetics, and safety profiles.
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com