Table of Contents
Introduction
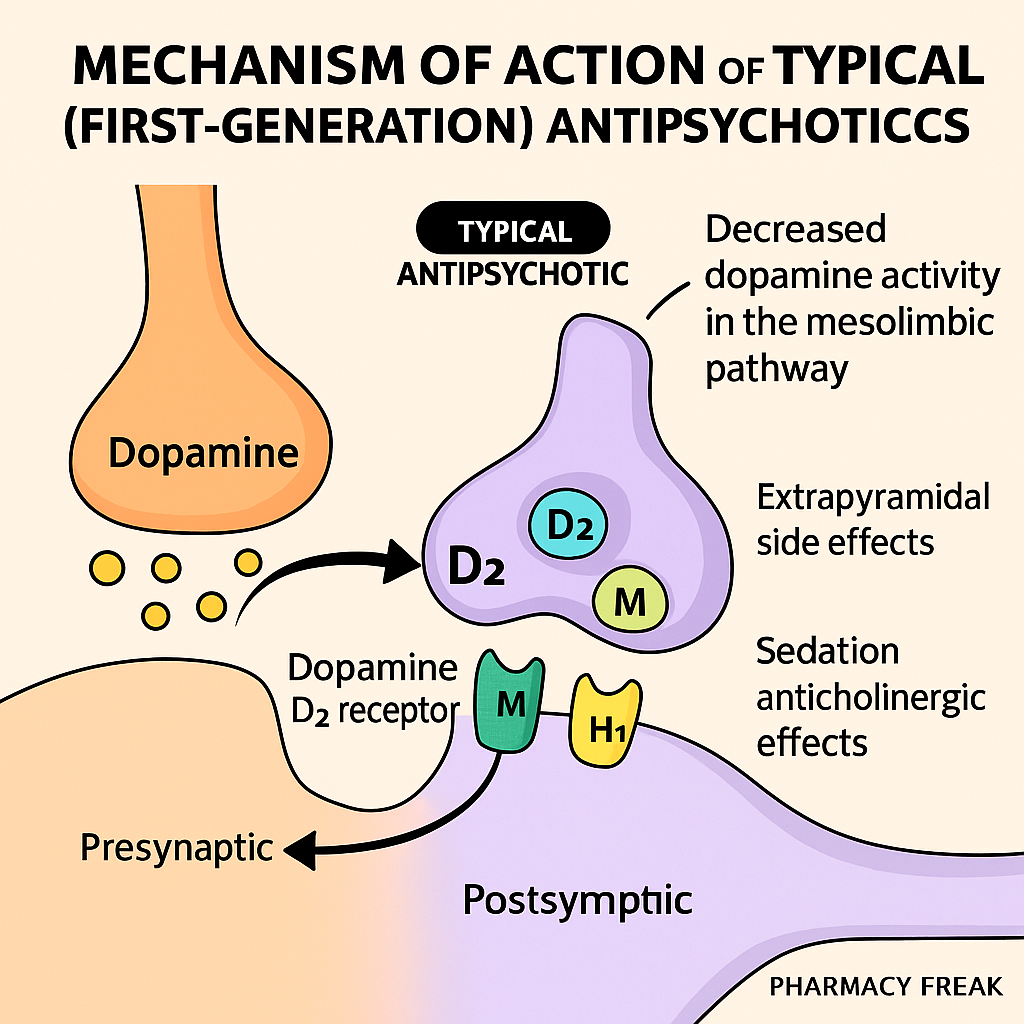
Typical antipsychotics, also known as first-generation antipsychotics (FGAs), are primarily used to treat schizophrenia, acute psychosis, and manic episodes. Their therapeutic effect is mainly due to dopamine D2 receptor antagonism in the brain. However, this same action also causes many extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) and hyperprolactinemia.
Common FGAs include:
- Haloperidol
- Chlorpromazine
- Fluphenazine
- Thioridazine
- Trifluoperazine
- Perphenazine
These drugs are frequently covered in USMLE, NCLEX, NEET-PG, and GPAT pharmacology sections.
Stepwise Mechanism of Action of Typical Antipsychotics
- Blockade of dopamine D2 receptors in mesolimbic pathway
The antipsychotic effect comes from D2 receptor antagonism in the mesolimbic tract, which reduces positive symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusions) of schizophrenia. - D2 receptor blockade in other brain regions
- Nigrostriatal pathway: causes EPS (e.g., parkinsonism, dystonia, akathisia).
- Tuberoinfundibular pathway: causes increased prolactin levels (galactorrhea, gynecomastia).
- Mesocortical pathway: may worsen negative symptoms and cognitive dysfunction.
- Additional receptor blockade (especially low-potency FGAs)
- Alpha-1 adrenergic blockade: orthostatic hypotension
- H1 histamine blockade: sedation, weight gain
- Muscarinic blockade: dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Typical Antipsychotics
| Drug | Potency | Half-life | Metabolism | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haloperidol | High | 12–36 hrs | Hepatic (CYP3A4) | Most used in acute settings |
| Chlorpromazine | Low | ~30 hrs | Hepatic | More sedating, anticholinergic |
| Fluphenazine | High | ~15–30 hrs | Hepatic | Available in depot form |
| Thioridazine | Low | ~12–24 hrs | Hepatic | Causes retinal pigmentation |
| Trifluoperazine | High | ~18 hrs | Hepatic | Potent antipsychotic |
Clinical Uses of Typical Antipsychotics
- Schizophrenia (positive symptoms)
- Acute psychosis
- Mania
- Tourette syndrome (haloperidol)
- Delirium (short-term)
- Severe agitation in ICU
- Nausea and vomiting (prochlorperazine, a related drug)
Adverse Effects of Typical Antipsychotics
- Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS)
- Acute dystonia
- Akathisia
- Parkinsonism
- Tardive dyskinesia (long-term)
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Galactorrhea, gynecomastia, amenorrhea
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
- Rigidity, hyperthermia, altered mental status
- Sedation (H1 blockade)
- Anticholinergic effects – dry mouth, constipation
- Orthostatic hypotension (α1-blockade)
- QT prolongation
- Retinal deposits (thioridazine)
Comparative Analysis: Typical vs Atypical Antipsychotics
| Feature | Typical Antipsychotics | Atypical Antipsychotics |
|---|---|---|
| D2 blockade | Strong | Moderate |
| 5-HT2A blockade | Minimal | Prominent |
| EPS risk | High | Lower |
| Effect on negative symptoms | Minimal or worsens | Better effect |
| Sedation and weight gain | Higher with low-potency | Variable |
Practice MCQs
Q1. Typical antipsychotics primarily act on which receptor?
a. 5-HT2A
b. D2 dopamine receptor ✅
c. GABA-A
d. NMDA receptor
Q2. Which pathway is responsible for EPS in FGAs?
a. Mesolimbic
b. Tuberoinfundibular
c. Nigrostriatal ✅
d. Mesocortical
Q3. Hyperprolactinemia is due to blockade of D2 in which pathway?
a. Nigrostriatal
b. Mesolimbic
c. Tuberoinfundibular ✅
d. Cortical
Q4. Which of the following is a high-potency FGA?
a. Chlorpromazine
b. Haloperidol ✅
c. Thioridazine
d. Olanzapine
Q5. Tardive dyskinesia occurs after:
a. One dose
b. Few days
c. Long-term use ✅
d. Overdose
Q6. A life-threatening complication of FGAs is:
a. EPS
b. Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome ✅
c. Hypertension
d. Anemia
Q7. Which receptor blockade causes sedation in FGAs?
a. D2
b. H1 ✅
c. Alpha-2
d. GABA-B
Q8. What visual side effect is associated with thioridazine?
a. Myopia
b. Retinal deposits ✅
c. Optic neuritis
d. Cataract
Q9. Haloperidol is preferred in:
a. Sleep disorders
b. Chronic depression
c. Acute psychosis ✅
d. OCD
Q10. FGAs are more effective in controlling:
a. Hallucinations ✅
b. Social withdrawal
c. Blunted affect
d. Cognitive symptoms
FAQs
Q1: Do typical antipsychotics treat both positive and negative symptoms?
Primarily effective for positive symptoms only. Negative and cognitive symptoms may worsen.
Q2: Are FGAs safe in pregnancy?
Some are used with caution. Haloperidol has the most safety data.
Q3: Which side effect needs immediate discontinuation of the drug?
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome – a medical emergency.
Q4: Can FGAs be used long-term?
Yes, but with monitoring for EPS and tardive dyskinesia.
Q5: Which FGA is available in depot form for long-term use?
Fluphenazine and haloperidol decanoate.
References
- KD Tripathi – Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
- Goodman & Gilman – The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
- Review of Pharmacology – Sparsh Gupta
- NCBI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557852/
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com