Table of Contents
Introduction
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by pancreatic β‑cells. It belongs to the class of anabolic hormones. It plays a vital role in maintaining blood glucose homeostasis. Insulin therapy is crucial for managing type 1 diabetes and advanced type 2 diabetes.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Receptor Binding
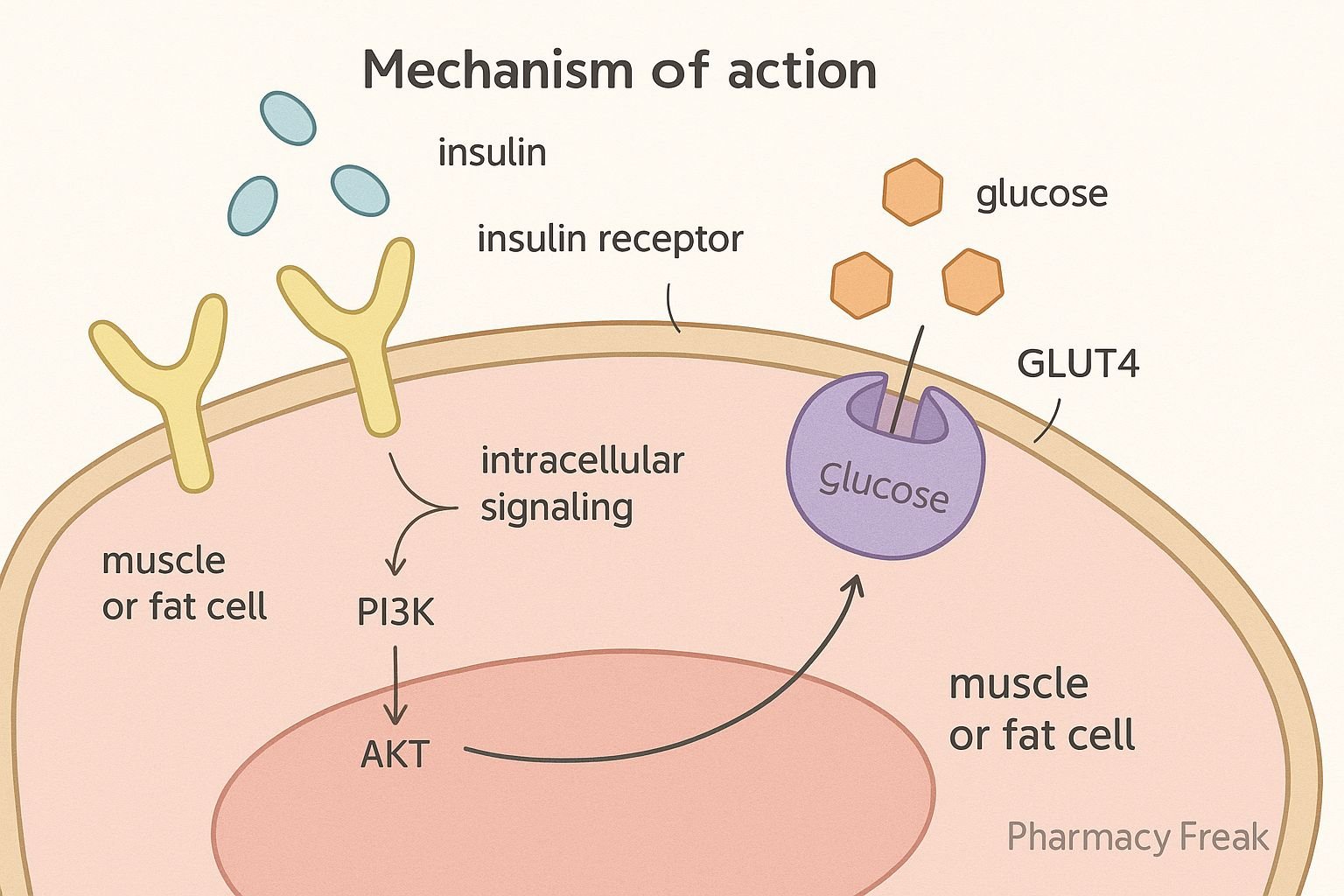
- Insulin binds to the α‑subunits of the insulin receptor, a tetrameric receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) on cell membranes (liver, muscle, adipose)
- Autophosphorylation
- Binding triggers receptor β‑subunit autophosphorylation on tyrosine residues
- IRS Activation
- Phosphorylated receptor recruits IRS proteins, activating PI3K → PIP3 cascade .
- AKT Activation
- PIP3 activates AKT (PKB), a key mediator of insulin action.
- GLUT4 Translocation
- AKT promotes GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane in muscle and adipose tissue, increasing glucose uptake
- Glycogen Synthesis
- AKT inhibits GSK‑3, activating glycogen synthase and enhancing glycogenesis.
- Hepatic Effects
- Insulin reduces gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis by regulating key enzymes
- Lipogenesis & Protein Synthesis
- Insulin promotes lipogenesis, protein synthesis and inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis .
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Absorption | Administered SC or IV; absorption varies by insulin formulation |
| Distribution | Remains extracellular; rapid portal to systemic gradient with endogenous insulin |
| Half‑life | 4–6 minutes in plasma |
| Metabolism | Degraded via receptor-mediated endocytosis; primarily in liver and kidneys |
| Excretion | Broken into amino acids; renal elimination of fragments |
Clinical Uses
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Advanced type 2 diabetes
- Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states
- Hyperkalemia (promotes cellular K⁺ uptake)
Adverse Effects
- Hypoglycemia – sweating, tremors, confusion
- Weight gain – due to anabolic effects
- Hypokalemia – from increased cellular K⁺ uptake
- Injection‑site reactions – lipodystrophy, erythema
- Allergic reactions – rare; often due to excipients
Comparative Analysis
- Short‑acting (regular): Onset ~30 min; duration ~6–8 h
- Rapid‑acting analogues (e.g., lispro): Onset <15 min; better postprandial control
- Long‑acting analogues (e.g., glargine): Provide basal coverage (~24 h); lower hypoglycemia risk
MCQs Section
- Which receptor class does insulin bind?
Receptor tyrosine kinase. - What effect does AKT have on GLUT4?
Promotes translocation of GLUT4 to cell membrane. - Which enzyme does AKT inhibit to promote glycogen synthesis?
Glycogen synthase kinase‑3 (GSK‑3). - Main organs responsible for insulin metabolism?
Liver and kidneys. - What is the main risk of insulin overdose?
Hypoglycemia. - Which insulin type is optimal for post-prandial glucose control?
Rapid‑acting analogues. - Why does insulin therapy cause weight gain?
Due to increased lipogenesis and protein anabolism. - Which electrolyte disturbance may insulin induce?
Hypokalemia. - Best insulin for basal coverage?
Long‑acting analogues (e.g., glargine). - Why isn’t insulin given orally?
It degrades in the gastrointestinal tract, hence no bioavailability.
FAQs
- Can insulin treat type 2 diabetes?
Yes, especially in later stages or during pregnancy. - How do you treat insulin-induced hypoglycemia?
Fast-acting carbohydrates; IV glucagon or dextrose for severe cases. - Why rotate injection sites?
To prevent lipodystrophy and ensure consistent absorption. - Why might insulin dose need adjustment during illness or stress?
Stress hormones can increase insulin resistance, requiring dose adjustments. - Can patients develop antibodies to insulin?
Yes; rare immune reactions may require changing the insulin formulation.
References
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology (Insulin chapter)
- Goodman & Gilman, The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (Pharmacokinetics of insulin)
- Petersen & Shulman, “Mechanisms of Insulin Action and Insulin Resistance,” Physiol Rev (NCBI) pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+1journals.physiology.org+1
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com