Table of Contents
Introduction
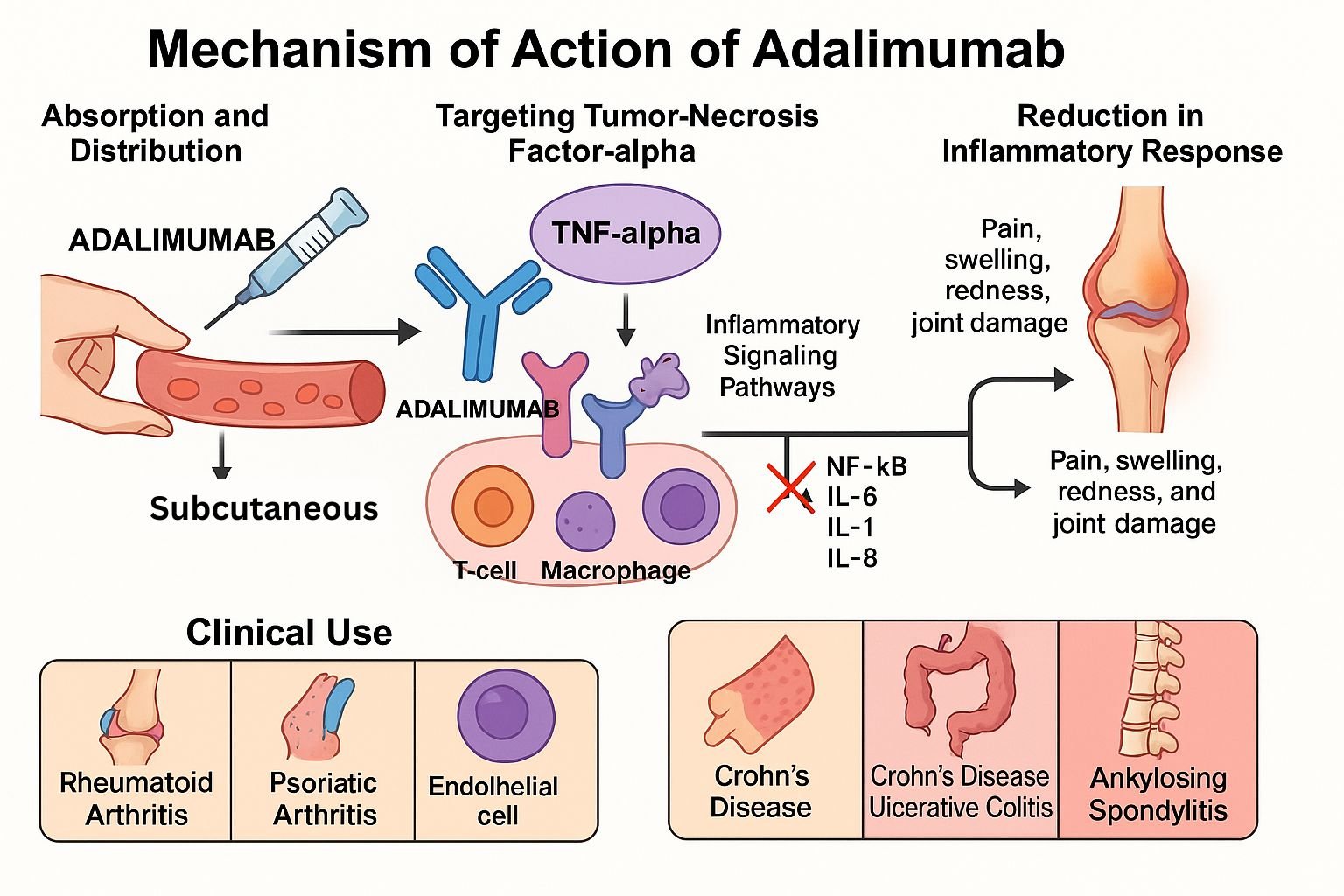
Adalimumab is a fully human monoclonal IgG1 antibody that specifically targets tumor necrosis factor‑α (TNF‑α). By neutralizing TNF‑α, it reduces inflammation across a variety of autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and plaque psoriasis.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Specific binding to TNF‑α
Adalimumab attaches with high affinity to both soluble and membrane-bound TNF‑α. - Neutralization of TNF‑α activity
Binding prevents TNF‑α from interacting with TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) on target cells. - Inhibition of downstream signaling
By blocking TNF‑α, activation of the NF‑κB and MAPK pathways is reduced. - Reduction of inflammatory mediator production
This leads to decreased production of cytokines (IL‑1, IL‑6), adhesion molecules, and MMPs, lowering immune cell recruitment. - Modulation of immune functions
Results in decreased infiltration of inflammatory cells into tissue and improved clinical outcomes in autoimmune diseases.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Subcutaneous injection |
| Bioavailability | ~64% |
| Half-life | ~10–20 days |
| Distribution | ~5–6 L |
| Metabolism | Proteolytic catabolism |
| Excretion | Degraded to peptides and amino acids |
Clinical Uses
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Plaque psoriasis
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
Adverse Effects
- Increased risk of serious infections (e.g., TB, fungal infections)
- Injection-site and infusion reactions
- Rare lupus-like syndromes or demyelinating disorders
- Increased risk of certain malignancies (e.g., lymphoma)
- Possible development of antidrug antibodies reducing efficacy
Comparative Analysis
| Agent | Type | TNF Target | Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adalimumab | Human monoclonal IgG1 | TNF‑α | Comprehensive autoimmune coverage |
| Infliximab | Chimeric mAb | TNF‑α | Similar but IV infusion route |
| Etanercept | Receptor fusion protein | TNF‑α/β | Soluble receptor decoy |
MCQs
- Adalimumab specifically targets:
a) TNF‑α b) IL‑17 c) IL‑6 d) JAK
Answer: a) TNF‑α - It neutralizes TNF‑α by:
a) Binding to TNFR b) Binding TNF‑α directly c) Inhibiting TNF synthesis d) Activating TNF receptors
Answer: b) Binding TNF‑α directly - Main downstream pathways inhibited include:
a) cAMP b) NF‑κB and MAPK c) PI3K d) JAK‑STAT
Answer: b) NF‑κB and MAPK - Half-life of adalimumab is:
a) 1–2 hours b) 10–20 days c) 3–5 days d) 4–8 hours
Answer: b) 10–20 days - A major safety concern prior to initiation is:
a) Hypertension b) Latent TB c) Hyperthyroidism d) Diabetes
Answer: b) Latent TB - Compared to infliximab, adalimumab is:
a) Chimeric b) Fully human c) Small molecule d) Receptor decoy
Answer: b) Fully human - Risk of antidrug antibodies is:
a) Higher than etanercept b) Lower than infliximab c) Not present d) Highest among all biologics
Answer: a) Higher than etanercept - Common adverse effect is:
a) Hypoglycemia b) Infection c) Renal failure d) Hair loss
Answer: b) Infection - Mechanism involves reduction of:
a) IL‑1 and IL‑6 b) Dopamine release c) Glucagon secretion d) Histamine production
Answer: a) IL‑1 and IL‑6 - Route of elimination is mainly:
a) Renal excretion b) Proteolytic degradation c) Hepatic metabolism d) Fecal unchanged
Answer: b) Proteolytic degradation
FAQs
1. Do I need TB testing before starting?
Yes—tuberculosis screening is mandatory due to increased reactivation risk.
2. Can it be tapered or stopped during remission?
Possibly—with careful monitoring, but disease relapse may require dose adjustment.
3. Are live vaccines allowed?
No—live vaccines are contraindicated during therapy.
4. How often is injection administered?
Frequently every 1 or 2 weeks, depending on indication and dose.
5. What monitoring is needed?
Check for infections, CBC, and consider imaging if demyelination is suspected.
References
- FDA Label: Adalimumab (Humira)
- DrugBank: Adalimumab Summary
- StatPearls: Adalimumab Clinical Pharmacology
- PubMed: Adalimumab mechanism and immunogenicity
- PubMed Central: Anti-TNF therapy effects
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com