Table of Contents
Introduction
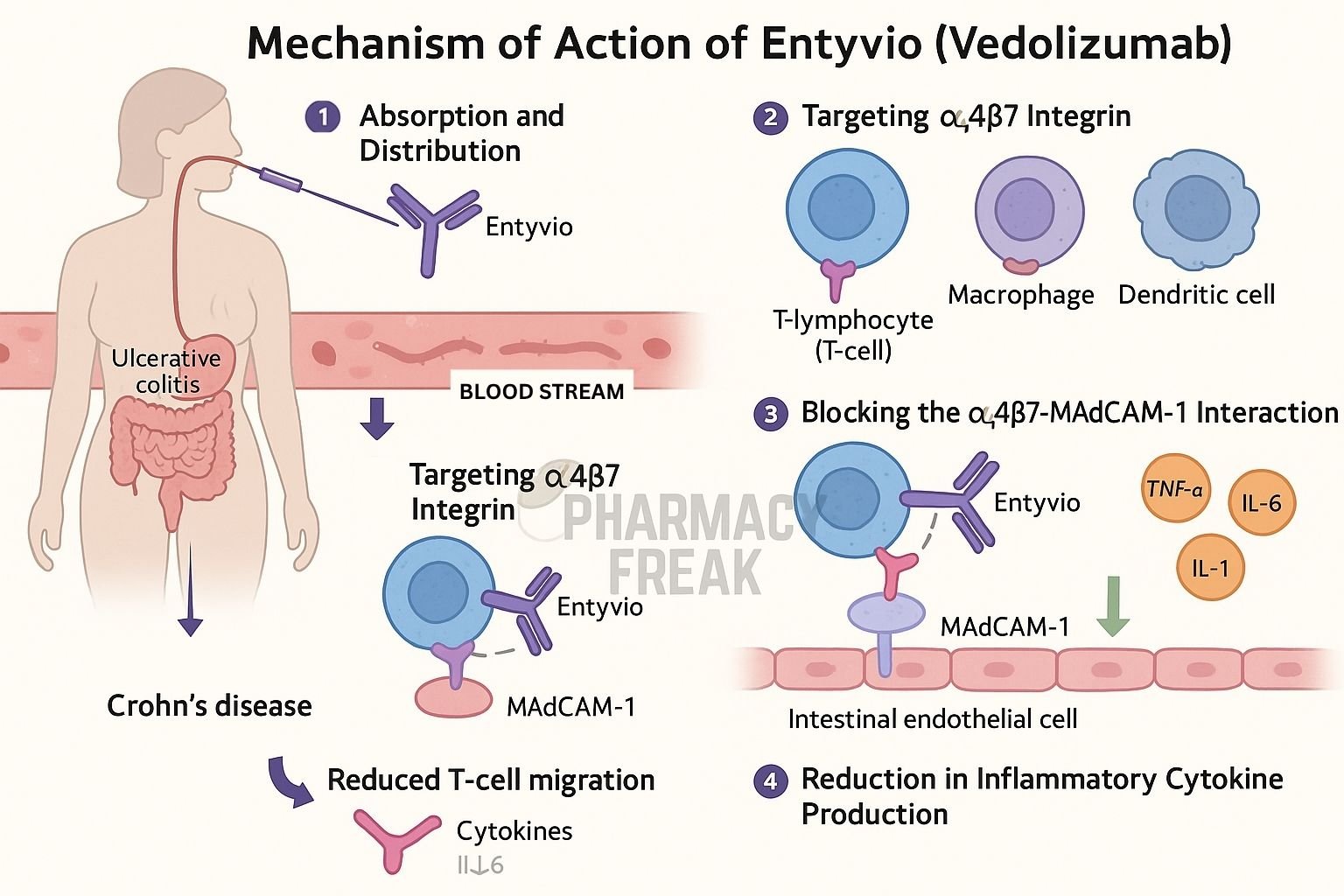
Entyvio (vedolizumab) is a recombinant humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the α4β7 integrin on gut-homing T-lymphocytes. It is approved for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, particularly in patients who have not responded to or cannot tolerate TNF antagonists.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
- Selective binding to α4β7 integrin
Vedolizumab specifically binds to the α4β7 integrin on a subset of gut-homing T-cells, blocking their interaction with mucosal endothelial cells. - Prevention of lymphocyte trafficking to the gut
By blocking α4β7 integrin binding to MAdCAM-1 on gut endothelial cells, it inhibits migration of inflammatory lymphocytes into intestinal tissue. - Gut-selective immune modulation
This gut-specific action reduces inflammatory cell infiltration without broadly suppressing systemic immunity. - Reduced pro-inflammatory signaling
Decreasing T-cell presence in the gut leads to lower activation of local inflammatory pathways, including NF-κB and MAPKs. - Amelioration of gut inflammation
The net effect is reduced mucosal inflammation, improved histology, and symptomatic relief in inflammatory bowel disease.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Intravenous infusion (300 mg) |
| Bioavailability | 100% (IV administration) |
| Half-life | ~25 days |
| Distribution | ~5 L (circulates in vascular compartment) |
| Metabolism | Proteolytic degradation |
| Excretion | No renal excretion; catabolized enzyme-dependently |
Clinical Uses
- Moderate to severe ulcerative colitis
- Moderate to severe Crohn’s disease
- Used when conventional therapies or TNF inhibitors fail or are contraindicated
Adverse Effects
- Infusion-related reactions
- Increased risk of serious infections (e.g., nasopharyngitis, less systemic immunosuppression)
- Hepatic enzyme elevation
- Rare risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) with non-gut-specific integrin drugs—no confirmed cases with Entyvio
Comparative Analysis
| Agent | Target Mechanism | Selectivity | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vedolizumab | α4β7 integrin antagonist | Gut-selective | UC, Crohn’s |
| Natalizumab | α4β7 and α4β1 antagonist | Systemic | Crohn’s, MS (limited by PML risk) |
| TNF inhibitors | TNF-α neutralizing | Systemic | IBD, RA, PsA, psoriasis |
MCQs
- Vedolizumab targets which integrin?
a) α4β1 b) α4β7 c) αEβ7 d) β1
Answer: b) α4β7 - By blocking α4β7, Entyvio prevents lymphocyte migration to:
a) Skin b) Gut c) Brain d) Heart
Answer: b) Gut - This mechanism is considered:
a) Systemic immunosuppression b) Gut-selective immunomodulation c) JAK inhibition d) TNF neutralization
Answer: b) Gut-selective immunomodulation - Primary downstream effect is reduced:
a) IL-1 production b) NF‑κB activation c) JAK-STAT signaling d) COX-2 expression
Answer: b) NF‑κB activation - Typical half-life of vedolizumab is:
a) 7 days b) 14 days c) 25 days d) 60 days
Answer: c) 25 days - Which route administers Entyvio?
a) Oral b) IV infusion c) Subcutaneous injection d) Inhalation
Answer: b) IV infusion - Compared with natalizumab, vedolizumab has lower risk of:
a) GI infection b) PML c) Allergy d) Joint pain
Answer: b) PML - Gut selectivity arises due to binding α4β7 and blocking:
a) VCAM-1 b) ICAM-1 c) MAdCAM-1 d) E-selectin
Answer: c) MAdCAM-1 - Common adverse effect:
a) Severe neutropenia b) Infusion reaction c) Hypertension d) Hyperglycemia
Answer: b) Infusion reaction - Vedolizumab is NOT indicated for:
a) Ulcerative colitis b) Crohn’s disease c) Rheumatoid arthritis d) TNF-refractory IBD
Answer: c) Rheumatoid arthritis
FAQs
1. Why doesn’t Entyvio cause widespread immunosuppression?
Its α4β7 integrin targeting restricts its action to gut-homing lymphocytes, avoiding systemic immune compromise.
2. How often is vedolizumab given?
After initial doses at weeks 0, 2, and 6, maintenance infusions are administered every 8 weeks.
3. Is there a PML risk with Entyvio?
No confirmed PML cases—but natalizumab (which targets α4β1) carries this risk.
4. Can Entyvio be used during pregnancy?
Data are limited—use only if benefits outweigh potential risks; monitor closely.
5. How quickly does it work?
Some patients show improvement by 6 weeks; maximal response may take several months.
References
- PubMed: Wyant et al. Vedolizumab mechanism of action overview (PMID: 27252400)
- DrugBank: Vedolizumab pharmacology summary
- Drugs.com: Entyvio MOA explanation
- Wikipedia: Vedolizumab entry (recently updated)
- PubMed Central: Vedolizumab blocks T-cell recruitment to gut
I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com