Table of Contents
Introduction
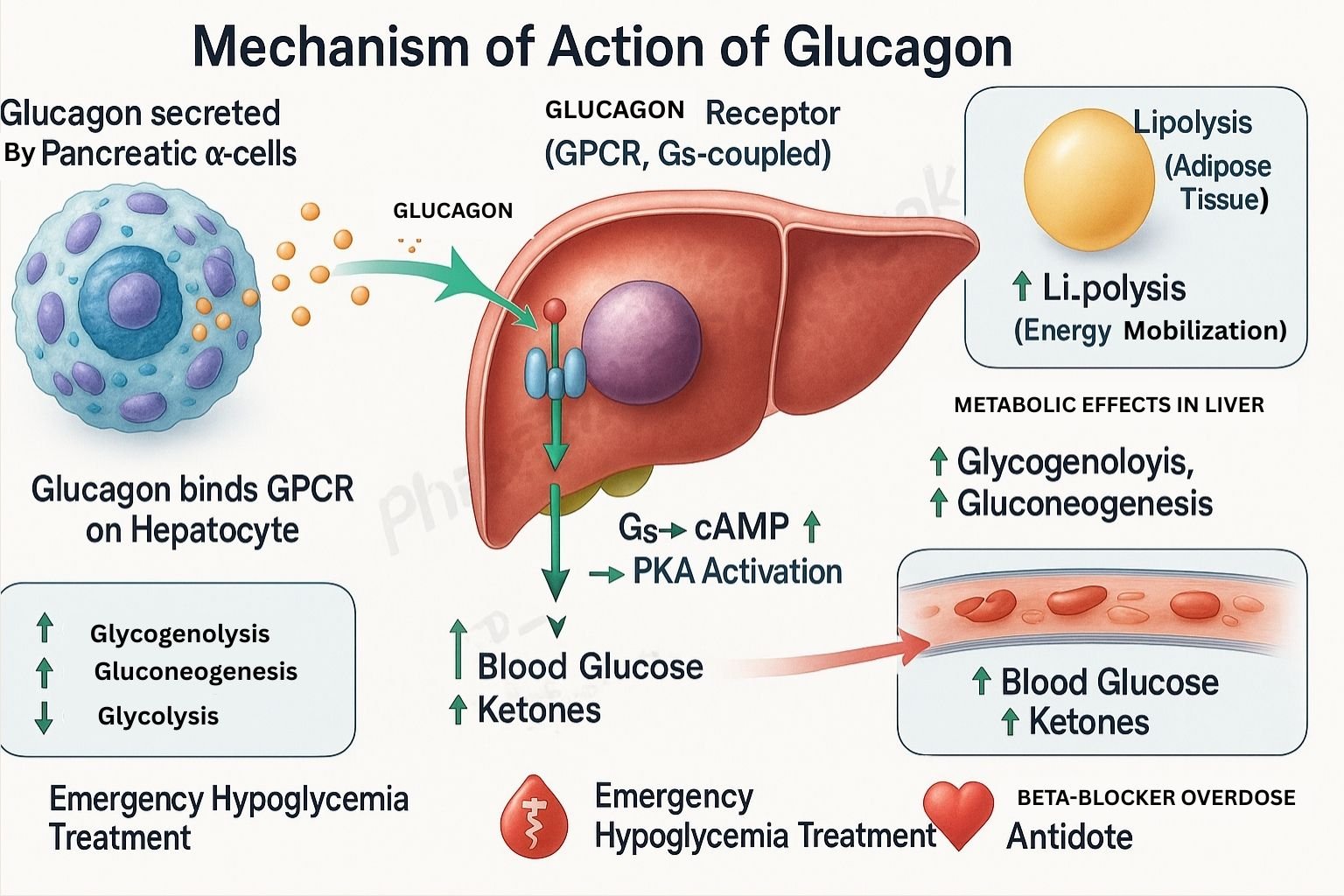
Glucagon is a peptide hormone secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas. It plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis by raising blood glucose levels, especially during fasting states. Clinically, it is used in the emergency treatment of severe hypoglycemia, as well as in diagnostic procedures involving the gastrointestinal tract. Glucagon acts via G protein-coupled receptors to stimulate glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
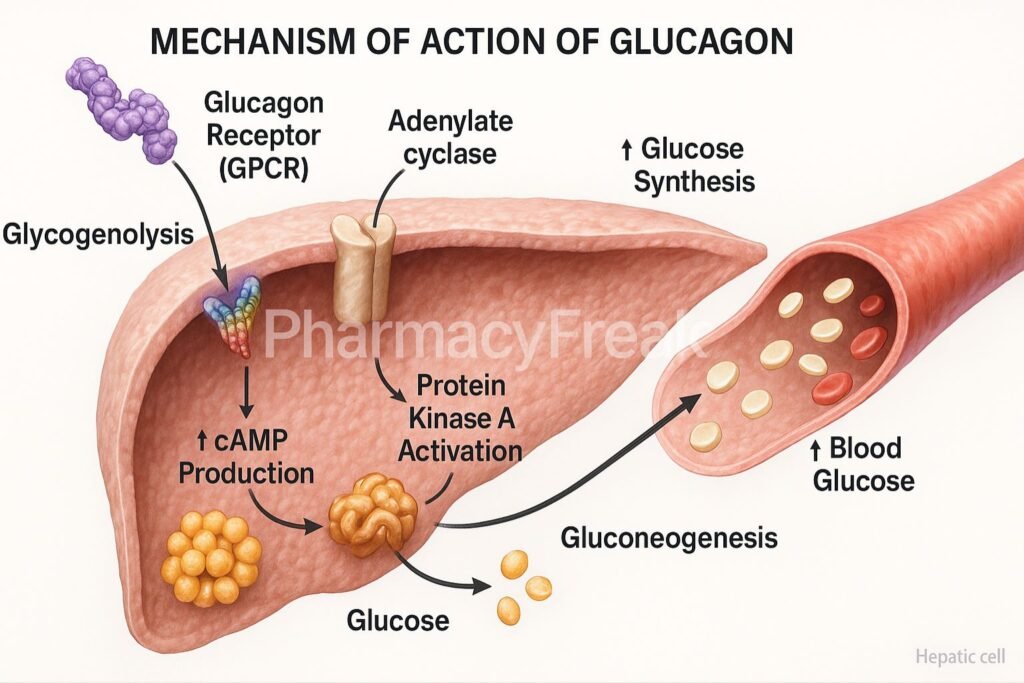
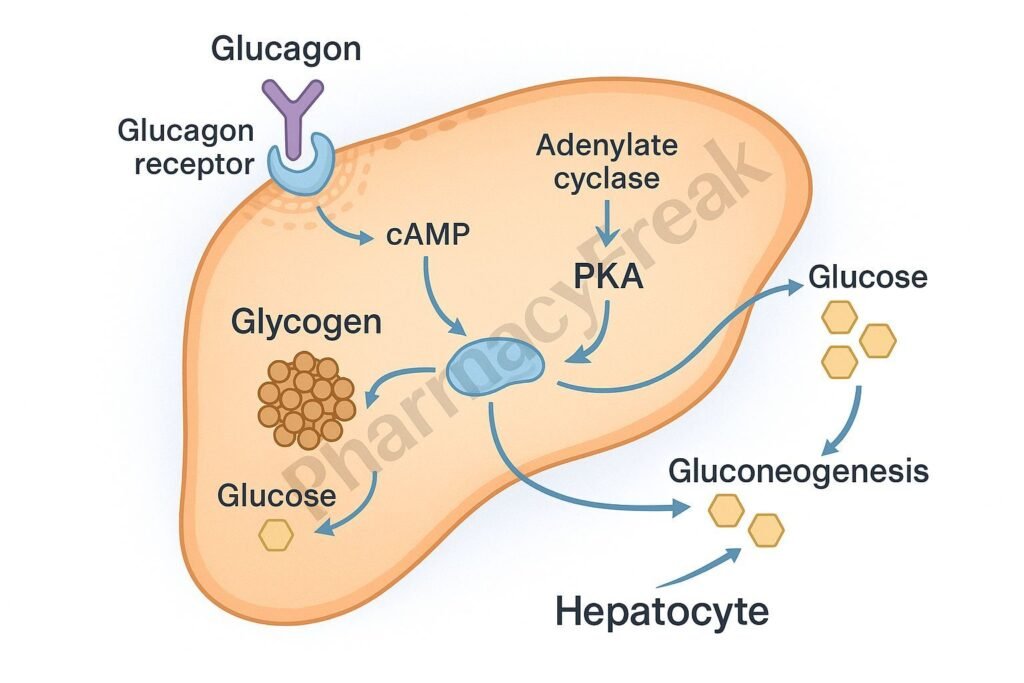
1. Binding to Glucagon Receptors
Glucagon binds to specific glucagon receptors, which are G protein-coupled receptors located primarily in the liver.
2. Activation of Gs Protein
The receptor activates the Gs protein, which in turn stimulates adenylate cyclase.
3. Increase in cAMP Production
Adenylate cyclase catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cyclic AMP (cAMP).
4. Activation of Protein Kinase A (PKA)
cAMP activates PKA, which phosphorylates key enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism.
5. Glycogenolysis
PKA phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase, stimulating the breakdown of glycogen into glucose.
6. Gluconeogenesis
PKA also activates enzymes that promote the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
7. Inhibition of Glycolysis and Glycogenesis
PKA inactivates enzymes that mediate glycolysis and glycogen synthesis, conserving glucose.

Pharmacokinetics
- Route of Administration: Intramuscular, subcutaneous, intravenous
- Onset of Action: 5–20 minutes (IM/SC), 1 minute (IV)
- Half-Life: 3–6 minutes
- Metabolism: Hepatic, renal, plasma proteases
- Excretion: Renal (as amino acid metabolites)
Clinical Uses
- Severe hypoglycemia (when oral/IV glucose not feasible)
- Bowel imaging procedures (to relax smooth muscle)
- Beta-blocker overdose (off-label)
- Calcium channel blocker toxicity (off-label)
Adverse Effects
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypotension (transient)
- Allergic reactions (rare)
- Contraindications: Pheochromocytoma, insulinoma, known hypersensitivity
Comparative Analysis
| Parameter | Glucagon | Insulin |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Action | Increases blood glucose | Decreases blood glucose |
| Receptor Type | Gs-coupled receptor | Tyrosine kinase receptor |
| Glucose Production | Stimulates | Inhibits |
| Clinical Use in Hypoglycemia | Yes | No (causes hypoglycemia) |
| Half-Life | 3–6 minutes | 5–10 minutes (IV insulin) |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Glucagon primarily raises blood glucose by stimulating:
a) Glycolysis
b) Lipolysis
c) Glycogenolysis
d) Ketogenesis
Answer: c) Glycogenolysis
2. What type of receptor does glucagon act upon?
a) Tyrosine kinase receptor
b) Gq-coupled receptor
c) Gi-coupled receptor
d) Gs-coupled receptor
Answer: d) Gs-coupled receptor
3. Glucagon’s activation of PKA leads to:
a) Inhibition of glycogen phosphorylase
b) Inhibition of gluconeogenesis
c) Activation of glycogenolysis
d) Activation of glycolysis
Answer: c) Activation of glycogenolysis
4. Which is a known off-label use of glucagon?
a) Hyperthyroidism
b) Beta-blocker overdose
c) Asthma
d) Seizures
Answer: b) Beta-blocker overdose
5. A major side effect of glucagon administration is:
a) Hyperkalemia
b) Nausea and vomiting
c) Hypoglycemia
d) Constipation
Answer: b) Nausea and vomiting
FAQs
Q1. How fast does glucagon work in hypoglycemia?
Usually within 15 minutes when given IM or SC; faster IV.
Q2. Can glucagon be used in diabetic patients?
Yes, particularly in type 1 diabetics during episodes of severe hypoglycemia.
Q3. Is glucagon effective in insulinoma?
No, it is contraindicated due to risk of rebound hypoglycemia.
Q4. Can glucagon be self-administered?
Yes, glucagon auto-injectors are available for emergency use.
Q5. Does glucagon affect insulin levels?
Indirectly, as it raises glucose, insulin secretion may increase in response.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- Glucagon Prescribing Information
- Clinical guidelines for hypoglycemia and endocrine emergencies
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com