Table of Contents
Introduction
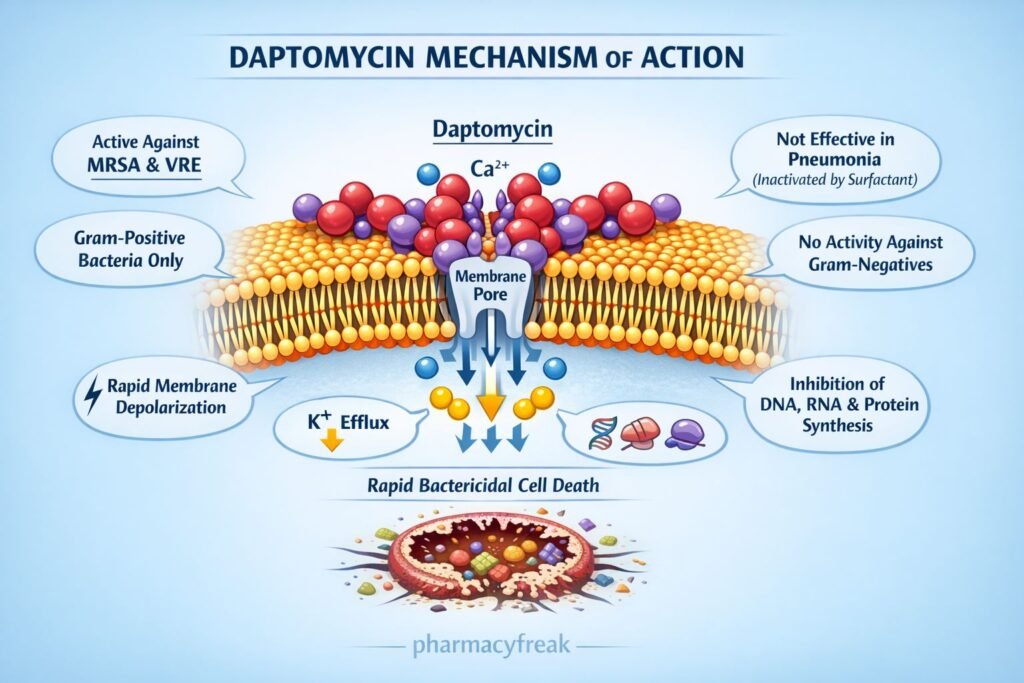
Daptomycin is a cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic with potent activity against Gram-positive bacteria, including multidrug-resistant organisms such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). It has a unique mechanism of action distinct from cell wall synthesis or protein synthesis inhibition, making it a high-yield topic in pharmacology, microbiology, and infectious disease examinations. Daptomycin is bactericidal and is reserved for serious systemic infections.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
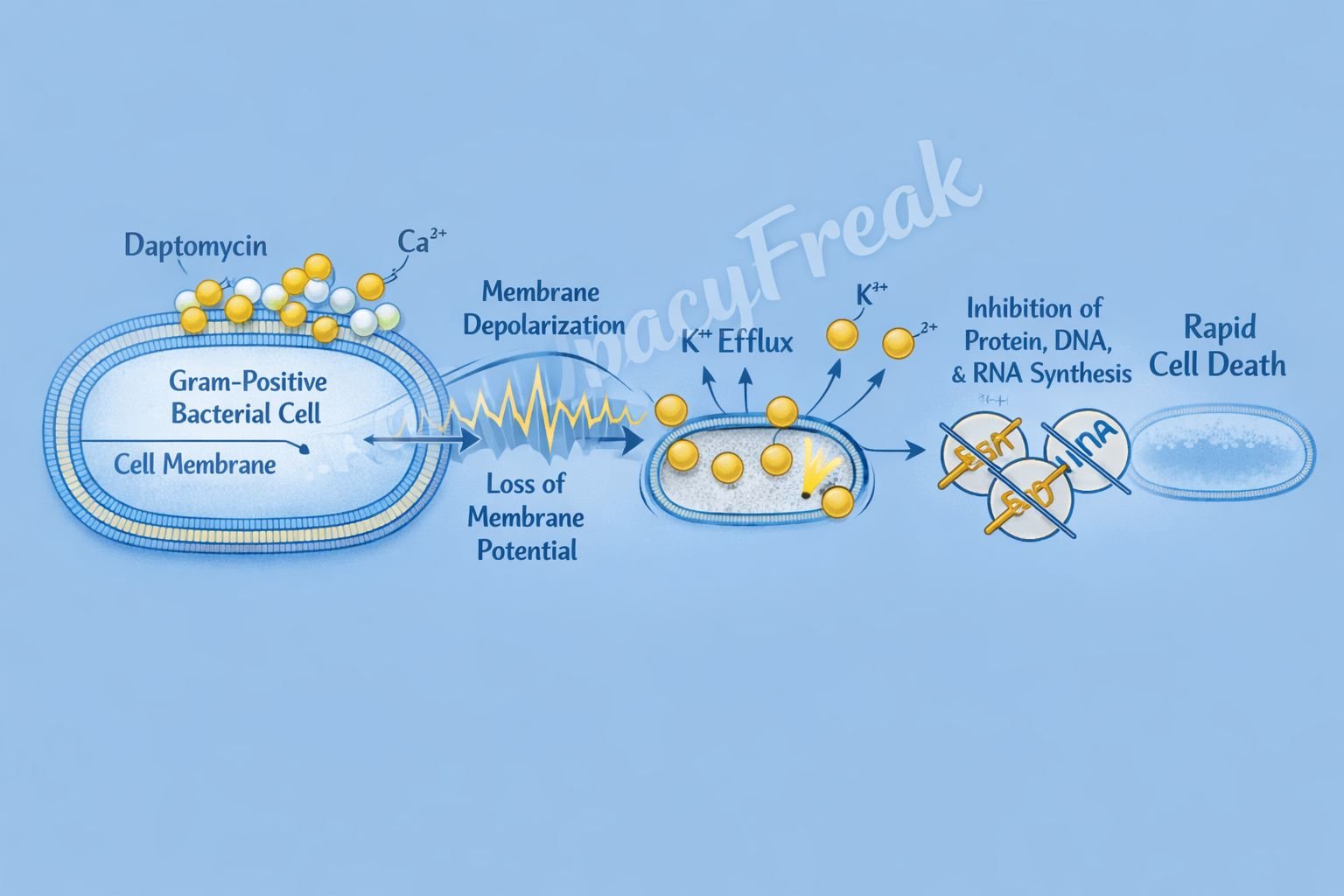
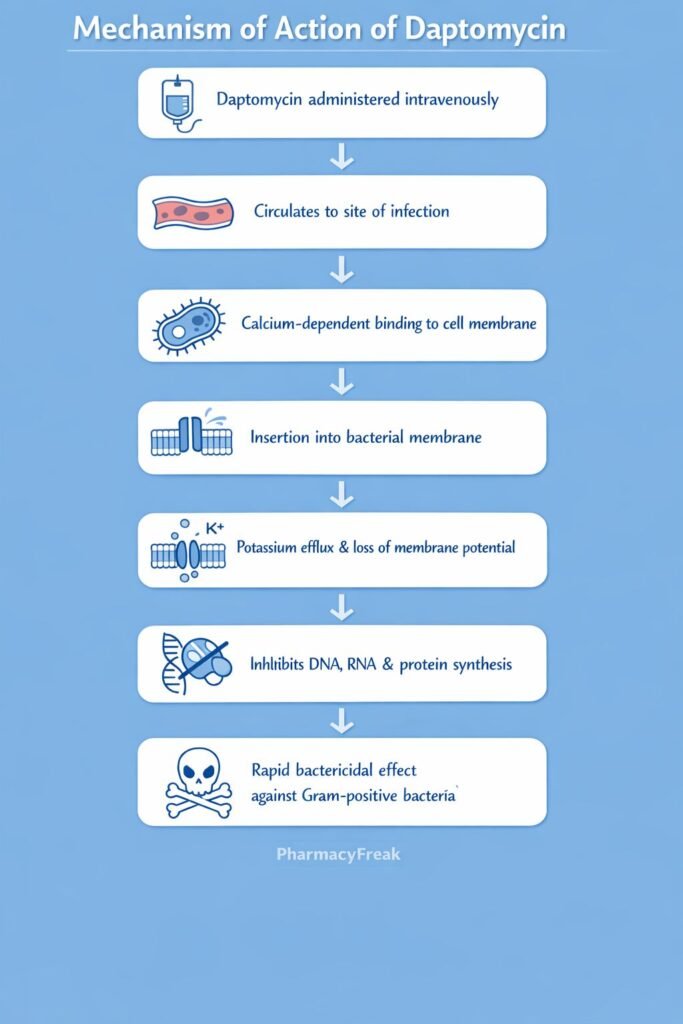
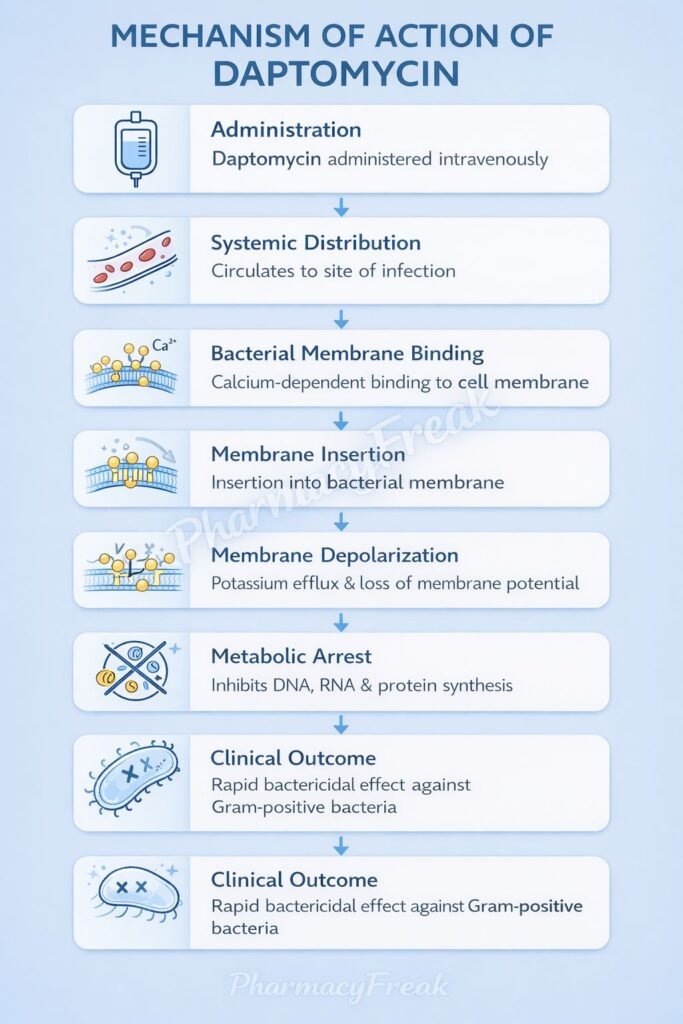
Daptomycin causes rapid bacterial cell death by disrupting the cell membrane potential.
Step-wise mechanism:
- Calcium-Dependent Binding
Daptomycin binds to bacterial cell membranes in the presence of calcium ions (Ca²⁺). - Insertion into Gram-Positive Cell Membrane
The lipophilic tail of daptomycin inserts into the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-positive bacteria. - Oligomerization and Channel Formation
Multiple daptomycin molecules aggregate to form transmembrane complexes. - Membrane Depolarization
These complexes create ion-conducting channels that allow potassium efflux. - Loss of Membrane Potential
Rapid depolarization of the bacterial membrane occurs. - Inhibition of Macromolecular Synthesis
Loss of membrane potential inhibits:- DNA synthesis
- RNA synthesis
- Protein synthesis
- Rapid Bactericidal Effect
The bacteria undergo cell death without cell lysis, reducing inflammatory response.
Pharmacokinetics
- Administration: Intravenous only
- Absorption: Not absorbed orally
- Distribution: Widely distributed; poor penetration into lungs
- Protein binding: High (~90%)
- Metabolism: Minimal hepatic metabolism
- Elimination: Renal excretion (dose adjustment required)
- Half-life: Approximately 8–9 hours
Important note:
Daptomycin is inactivated by pulmonary surfactant and therefore cannot be used for pneumonia.
Clinical Uses
Daptomycin is indicated for serious Gram-positive infections:
- Complicated skin and soft tissue infections
- MRSA bacteremia
- Right-sided infective endocarditis
- Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus infections
- Severe Gram-positive infections resistant to other agents
Adverse Effects
Key adverse effects include:
- Musculoskeletal:
- Myopathy
- Elevated creatine phosphokinase (CPK)
- Neurologic:
- Peripheral neuropathy (rare)
- Gastrointestinal:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Others:
- Eosinophilic pneumonia (rare but serious)
Monitoring:
Baseline and weekly CPK levels are recommended, especially when used with statins.
Comparative Analysis (must include a table + explanation)
Comparison of Anti–Gram-Positive Antibiotics
| Feature | Daptomycin | Vancomycin | Linezolid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Membrane depolarization | Cell wall synthesis inhibition | Protein synthesis inhibition |
| Bactericidal | Yes | Yes | No (bacteriostatic) |
| MRSA coverage | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| VRE coverage | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| Use in pneumonia | No | Yes | Yes |
Explanation:
Daptomycin is unique among antibiotics because it kills bacteria by disrupting membrane potential rather than inhibiting synthesis pathways. However, its inactivation by surfactant limits its use in pulmonary infections, where vancomycin or linezolid are preferred.
MCQs (10–15)
- Daptomycin kills bacteria primarily by:
a) Inhibiting cell wall synthesis
b) Inhibiting protein synthesis
c) Depolarizing cell membrane
d) Inhibiting DNA gyrase
Answer: c) Depolarizing cell membrane
- Daptomycin requires which ion for activity?
a) Sodium
b) Potassium
c) Calcium
d) Magnesium
Answer: c) Calcium
- Daptomycin is bactericidal because it:
a) Causes cell lysis
b) Inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis
c) Causes membrane depolarization
d) Inhibits ribosomal translocation
Answer: c) Causes membrane depolarization
- Daptomycin is ineffective in pneumonia because it is:
a) Rapidly metabolized
b) Inactivated by surfactant
c) Poorly absorbed
d) Nephrotoxic
Answer: b) Inactivated by surfactant
- Which organism is covered by daptomycin?
a) Escherichia coli
b) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
c) Enterococcus faecium (VRE)
d) Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Answer: c) Enterococcus faecium (VRE)
- Daptomycin is administered by which route?
a) Oral
b) Intramuscular
c) Intravenous
d) Subcutaneous
Answer: c) Intravenous
- A major adverse effect of daptomycin is:
a) Nephrotoxicity
b) Ototoxicity
c) Myopathy
d) QT prolongation
Answer: c) Myopathy
- Which lab parameter should be monitored during daptomycin therapy?
a) Serum potassium
b) CPK levels
c) Liver enzymes
d) INR
Answer: b) CPK levels
- Daptomycin does NOT inhibit:
a) DNA synthesis
b) RNA synthesis
c) Protein synthesis
d) Cell wall synthesis
Answer: d) Cell wall synthesis
- Daptomycin is classified as a:
a) Glycopeptide
b) Lipopeptide
c) Macrolide
d) Aminoglycoside
Answer: b) Lipopeptide
FAQs (minimum 5)
- What is the primary mechanism of daptomycin?
Calcium-dependent disruption of bacterial cell membrane potential. - Why is daptomycin bactericidal?
Because membrane depolarization rapidly halts vital cellular processes. - Why can’t daptomycin be used in pneumonia?
Pulmonary surfactant inactivates the drug. - Does daptomycin cause cell lysis?
No, it causes cell death without lysis. - Why must CPK be monitored?
Due to risk of muscle toxicity and myopathy. - Is daptomycin effective against Gram-negative bacteria?
No, it is active only against Gram-positive organisms.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://www.jaypeebrothers.com - Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com