Table of Contents
Introduction
Dapsone (diaminodiphenyl sulfone) is a synthetic sulfone antibiotic with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. It is most famously used in the treatment of leprosy (Hansen’s disease) and dermatitis herpetiformis, and also plays an important role in certain opportunistic infections. Dapsone is a high-yield drug in pharmacology, microbiology, dermatology, and infectious disease examinations because of its folate synthesis inhibition, similarity to sulfonamides, and characteristic adverse effects.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
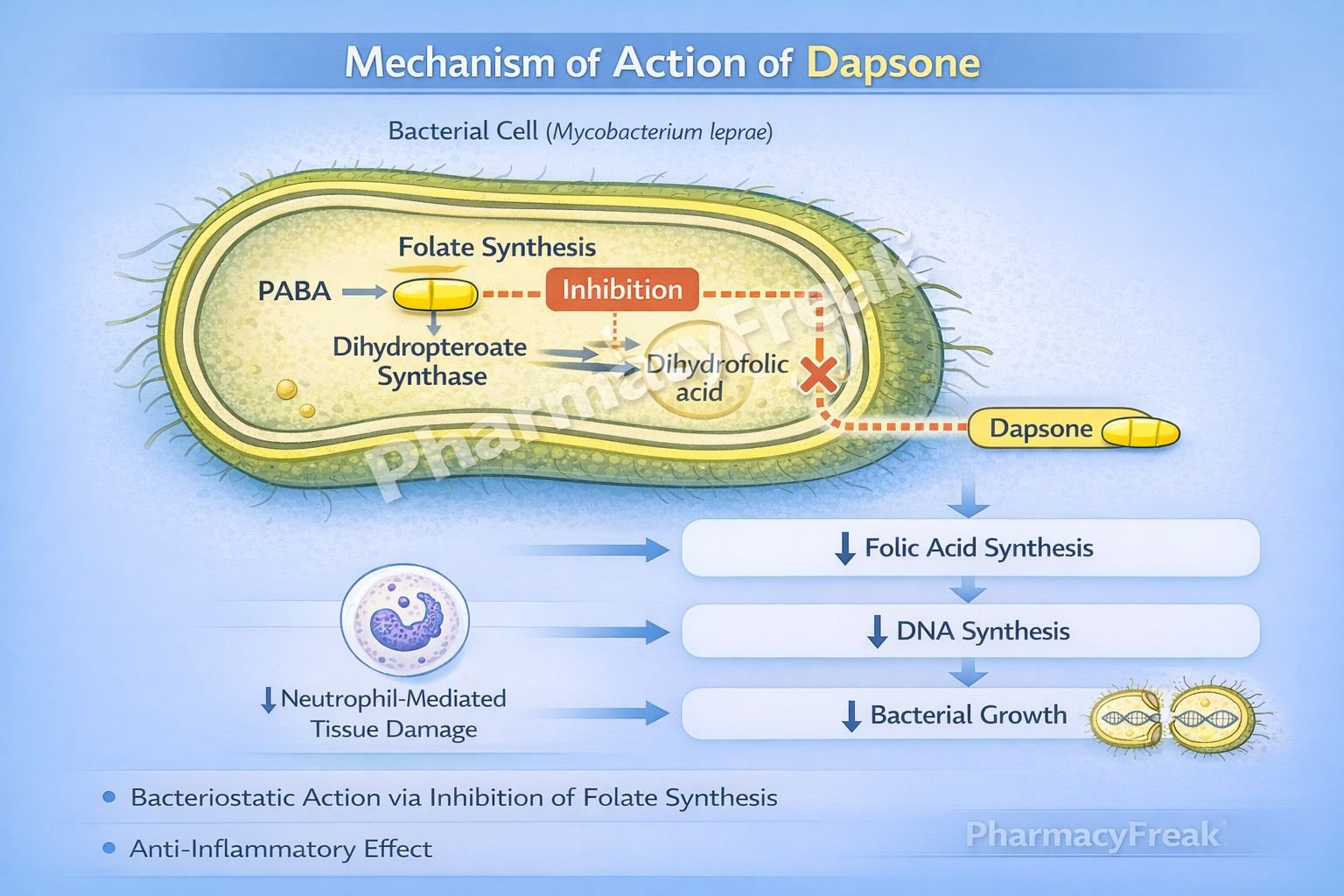
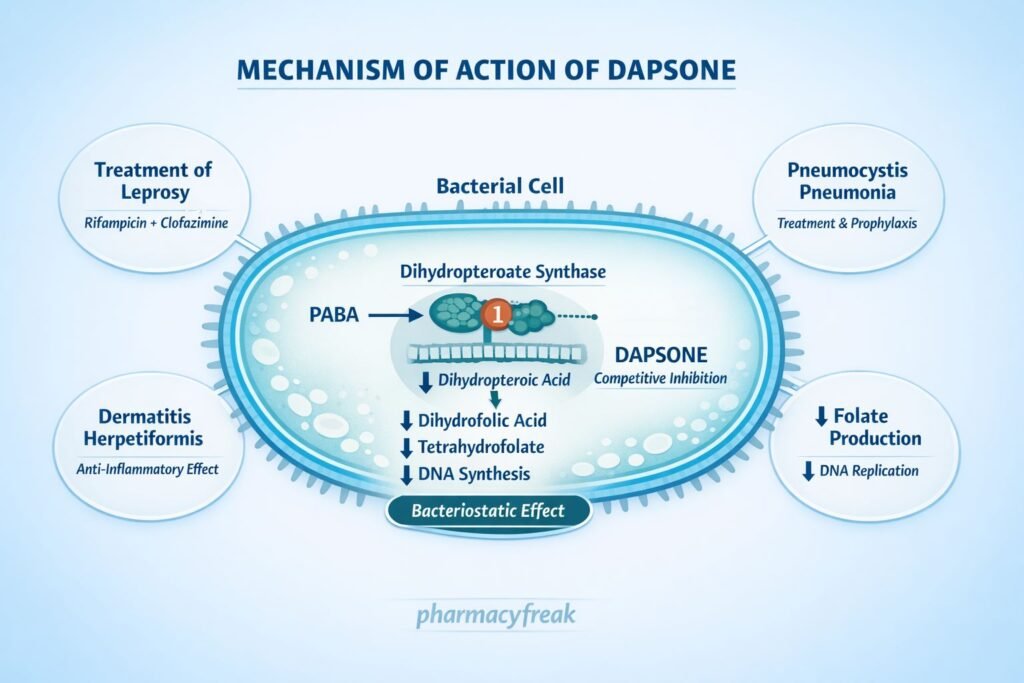
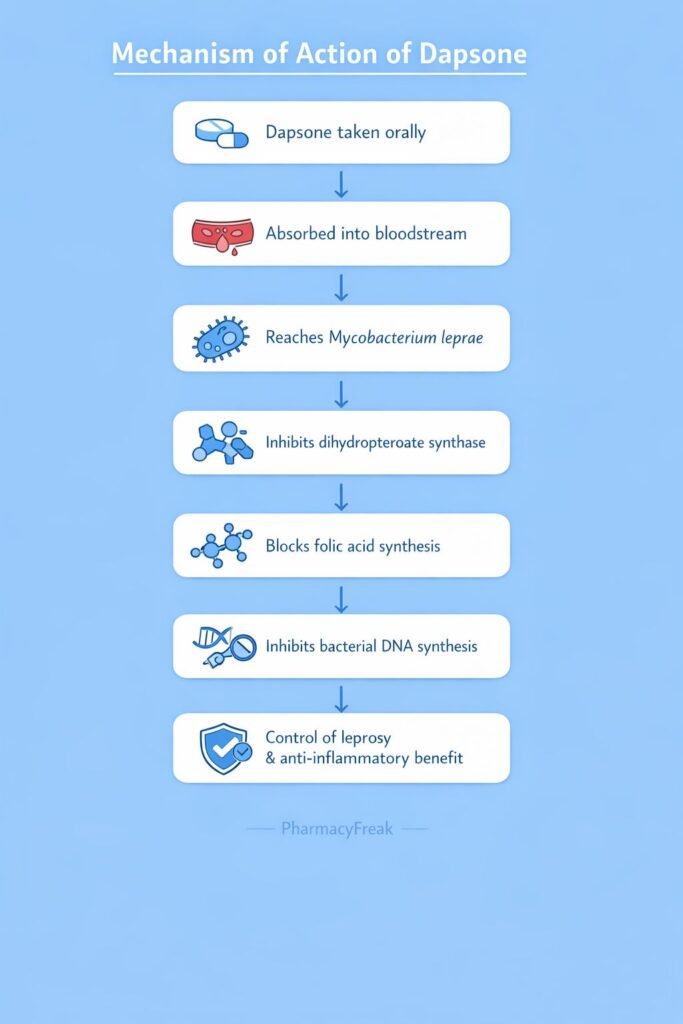
Dapsone inhibits bacterial folate synthesis, leading to impaired DNA synthesis and bacterial growth inhibition.
Step-wise mechanism:
- Structural Similarity to Para-Aminobenzoic Acid (PABA)
Dapsone is structurally similar to PABA, a substrate required for folic acid synthesis in bacteria. - Target Enzyme: Dihydropteroate Synthase
Bacteria synthesize folic acid de novo using the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase. - Competitive Enzyme Inhibition
Dapsone competitively inhibits dihydropteroate synthase by competing with PABA. - Inhibition of Dihydrofolic Acid Formation
Blocking this enzyme prevents the formation of dihydrofolic acid. - Reduced Tetrahydrofolate Production
Decreased dihydrofolate leads to reduced tetrahydrofolate availability. - Impaired DNA and RNA Synthesis
Folate deficiency disrupts synthesis of purines and thymidine. - Bacteriostatic Effect
Growth of susceptible organisms, especially Mycobacterium leprae, is inhibited. - Anti-inflammatory Action (Non-antibacterial)
Dapsone also inhibits neutrophil myeloperoxidase activity and reduces reactive oxygen species, explaining its efficacy in inflammatory dermatoses.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Well absorbed orally
- Bioavailability: High
- Distribution: Widely distributed; concentrates in skin and peripheral nerves
- Metabolism: Hepatic acetylation and hydroxylation
- Elimination: Renal excretion (urine)
- Half-life: Long (20–30 hours; prolonged with chronic use)
- Special feature: Undergoes enterohepatic circulation
Clinical Uses
Dapsone is used in infectious and inflammatory conditions:
- Leprosy (Hansen’s disease) – part of multidrug therapy
- Dermatitis herpetiformis (drug of choice)
- Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) prophylaxis (alternative)
- Toxoplasmosis prophylaxis (with pyrimethamine)
- Acne vulgaris (topical formulation)
- Immune-mediated blistering disorders
Adverse Effects
Dapsone has characteristic dose-related and idiosyncratic adverse effects:
- Hematologic:
- Hemolytic anemia (especially in G6PD deficiency)
- Methemoglobinemia
- Dermatologic:
- Rash
- Exfoliative dermatitis
- Neurologic:
- Peripheral neuropathy (long-term use)
- Dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome:
- Fever
- Rash
- Hepatitis
- Lymphadenopathy
Regular monitoring of hemoglobin and liver function is recommended.
Comparative Analysis (must include a table + explanation)
Comparison of Folate Synthesis Inhibitors
| Feature | Dapsone | Sulfonamides | Trimethoprim |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target enzyme | Dihydropteroate synthase | Dihydropteroate synthase | Dihydrofolate reductase |
| Structural similarity | PABA | PABA | Folic acid |
| Use in leprosy | Yes | No | No |
| Anti-inflammatory effect | Yes | No | No |
| Hemolysis risk | High (G6PD) | Moderate | Low |
Explanation:
Dapsone shares a sulfonamide-like mechanism but has additional anti-inflammatory effects that make it uniquely effective in leprosy and dermatitis herpetiformis. Trimethoprim acts downstream in folate synthesis, and combination therapy enhances antibacterial efficacy.
MCQs (10–15)
- Dapsone inhibits bacterial growth by blocking synthesis of:
a) Peptidoglycan
b) Ergosterol
c) Folic acid
d) DNA gyrase
Answer: c) Folic acid
- The enzyme inhibited by dapsone is:
a) Dihydrofolate reductase
b) DNA polymerase
c) Dihydropteroate synthase
d) Thymidylate synthase
Answer: c) Dihydropteroate synthase
- Dapsone is structurally similar to:
a) Folic acid
b) Thymidine
c) PABA
d) Pyrimidine
Answer: c) PABA
- Dapsone is most commonly used in:
a) Tuberculosis
b) Leprosy
c) Syphilis
d) Malaria
Answer: b) Leprosy
- The effect of dapsone on bacteria is:
a) Bactericidal
b) Fungicidal
c) Bacteriostatic
d) Virucidal
Answer: c) Bacteriostatic
- A major risk factor for hemolysis with dapsone is:
a) Renal failure
b) G6PD deficiency
c) Iron deficiency
d) Vitamin B12 deficiency
Answer: b) G6PD deficiency
- Dapsone is the drug of choice for:
a) Bullous pemphigoid
b) Dermatitis herpetiformis
c) Psoriasis
d) Atopic dermatitis
Answer: b) Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Dapsone also exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting:
a) Mast cell degranulation
b) Neutrophil function
c) T-cell proliferation
d) Complement activation
Answer: b) Neutrophil function
- Which adverse effect is characteristic of dapsone?
a) QT prolongation
b) Methemoglobinemia
c) Ototoxicity
d) Nephrotoxicity
Answer: b) Methemoglobinemia
- Dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome includes all EXCEPT:
a) Fever
b) Rash
c) Hepatitis
d) Nephrolithiasis
Answer: d) Nephrolithiasis
FAQs (minimum 5)
- What is the primary mechanism of dapsone?
Inhibition of bacterial folate synthesis by blocking dihydropteroate synthase. - Why is dapsone effective in leprosy?
Mycobacterium leprae relies on folate synthesis for replication. - Why does dapsone cause hemolysis?
It induces oxidative stress in red blood cells, especially in G6PD deficiency. - Does dapsone have anti-inflammatory effects?
Yes, it inhibits neutrophil-mediated tissue damage. - Is dapsone bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
It is bacteriostatic. - Why is dapsone combined with other drugs in leprosy?
To prevent resistance and improve treatment efficacy.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://www.jaypeebrothers.com - Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com