Table of Contents
Introduction
Danazol is a synthetic isoxazole derivative of 17-α-ethinyl testosterone with antigonadotropic, antiestrogenic, and weak androgenic properties. It is primarily used in the management of endometriosis, fibrocystic breast disease, hereditary angioedema, and certain gynecologic disorders. Danazol is a high-yield drug in pharmacology, gynecology, and endocrinology examinations because of its hypothalamic–pituitary axis suppression and unique hormonal effects.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
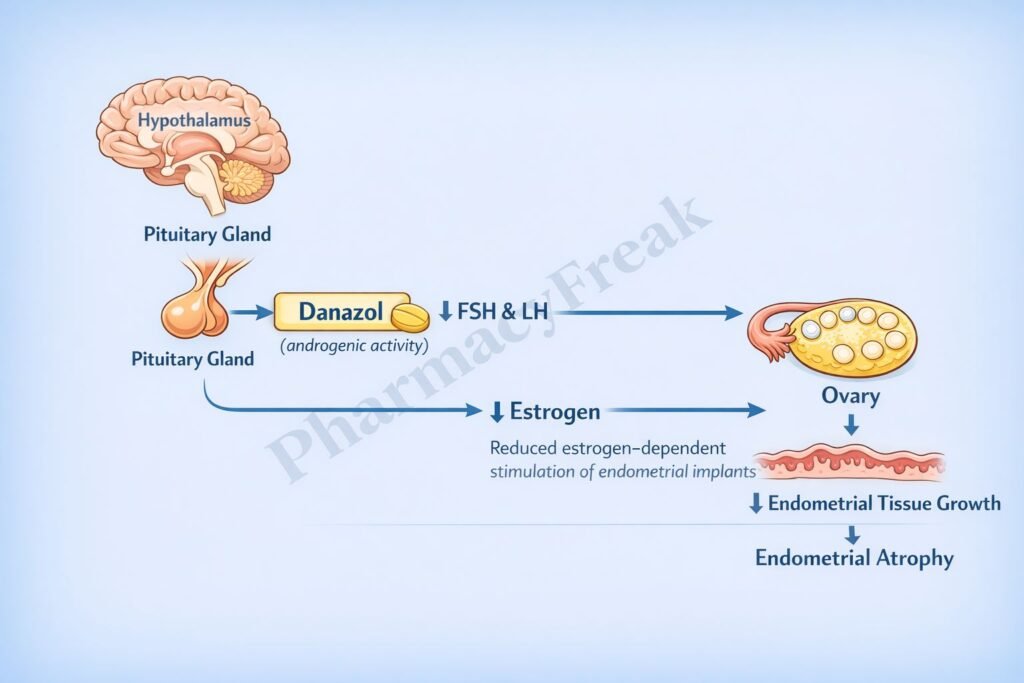
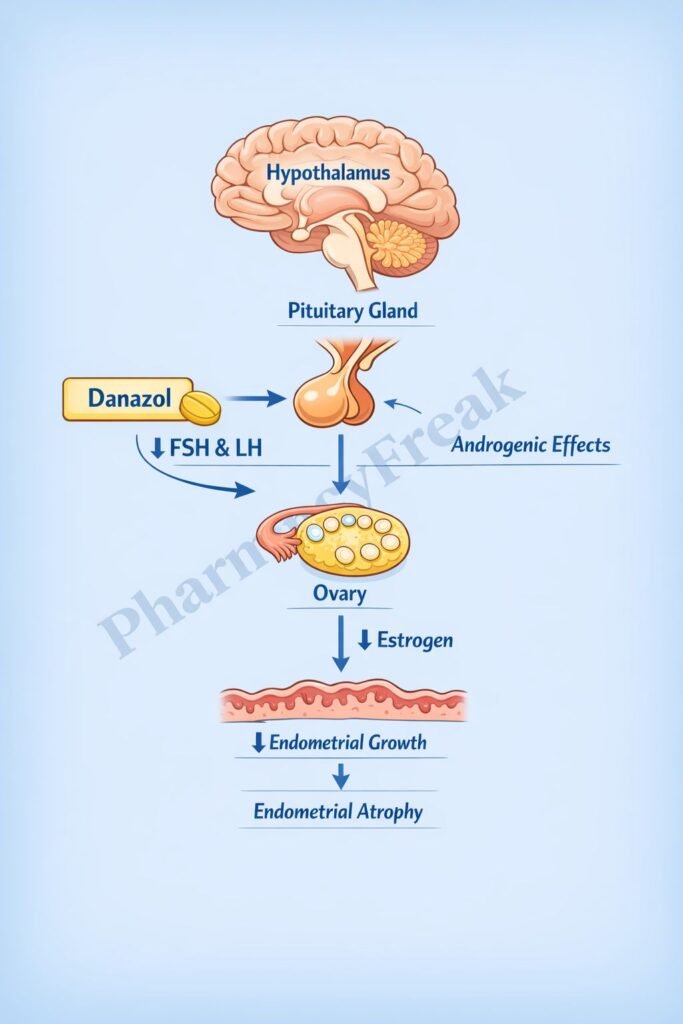
Danazol exerts its therapeutic effects by suppressing gonadotropin secretion and altering sex hormone dynamics.
Step-wise mechanism:
- Hypothalamic–Pituitary Axis Suppression
Danazol acts centrally to inhibit the pulsatile release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus. - Reduced Gonadotropin Secretion
Suppression of GnRH leads to decreased secretion of:- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Inhibition of Ovarian Steroidogenesis
Reduced LH and FSH levels result in decreased ovarian production of estrogen and progesterone. - Direct Inhibition of Steroidogenic Enzymes
Danazol directly inhibits enzymes involved in steroid hormone synthesis in the ovary and adrenal glands. - Antiestrogenic Effect
Lower estrogen levels lead to endometrial atrophy and suppression of ectopic endometrial tissue growth. - Weak Androgenic Activity
Danazol binds weakly to androgen receptors, contributing to its therapeutic and adverse effects. - Increase in Complement C1 Esterase Inhibitor
In hereditary angioedema, danazol increases hepatic synthesis of C1 esterase inhibitor, preventing bradykinin-mediated edema.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Well absorbed orally
- Bioavailability: High
- Distribution: Widely distributed; high protein binding
- Metabolism: Extensive hepatic metabolism
- Elimination: Fecal and renal excretion of metabolites
- Half-life: Approximately 15–18 hours
Danazol should be used cautiously in patients with hepatic dysfunction.
Clinical Uses
Danazol is used in hormone-dependent and complement-mediated disorders:
- Endometriosis
- Fibrocystic breast disease
- Hereditary angioedema (prophylaxis)
- Menorrhagia (selected cases)
- Precocious puberty (rare use)
Its use has declined due to androgenic adverse effects and availability of safer alternatives.
Adverse Effects
Adverse effects are largely related to androgenic and metabolic actions:
- Androgenic effects:
- Weight gain
- Acne
- Hirsutism
- Voice deepening
- Menstrual disturbances:
- Amenorrhea
- Irregular bleeding
- Metabolic:
- Dyslipidemia (↓ HDL, ↑ LDL)
- Hepatic:
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Rare hepatotoxicity
- Others:
- Hot flashes
- Mood changes
Danazol is contraindicated in pregnancy due to risk of virilization of the fetus.
Comparative Analysis (must include a table + explanation)
Comparison of Drugs Used in Endometriosis
| Feature | Danazol | GnRH Agonists | Progestins |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary action | ↓ LH & FSH | Pituitary downregulation | Endometrial suppression |
| Estrogen levels | Decreased | Markedly decreased | Moderately decreased |
| Androgenic effects | Present | Absent | Minimal |
| Bone loss risk | Low | High | Low |
| Current clinical use | Limited | Common | Common |
Explanation:
Danazol effectively suppresses estrogen production but is limited by androgenic side effects. GnRH agonists are more commonly used today despite hypoestrogenic effects, while progestins provide a safer long-term option.
MCQs (10–15)
- Danazol primarily suppresses the release of:
a) Prolactin
b) Cortisol
c) LH and FSH
d) Thyroxine
Answer: c) LH and FSH
- Danazol is chemically related to:
a) Estrogen
b) Progesterone
c) Testosterone
d) Cortisol
Answer: c) Testosterone
- Danazol is most commonly used in the treatment of:
a) Polycystic ovary syndrome
b) Endometriosis
c) Breast cancer
d) Ovarian cancer
Answer: b) Endometriosis
- The antiestrogenic effect of danazol is due to:
a) Estrogen receptor blockade
b) Decreased estrogen synthesis
c) Increased estrogen metabolism
d) Aromatase inhibition
Answer: b) Decreased estrogen synthesis
- Danazol is beneficial in hereditary angioedema because it:
a) Blocks histamine
b) Inhibits mast cells
c) Increases C1 esterase inhibitor
d) Blocks bradykinin receptors
Answer: c) Increases C1 esterase inhibitor
- A major adverse effect of danazol is:
a) Osteoporosis
b) Androgenic effects
c) QT prolongation
d) Agranulocytosis
Answer: b) Androgenic effects
- Danazol reduces estrogen levels by inhibiting:
a) Aromatase only
b) Ovarian steroidogenesis
c) Estrogen receptors
d) Estrogen transport proteins
Answer: b) Ovarian steroidogenesis
- Danazol is contraindicated in:
a) Endometriosis
b) Pregnancy
c) Fibrocystic breast disease
d) Hereditary angioedema
Answer: b) Pregnancy
- Danazol decreases menstrual bleeding by causing:
a) Endometrial proliferation
b) Endometrial atrophy
c) Ovulation induction
d) Cervical dilation
Answer: b) Endometrial atrophy
- Which lipid change is seen with danazol therapy?
a) ↑ HDL
b) ↓ LDL
c) ↓ HDL
d) ↓ Triglycerides
Answer: c) ↓ HDL
FAQs (minimum 5)
- What is the primary mechanism of danazol?
Suppression of LH and FSH leading to reduced estrogen production. - Why is danazol effective in endometriosis?
It induces a hypoestrogenic state causing endometrial atrophy. - Does danazol have androgenic effects?
Yes, due to its weak androgen receptor activity. - Why is danazol used in hereditary angioedema?
It increases synthesis of C1 esterase inhibitor. - Is danazol commonly used today?
Its use has declined due to side effects and availability of safer alternatives. - Can danazol cause liver toxicity?
Yes, liver function monitoring is recommended.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://www.jaypeebrothers.com - Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com

