Table of Contents
Introduction
Daflon is a micronized purified flavonoid fraction (MPFF) widely used in the management of chronic venous disorders and hemorrhoidal disease. It primarily contains diosmin (90%) and hesperidin (10%), both of which are naturally occurring flavonoids with venotonic and vasculoprotective properties. Daflon is extensively prescribed in vascular medicine and surgery and is a high-yield drug in pharmacology and clinical examinations due to its multimodal action on venous tone, microcirculation, and inflammation.


Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
Daflon exerts its therapeutic effects through combined venotonic, anti-inflammatory, and microcirculatory actions.
Step-wise mechanism:
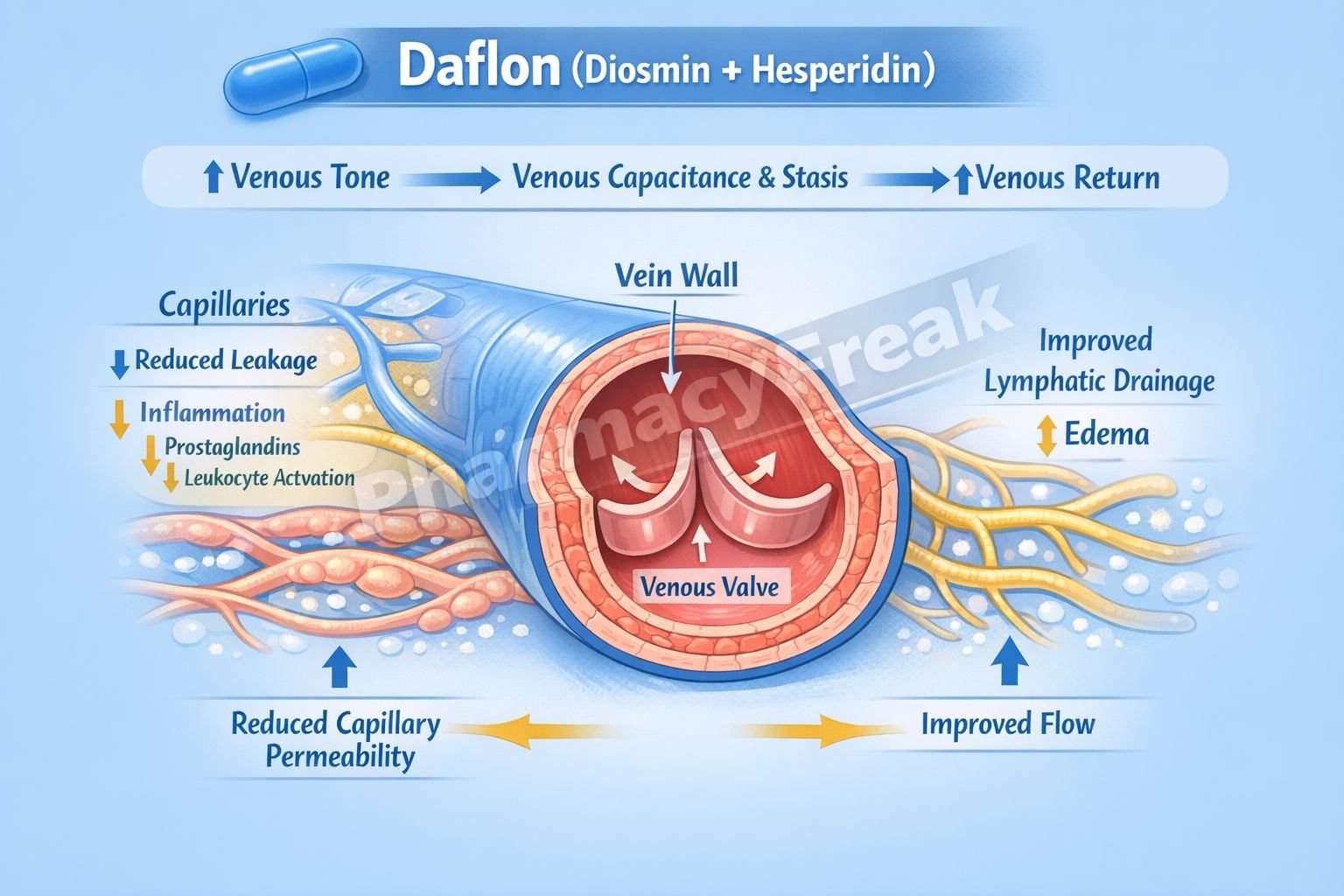
- Venous Tone Enhancement
Daflon increases venous tone by prolonging the vasoconstrictor effect of norepinephrine on venous smooth muscle. - Reduction of Venous Capacitance and Distensibility
Increased venous tone reduces venous pooling and venous stasis, especially in the lower limbs. - Improvement of Lymphatic Drainage
Daflon enhances lymphatic contraction frequency and flow, reducing tissue edema. - Microcirculatory Protection
It decreases capillary hyperpermeability and increases capillary resistance, preventing plasma leakage into interstitial tissues. - Anti-inflammatory Action
Daflon inhibits leukocyte activation, adhesion, and migration by:- Reducing expression of adhesion molecules
- Decreasing release of inflammatory mediators (prostaglandins, thromboxane, free radicals)
- Improved Venous Hemodynamics
Reduced inflammation and improved vessel integrity lead to better venous return and symptom relief. - Symptom Relief
The combined effects result in reduced edema, pain, heaviness, and bleeding in venous disorders.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Well absorbed orally (enhanced by micronization)
- Distribution: Widely distributed in venous tissue
- Metabolism: Hepatic metabolism by intestinal flora to phenolic acids
- Elimination: Primarily via feces; minor urinary excretion
- Half-life: Approximately 11 hours
- Special feature: Micronized formulation improves bioavailability
Clinical Uses
Daflon is primarily used in venous and hemorrhoidal conditions:
- Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI)
- Varicose veins
- Venous leg edema
- Hemorrhoids (acute and chronic)
- Post-thrombotic syndrome (adjunct)
- Venous ulcer support therapy
It is commonly used as long-term symptomatic therapy.
Adverse Effects
Daflon is generally well tolerated with a favorable safety profile:
- Gastrointestinal:
- Nausea
- Dyspepsia
- Diarrhea
- Central nervous system:
- Headache
- Dizziness (rare)
- Dermatologic:
- Rash (rare)
Serious adverse effects are extremely uncommon.
Comparative Analysis (must include a table + explanation)
Comparison of Venotonic Drugs
| Feature | Daflon (MPFF) | Rutosides | Horse Chestnut Extract |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Diosmin + hesperidin | Flavonoids | Aescin |
| Venous tone | Strong | Moderate | Moderate |
| Anti-inflammatory effect | Yes | Mild | Yes |
| Use in hemorrhoids | Yes | Limited | Limited |
| Evidence base | Strong | Moderate | Variable |
Explanation:
Daflon has a stronger evidence base and broader mechanism compared to other venotonics. Its combined effects on venous tone, inflammation, and microcirculation make it particularly effective in chronic venous insufficiency and hemorrhoidal disease.
MCQs (10–15)
- Daflon primarily contains which components?
a) Diosmin and rutin
b) Diosmin and hesperidin
c) Aescin and rutin
d) Flavone and quercetin
Answer: b) Diosmin and hesperidin
- Daflon improves venous tone by enhancing the effect of:
a) Acetylcholine
b) Histamine
c) Norepinephrine
d) Serotonin
Answer: c) Norepinephrine
- Daflon reduces edema mainly by:
a) Diuretic action
b) Lymphatic drainage improvement
c) Arterial dilation
d) Platelet inhibition
Answer: b) Lymphatic drainage improvement
- Daflon decreases inflammation by inhibiting:
a) Platelet aggregation
b) Leukocyte activation
c) Calcium channels
d) Beta receptors
Answer: b) Leukocyte activation
- Daflon is most commonly used in:
a) Hypertension
b) Peripheral arterial disease
c) Chronic venous insufficiency
d) Raynaud phenomenon
Answer: c) Chronic venous insufficiency
- Micronization of Daflon improves:
a) Elimination
b) Bioavailability
c) Renal clearance
d) Protein binding
Answer: b) Bioavailability
- Daflon reduces capillary permeability by:
a) Increasing prostaglandins
b) Stabilizing capillary walls
c) Increasing sodium retention
d) Blocking calcium influx
Answer: b) Stabilizing capillary walls
- Daflon is effective in hemorrhoids because it:
a) Acts as a laxative
b) Reduces venous inflammation
c) Causes vasodilation
d) Increases platelet count
Answer: b) Reduces venous inflammation
- Daflon belongs to which drug class?
a) Anticoagulant
b) Vasodilator
c) Venotonic flavonoid
d) Beta blocker
Answer: c) Venotonic flavonoid
- A common adverse effect of Daflon is:
a) Severe hypotension
b) Hepatotoxicity
c) Gastrointestinal upset
d) Agranulocytosis
Answer: c) Gastrointestinal upset
FAQs (minimum 5)
- What is the primary mechanism of Daflon?
Enhancement of venous tone with anti-inflammatory and capillary-protective effects. - Is Daflon a diuretic?
No, it reduces edema by improving venous and lymphatic drainage. - Why is Daflon effective in hemorrhoids?
It reduces venous inflammation and capillary permeability. - Does Daflon affect blood coagulation?
No, it does not have anticoagulant effects. - Is Daflon safe for long-term use?
Yes, it is generally safe with minimal adverse effects. - What advantage does micronization provide?
Improved absorption and therapeutic efficacy.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://www.jaypeebrothers.com - Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com