Table of Contents
Introduction
Citalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) widely prescribed for the treatment of major depressive disorder and other mood-related conditions. It is valued for its high selectivity toward the serotonin transporter (SERT), resulting in effective antidepressant action with relatively fewer off-target effects compared to older antidepressants. Citalopram and its S-enantiomer (escitalopram) are frequently tested in pharmacology, psychiatry, and clinical entrance examinations due to their clear mechanism and safety considerations.

Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
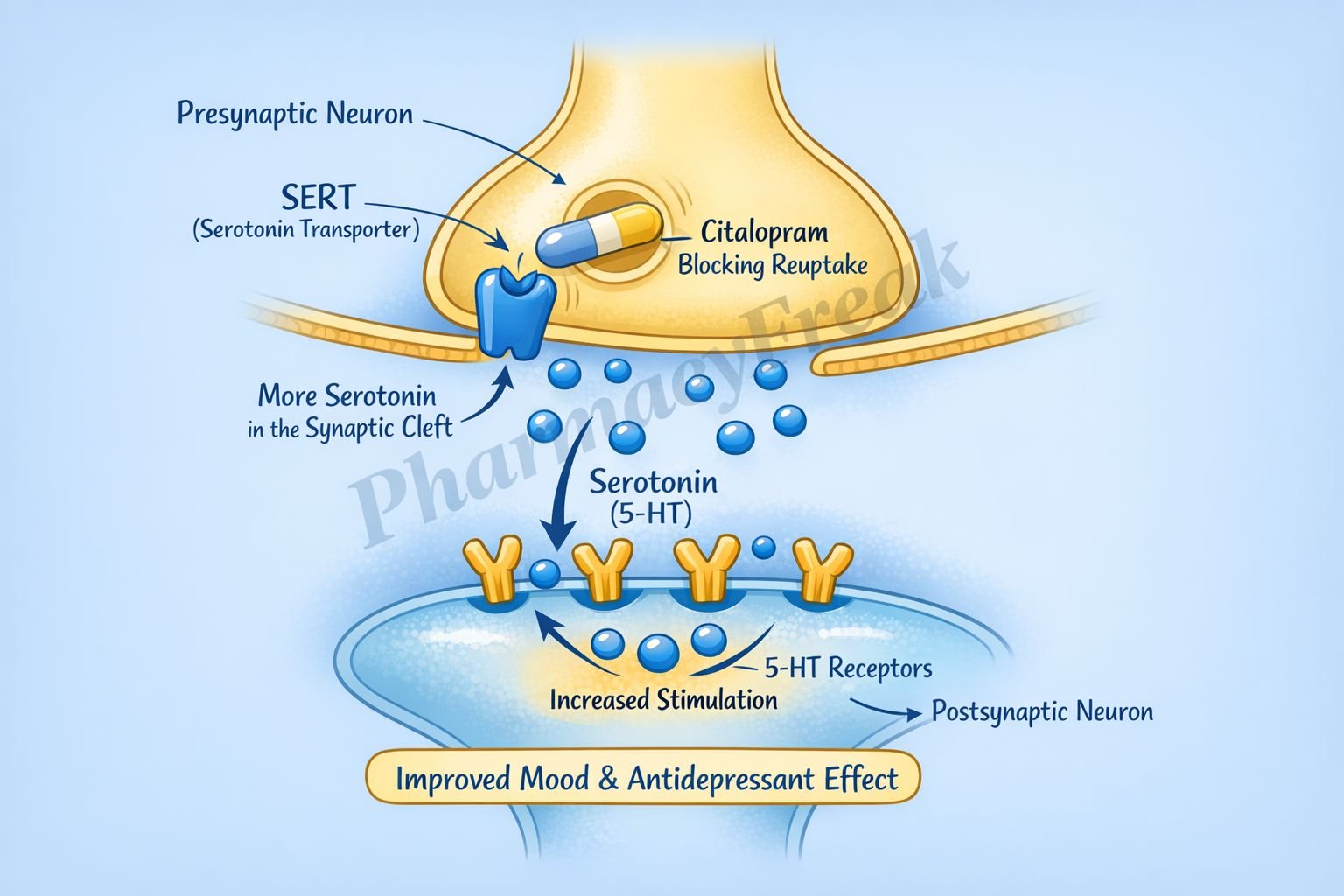
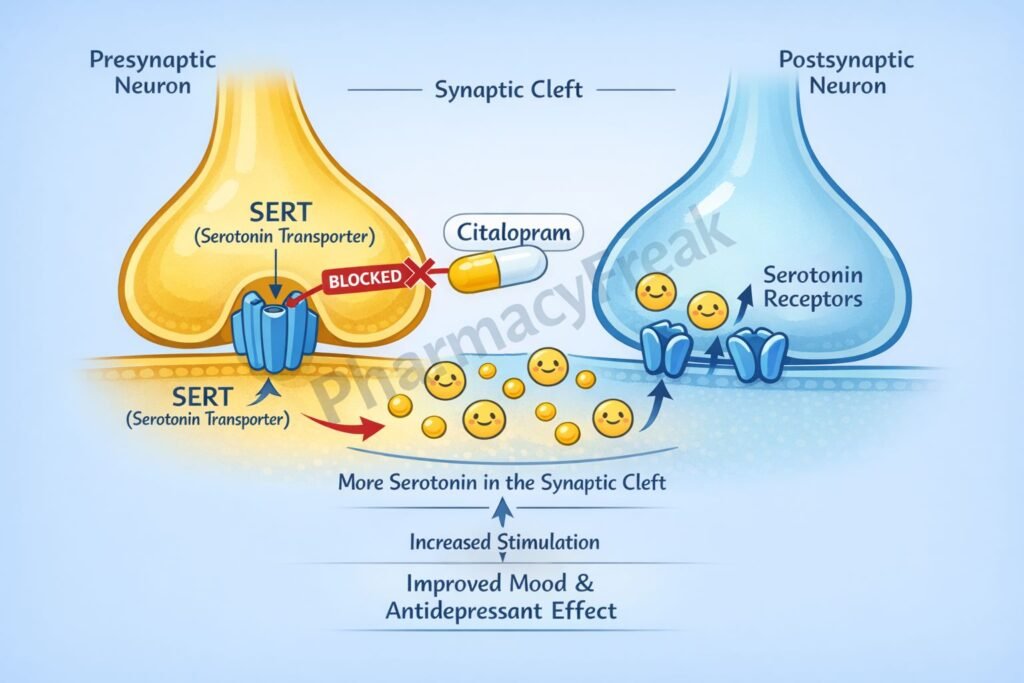
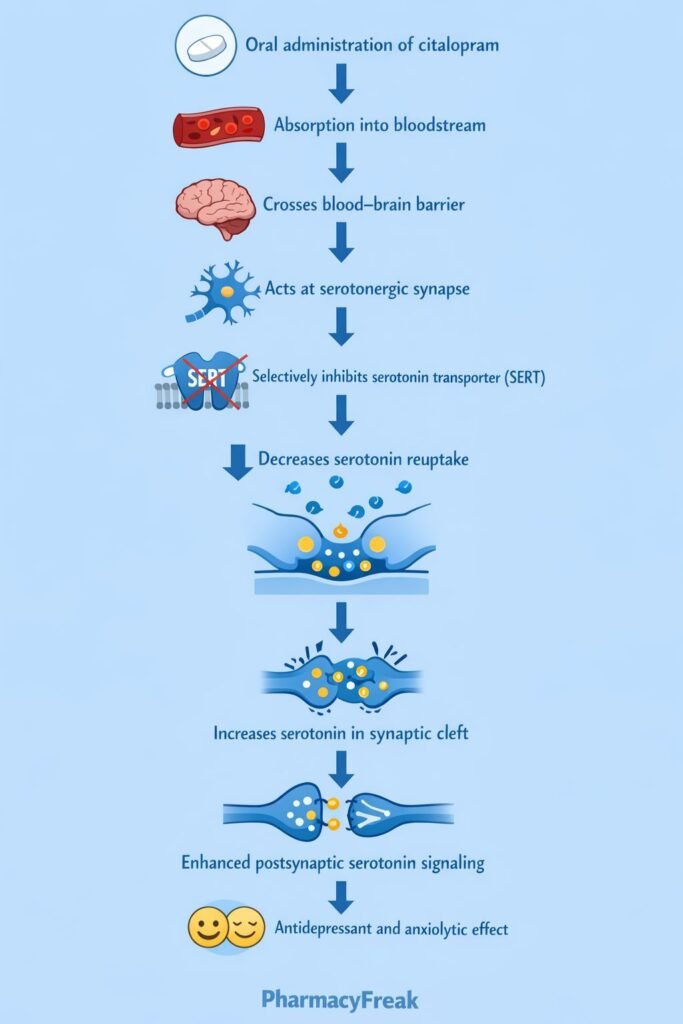
Citalopram exerts its antidepressant effect by selectively inhibiting serotonin reuptake in the central nervous system.
Step-wise mechanism:
- Serotonin Release
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) is released from presynaptic neurons into the synaptic cleft in serotonergic pathways of the brain. - Normal Reuptake via SERT
Under physiological conditions, serotonin is taken back into the presynaptic neuron by the serotonin transporter (SERT), terminating its synaptic action. - Selective SERT Inhibition
Citalopram selectively and competitively inhibits SERT on presynaptic neurons. - Increased Synaptic Serotonin
Inhibition of reuptake leads to increased serotonin concentration in the synaptic cleft. - Enhanced Postsynaptic Receptor Activation
Elevated serotonin levels result in prolonged stimulation of postsynaptic 5-HT receptors. - Neuroadaptive Changes
Chronic SSRI use leads to downregulation of presynaptic autoreceptors (5-HT₁A), enhancing serotonergic neurotransmission and improving mood over time.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Well absorbed orally
- Bioavailability: Approximately 80%
- Distribution: Widely distributed; crosses the blood–brain barrier
- Metabolism: Hepatic metabolism mainly via CYP2C19, CYP3A4, and CYP2D6
- Elimination: Renal and fecal excretion
- Half-life: Approximately 35 hours
- Steady state: Achieved in 1–2 weeks
Dose adjustment may be required in hepatic impairment and elderly patients.
Clinical Uses
Citalopram is indicated for several psychiatric conditions:
- Major depressive disorder
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Panic disorder
- Obsessive–compulsive disorder (off-label)
- Social anxiety disorder (off-label)
Its favorable tolerability profile makes it a commonly prescribed first-line antidepressant.
Adverse Effects
Common and important adverse effects include:
- Central nervous system:
- Insomnia
- Somnolence
- Headache
- Gastrointestinal:
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Diarrhea
- Sexual dysfunction:
- Decreased libido
- Delayed ejaculation
- Anorgasmia
- Cardiac:
- QT interval prolongation (dose-dependent, clinically significant)
- Others:
- Serotonin syndrome (when combined with other serotonergic agents)
Comparative Analysis (must include a table + explanation)
Comparison of Antidepressant Classes
| Feature | Citalopram | Tricyclic Antidepressants | MAO Inhibitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary mechanism | SERT inhibition | NE and 5-HT reuptake inhibition | MAO inhibition |
| Selectivity | High | Low | Moderate |
| Anticholinergic effects | Absent | Prominent | Absent |
| Cardiotoxicity | QT prolongation | High | Low |
| Drug interactions | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Clinical use | First-line | Second-line | Refractory cases |
Explanation:
Citalopram offers effective antidepressant action with fewer autonomic and sedative effects compared to tricyclic antidepressants. Unlike MAO inhibitors, it does not require dietary restrictions, improving safety and adherence. However, its risk of QT prolongation limits high-dose use.
MCQs
- Citalopram primarily inhibits which transporter?
a) Dopamine transporter
b) Norepinephrine transporter
c) Serotonin transporter
d) GABA transporter
Answer: c) Serotonin transporter
- Citalopram belongs to which drug class?
a) SNRI
b) SSRI
c) TCA
d) MAOI
Answer: b) SSRI
- Increased synaptic serotonin occurs due to:
a) Increased synthesis
b) Reduced metabolism
c) Reuptake inhibition
d) Vesicular storage
Answer: c) Reuptake inhibition
- The antidepressant effect of citalopram is delayed because of:
a) Slow absorption
b) Autoreceptor downregulation
c) Poor bioavailability
d) Rapid clearance
Answer: b) Autoreceptor downregulation
- Which adverse effect is dose-limiting for citalopram?
a) Hepatotoxicity
b) QT prolongation
c) Nephrotoxicity
d) Agranulocytosis
Answer: b) QT prolongation
- Citalopram has minimal effect on which receptor system?
a) Muscarinic
b) Histaminic
c) Alpha-1
d) All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
- Which enzyme is most involved in citalopram metabolism?
a) CYP1A2
b) CYP2C19
c) CYP2E1
d) CYP4A
Answer: b) CYP2C19
- Sexual dysfunction with citalopram is due to:
a) Dopamine blockade
b) Excess serotonin
c) Reduced GABA
d) Increased norepinephrine
Answer: b) Excess serotonin
- Serotonin syndrome is caused by:
a) Overdose of SSRIs alone
b) SSRI and MAOI combination
c) SSRI withdrawal
d) SSRI with antipsychotics
Answer: b) SSRI and MAOI combination
- Which antidepressant is more selective than citalopram?
a) Fluoxetine
b) Paroxetine
c) Escitalopram
d) Sertraline
Answer: c) Escitalopram
FAQs
- What is the primary mechanism of citalopram?
Selective inhibition of serotonin reuptake via SERT. - Why does citalopram take weeks to show effect?
Due to neuroadaptive changes and downregulation of presynaptic autoreceptors. - Does citalopram affect norepinephrine or dopamine?
No, it is highly selective for serotonin. - Why is QT prolongation a concern with citalopram?
It increases the risk of arrhythmias at higher doses. - Is citalopram safe in elderly patients?
Yes, but lower doses are recommended due to QT risk. - Can citalopram cause serotonin syndrome?
Yes, especially when combined with other serotonergic drugs.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://www.jaypeebrothers.com - Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com