Table of Contents
Introduction
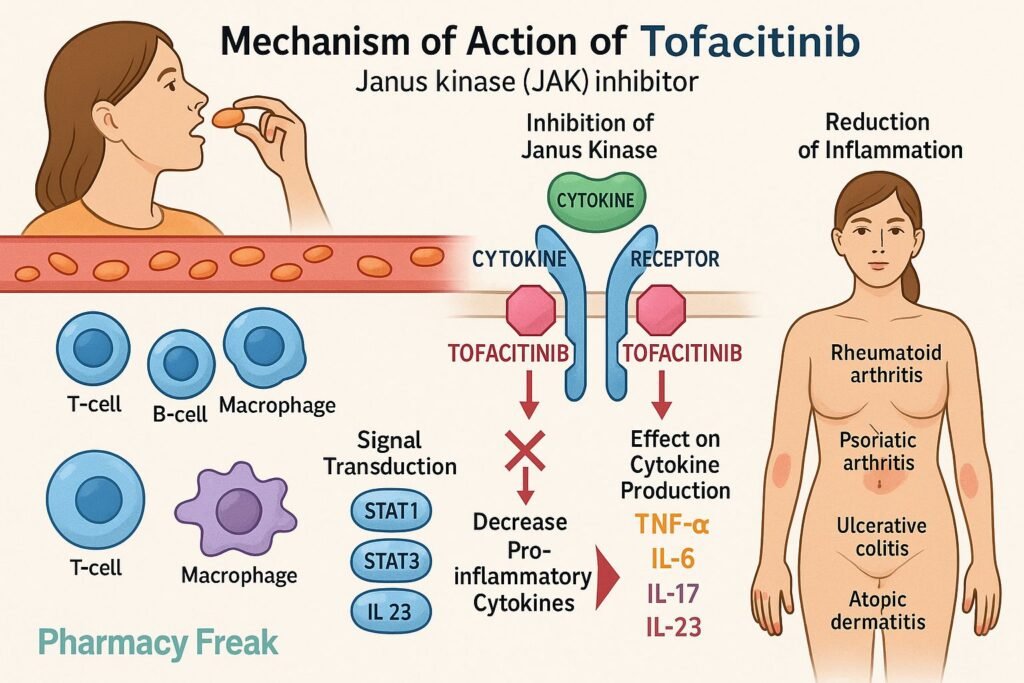
Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, primarily targeting JAK1 and JAK3. It blocks intracellular signaling of multiple inflammatory cytokines and is approved for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ulcerative colitis (UC), and other immune-mediated diseases.
Step-by-Step Mechanism of Action
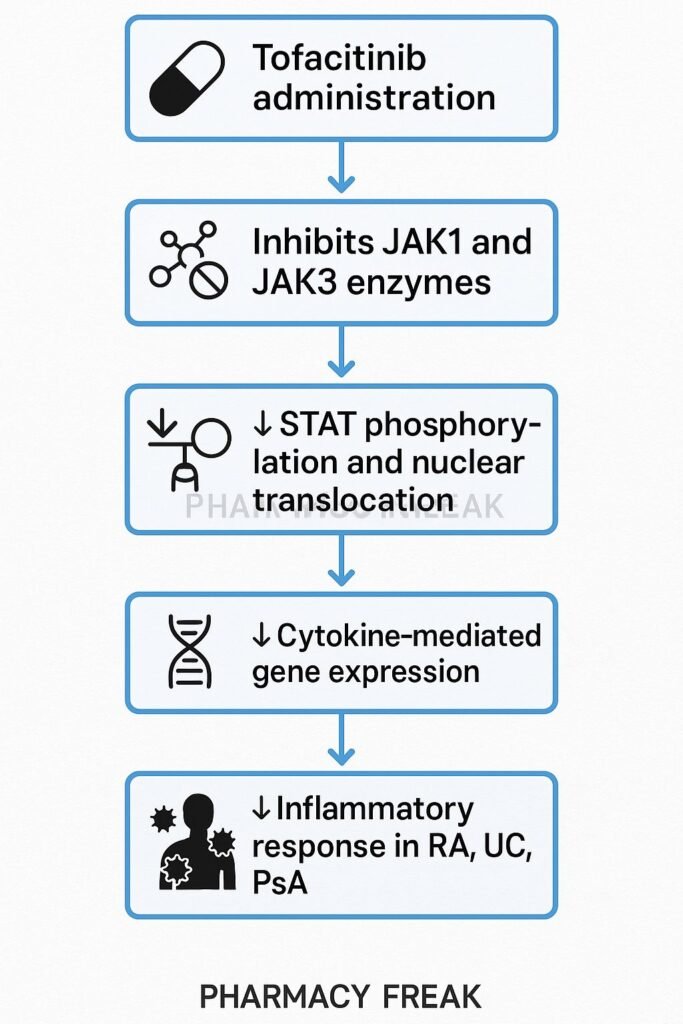
- Inhibition of JAK1 and JAK3
Tofacitinib competitively blocks ATP-binding sites of JAK1 and JAK3, thus preventing their phosphorylation and activation. - Disruption of STAT phosphorylation
Without activated JAKs, STAT transcription factors can’t be phosphorylated and fail to translocate to the nucleus. - Downregulation of cytokine gene expression
Inhibition of STAT signaling leads to reduced transcription of genes encoding inflammatory cytokines like IL‑2, IL‑4, IL‑6, IL‑7, IL‑9, IL‑15, and IL‑21. - Dampening of immune cell activation
The result is reduced T-cell, B-cell, and natural killer (NK) cell activity, and decreased production of inflammatory mediators. - Clinical anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects
These molecular actions translate to improved symptoms and reduced tissue damage in various autoimmune and inflammatory conditions.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Route | Oral |
| Bioavailability | ~74% |
| Time to Peak (Tmax) | ~1 hour |
| Protein Binding | ~40% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic via CYP3A4 (primary) and CYP2C19 (minor) |
| Half-life | ~3 hours |
| Excretion | ~70% via urine (mostly metabolites), ~30% feces |
Clinical Uses
- Moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (alone or with methotrexate)
- Active psoriatic arthritis
- Moderate to severe ulcerative colitis
- Off-label uses: alopecia areata, ankylosing spondylitis
Adverse Effects
- Increased risk of serious infections (e.g., herpes zoster, tuberculosis)
- Elevated LDL and total cholesterol levels
- Cytopenias (lymphopenia, neutropenia, anemia)
- Mild elevation in liver enzymes
- Rare pulmonary embolism and venous thromboembolism—especially at higher doses
Comparative Analysis
| Drug | JAK Target | Dosing | Primary Indications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tofacitinib | JAK1/3 | 5 mg twice daily | RA, PsA, UC |
| Baricitinib | JAK1/2 | 4 mg once daily | RA |
| Upadacitinib | JAK1-selective | 15 mg once daily | RA, PsA |
MCQs
- Tofacitinib primarily inhibits which kinases?
a) JAK2/3 b) JAK1/3 c) SYK d) mTOR
Answer: b) JAK1/3 - Its effect on STAT signaling is:
a) Enhanced phosphorylation b) Blocked phosphorylation c) No effect d) Increased degradation
Answer: b) Blocked phosphorylation - Which cytokine signaling is reduced?
a) IL‑2 b) IL‑1β c) TNF‑α d) IFN‑γ
Answer: a) IL‑2 - Main route of elimination is:
a) Renal unchanged b) Hepatic excretion c) Metabolite elimination via urine and feces d) Pulmonary
Answer: c) Metabolite elimination via urine and feces - Common adverse effect includes:
a) Hypoglycemia b) Increased infections c) Hyperthyroidism d) Hypotension
Answer: b) Increased infections - Compared to baricitinib, tofacitinib is:
a) JAK1/2 selective b) JAK1/3 selective c) Non-selective kinase inhibitor d) A biologic
Answer: b) JAK1/3 selective - It can cause elevation in:
a) LDL cholesterol b) Sodium c) Bilirubin d) Magnesium
Answer: a) LDL cholesterol - Half-life of tofacitinib is approximately:
a) 1 hour b) 3 hours c) 8 hours d) 24 hours
Answer: b) 3 hours - Serious but rare risk is:
a) Myocardial infarction b) Pulmonary embolism c) Hyperkalemia d) Diabetes
Answer: b) Pulmonary embolism - A typical dose for RA is:
a) 5 mg once daily b) 5 mg twice daily c) 15 mg once daily d) 30 mg weekly
Answer: b) 5 mg twice daily
FAQs
1. Are vaccinations required before initiation?
Yes—varicella and zoster vaccines should be updated prior to starting.
2. Should lipids be monitored?
Yes; LDL and total cholesterol typically rise and require monitoring.
3. Can tofacitinib be used with biologics like TNF inhibitors?
No—combining with biologics increases infection risk and is contraindicated.
4. Is dose adjustment needed in renal impairment?
Yes—lower doses are necessary in moderate to severe renal dysfunction.
5. What monitoring is recommended?
Regular CBC, liver enzymes, lipids, and infection screening are advised.
References

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com