Table of Contents
Introduction
Cymbalta is the brand name for duloxetine, a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) widely used in the treatment of depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and chronic pain conditions. Unlike selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), duloxetine enhances both serotonergic and noradrenergic neurotransmission, making it particularly effective in neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. Its dual mechanism and pain-modulating properties make duloxetine a high-yield topic in pharmacology, psychiatry, neurology, and clinical entrance examinations.

Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
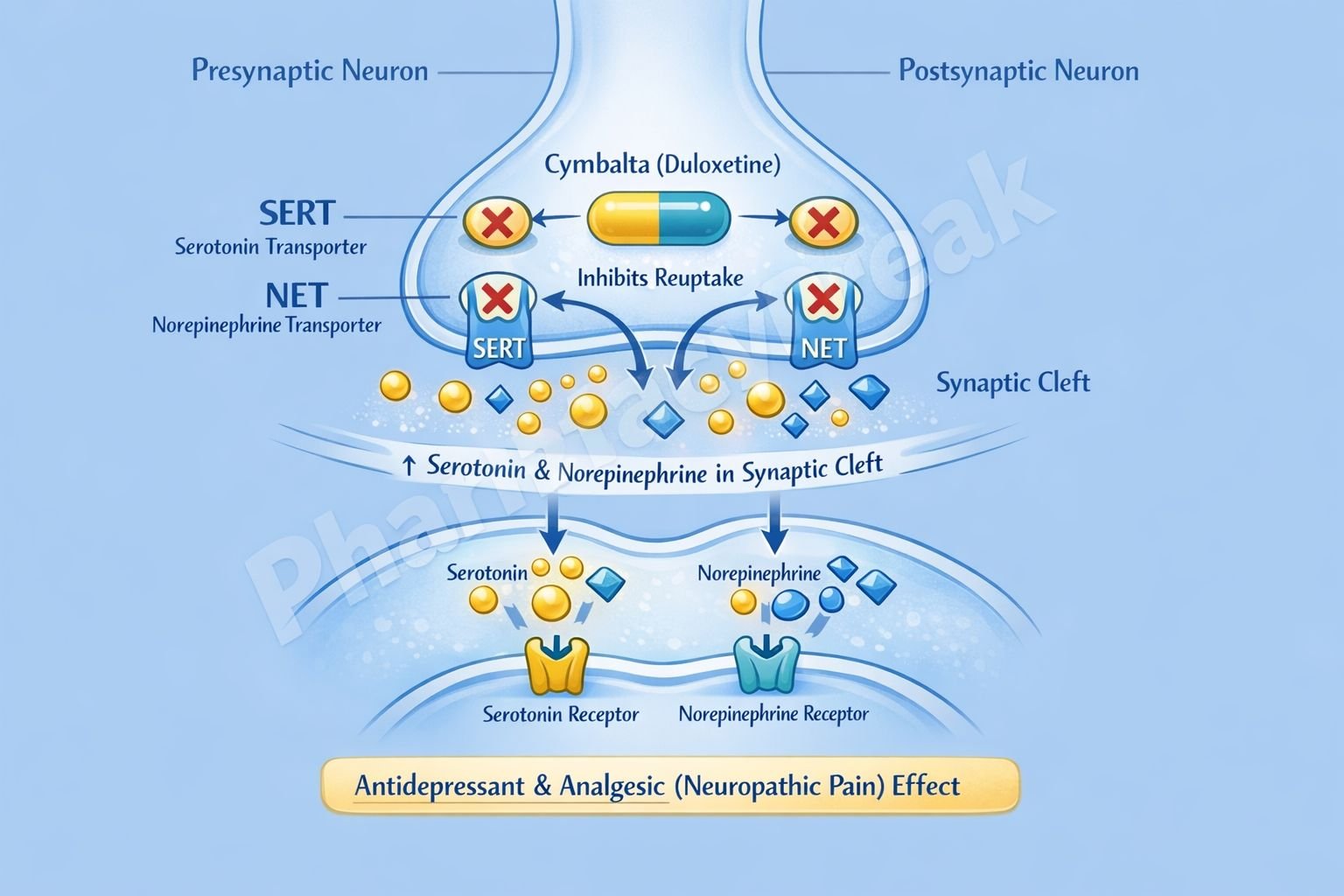
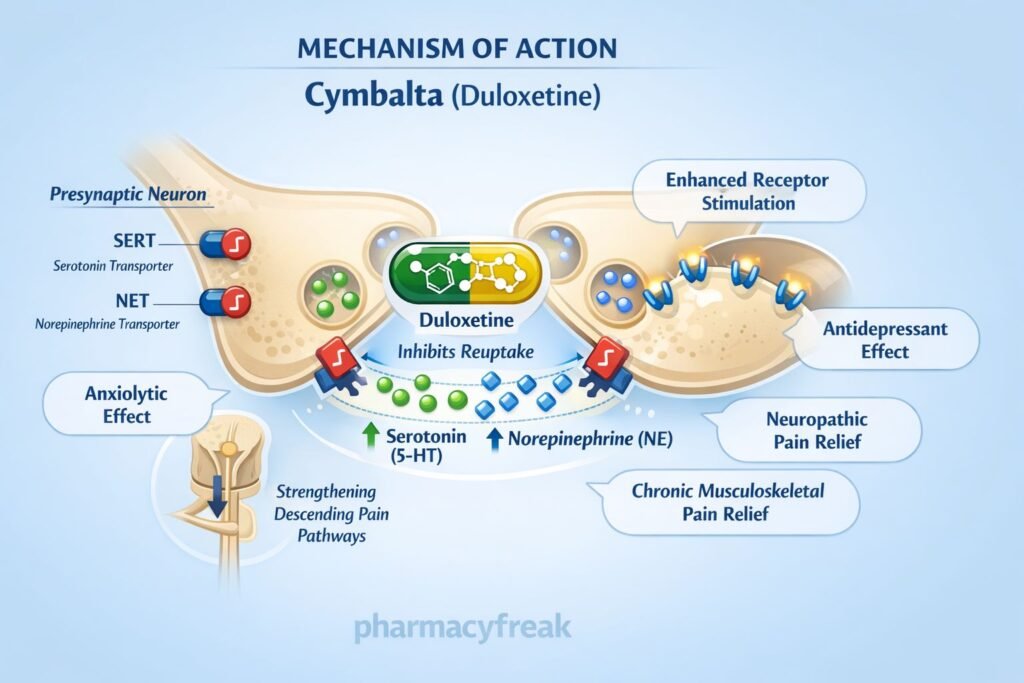
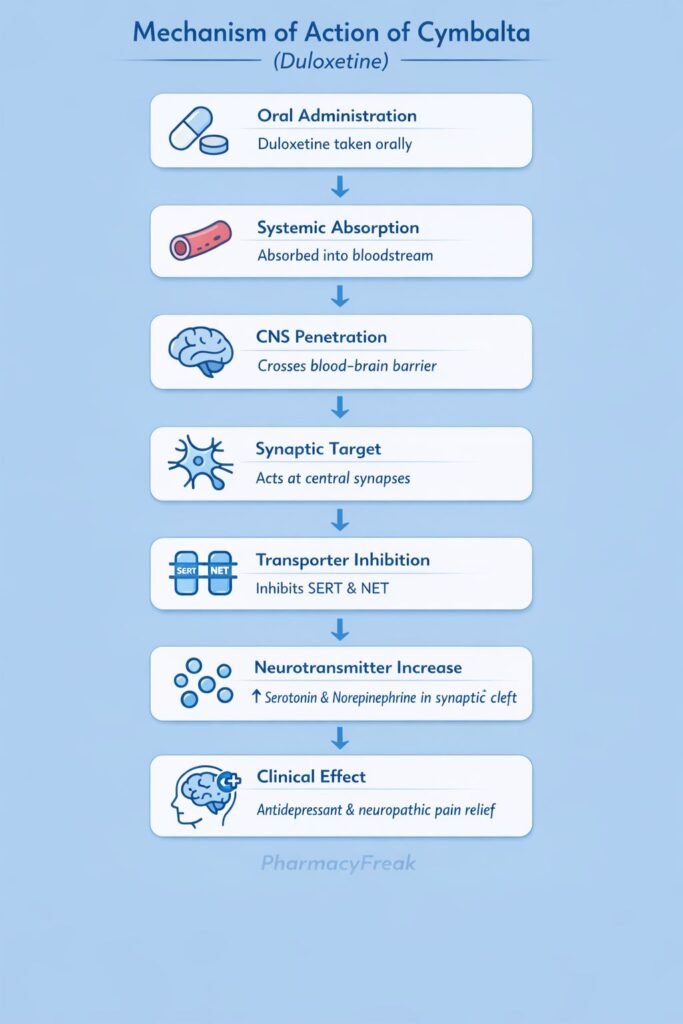
Duloxetine exerts its therapeutic effects by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine in the central nervous system.
Step-wise mechanism:
- Release of Monoamines
Serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine (NE) are released from presynaptic neurons into the synaptic cleft in the brain and spinal cord. - Normal Reuptake Process
Under physiological conditions, serotonin is reabsorbed via the serotonin transporter (SERT), and norepinephrine is reabsorbed via the norepinephrine transporter (NET). - Inhibition of SERT and NET
Duloxetine selectively and competitively inhibits both SERT and NET on presynaptic neurons. - Increased Synaptic Monoamine Levels
Inhibition of reuptake leads to increased concentrations of serotonin and norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft. - Enhanced Postsynaptic Receptor Activation
Elevated monoamine levels result in prolonged stimulation of postsynaptic 5-HT and adrenergic receptors. - Mood Elevation
Enhanced serotonergic and noradrenergic neurotransmission improves depressive and anxiety symptoms. - Central Pain Modulation
Increased norepinephrine and serotonin in descending inhibitory pain pathways of the spinal cord suppress pain signal transmission.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Well absorbed orally
- Bioavailability: ~50% (due to first-pass metabolism)
- Distribution: Widely distributed; highly protein bound
- Metabolism: Extensive hepatic metabolism via CYP1A2 and CYP2D6
- Elimination: Renal excretion of metabolites
- Half-life: Approximately 12 hours
- Special note: Contraindicated in severe hepatic impairment
Clinical Uses
Cymbalta (duloxetine) is approved for both psychiatric and pain-related conditions:
- Major depressive disorder
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain
- Fibromyalgia
- Chronic musculoskeletal pain
- Stress urinary incontinence (off-label in some regions)
Its efficacy in both mood disorders and chronic pain distinguishes it from SSRIs.
Adverse Effects
Adverse effects are related to enhanced monoaminergic activity:
- Central nervous system:
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Gastrointestinal:
- Nausea
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Autonomic:
- Increased blood pressure
- Sweating
- Sexual dysfunction
- Hepatotoxicity (rare but clinically important)
- Serotonin syndrome (with other serotonergic drugs)
Abrupt discontinuation may cause withdrawal symptoms.
Comparative Analysis (must include a table + explanation)
Comparison of Antidepressant Classes
| Feature | Duloxetine (SNRI) | SSRIs | Tricyclic Antidepressants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neurotransmitters affected | 5-HT + NE | 5-HT only | 5-HT + NE |
| Pain modulation | Strong | Weak | Moderate |
| Anticholinergic effects | Minimal | Minimal | Prominent |
| Cardiovascular risk | Moderate | Low | High |
| Clinical preference | Depression + pain | Depression | Second-line |
Explanation:
Duloxetine provides dual reuptake inhibition similar to TCAs but without prominent anticholinergic and cardiotoxic effects. Compared to SSRIs, it offers superior efficacy in neuropathic and chronic pain conditions due to enhanced noradrenergic transmission.
MCQs (10–15)
- Cymbalta inhibits reuptake of which neurotransmitters?
a) Dopamine only
b) Serotonin only
c) Serotonin and norepinephrine
d) Norepinephrine and dopamine
Answer: c) Serotonin and norepinephrine
- Duloxetine belongs to which drug class?
a) SSRI
b) SNRI
c) TCA
d) MAOI
Answer: b) SNRI
- Duloxetine relieves neuropathic pain by acting on:
a) Opioid receptors
b) NMDA receptors
c) Descending inhibitory pain pathways
d) Peripheral nociceptors
Answer: c) Descending inhibitory pain pathways
- Which transporter is inhibited by duloxetine?
a) DAT only
b) SERT and NET
c) NET only
d) VMAT
Answer: b) SERT and NET
- Duloxetine is extensively metabolized by:
a) CYP3A4 only
b) CYP2C9
c) CYP1A2 and CYP2D6
d) CYP2E1
Answer: c) CYP1A2 and CYP2D6
- Which condition is uniquely treated by duloxetine among antidepressants?
a) Bipolar disorder
b) Fibromyalgia
c) Schizophrenia
d) Parkinson disease
Answer: b) Fibromyalgia
- A dose-related adverse effect of duloxetine is:
a) Bradycardia
b) Hypotension
c) Hypertension
d) QT prolongation
Answer: c) Hypertension
- Duloxetine improves mood primarily by:
a) Dopamine receptor stimulation
b) Inhibiting monoamine oxidase
c) Enhancing monoaminergic transmission
d) Blocking glutamate receptors
Answer: c) Enhancing monoaminergic transmission
- Duloxetine should be avoided in patients with:
a) Renal stones
b) Liver disease
c) Asthma
d) Hypothyroidism
Answer: b) Liver disease
- Abrupt discontinuation of duloxetine may cause:
a) Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
b) Serotonin syndrome
c) Withdrawal symptoms
d) Agranulocytosis
Answer: c) Withdrawal symptoms
FAQs (minimum 5)
- What is the primary mechanism of Cymbalta?
Dual inhibition of serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. - Why is duloxetine effective in neuropathic pain?
It enhances descending inhibitory pain pathways in the spinal cord. - Is Cymbalta an SSRI?
No, it is an SNRI. - Does duloxetine increase blood pressure?
Yes, due to increased norepinephrine levels. - Can Cymbalta cause liver toxicity?
Rarely, but risk is higher in patients with preexisting liver disease. - Is duloxetine useful in fibromyalgia?
Yes, it is FDA-approved for fibromyalgia.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://www.jaypeebrothers.com - Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com