Table of Contents
Introduction
Clozapine is an atypical (second-generation) antipsychotic reserved for the treatment of treatment-resistant schizophrenia and for reducing suicidal behavior in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. It is considered the most effective antipsychotic for refractory psychosis but is limited by serious adverse effects requiring strict monitoring. Clozapine is frequently tested in pharmacology and psychiatry examinations because of its unique receptor profile, low extrapyramidal side effects, and risk of agranulocytosis.


Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
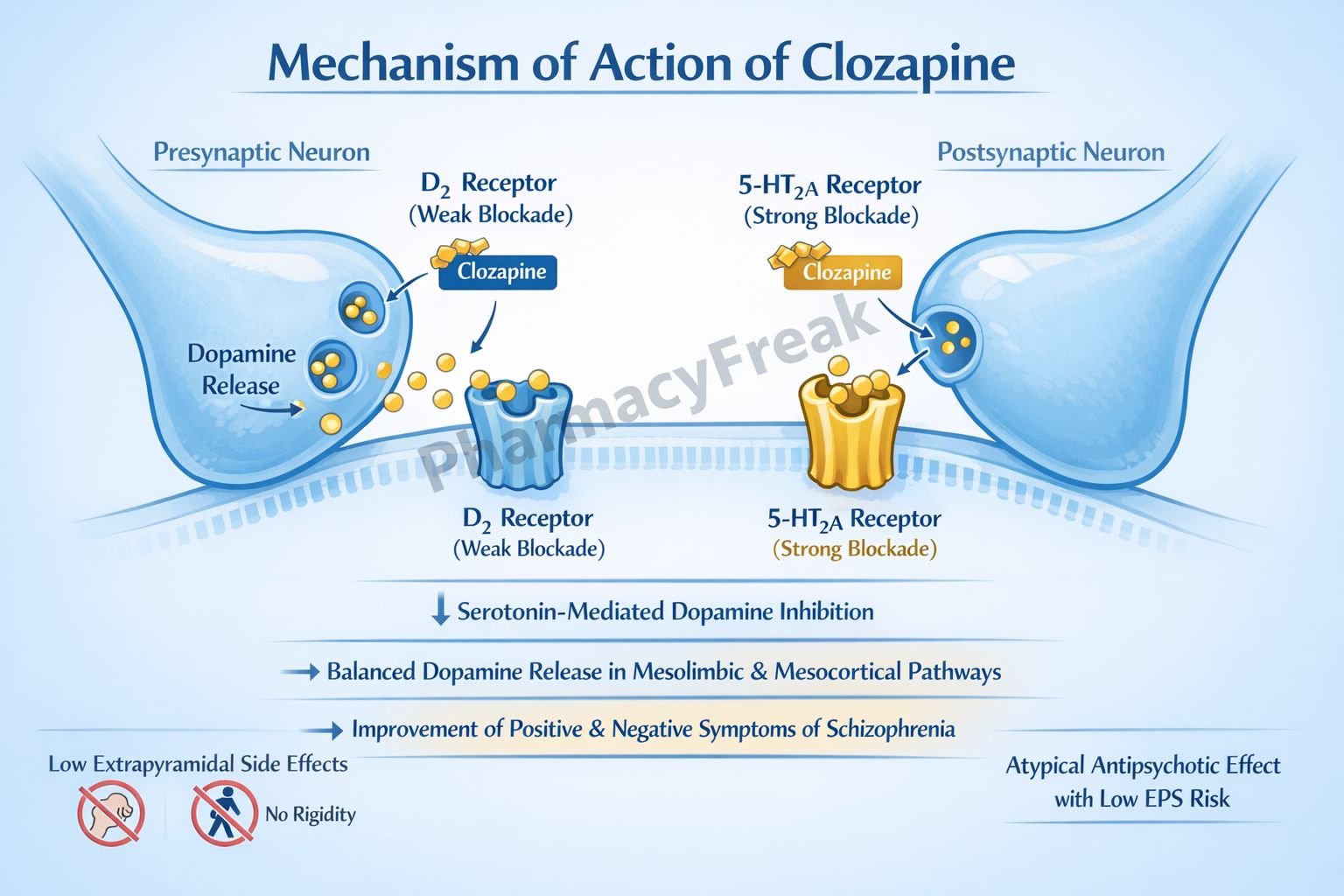
Clozapine produces antipsychotic effects through a complex, multi-receptor antagonistic profile rather than selective dopamine D₂ blockade.
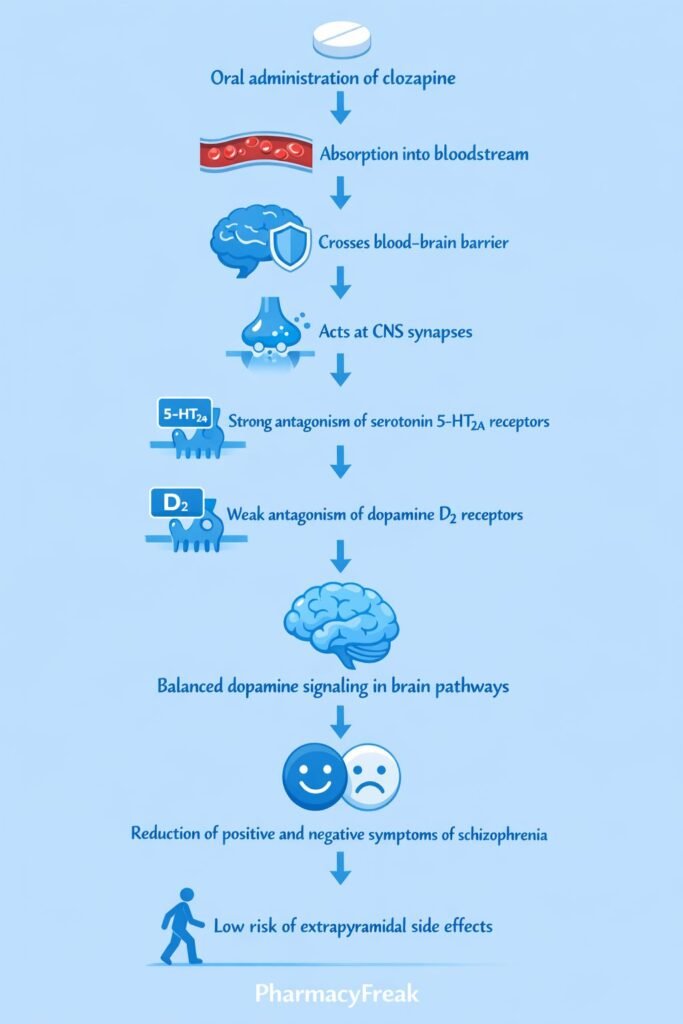
Step-wise mechanism:
- Dopamine Receptor Antagonism
Clozapine weakly antagonizes dopamine D₂ receptors and more strongly blocks D₄ receptors in the mesolimbic pathway. - Serotonin Receptor Blockade
It potently antagonizes serotonin 5-HT₂A and 5-HT₂C receptors. - Modulation of Dopamine Release
5-HT₂A blockade increases dopamine release in the nigrostriatal pathway, reducing extrapyramidal symptoms. - Reduction of Positive Symptoms
Dopamine receptor antagonism in the mesolimbic system decreases hallucinations and delusions. - Improvement of Negative Symptoms
Serotonin-dopamine balance improves negative symptoms and cognitive dysfunction. - Additional Receptor Effects
Clozapine also blocks:- α₁-adrenergic receptors
- Histamine H₁ receptors
- Muscarinic M₁ receptors
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Well absorbed orally
- Bioavailability: Approximately 60–70%
- Distribution: Highly protein bound; crosses blood–brain barrier
- Metabolism: Extensive hepatic metabolism via CYP1A2 (major), CYP3A4, and CYP2D6
- Elimination: Renal and fecal excretion
- Half-life: Approximately 12 hours (prolonged with chronic use)
- Special note: Smoking induces CYP1A2 and reduces clozapine levels
Clinical Uses
Clozapine is indicated for specific, high-risk psychiatric conditions:
- Treatment-resistant schizophrenia
- Schizoaffective disorder (refractory cases)
- Reduction of recurrent suicidal behavior in schizophrenia
- Severe psychosis unresponsive to other antipsychotics
Due to safety concerns, clozapine is not a first-line antipsychotic.
Adverse Effects
Clozapine is associated with serious and distinctive adverse effects:
- Hematologic:
- Agranulocytosis (most critical)
- Neutropenia
- Cardiovascular:
- Myocarditis
- Cardiomyopathy
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Metabolic:
- Weight gain
- Diabetes mellitus
- Dyslipidemia
- Neurologic:
- Seizures (dose-dependent)
- Others:
- Sedation
- Hypersalivation (sialorrhea)
- Constipation
Regular absolute neutrophil count (ANC) monitoring is mandatory.
Comparative Analysis (must include a table + explanation)
Comparison of Antipsychotic Drugs
| Feature | Clozapine | Typical Antipsychotics | Other Atypical Antipsychotics |
|---|---|---|---|
| D₂ blockade | Weak | Strong | Moderate |
| EPS risk | Very low | High | Low |
| Efficacy in resistant cases | Highest | Low | Moderate |
| Agranulocytosis risk | Present | Absent | Rare |
| Negative symptom control | Excellent | Poor | Moderate |
Explanation:
Clozapine is uniquely effective in treatment-resistant schizophrenia due to its broad receptor profile and strong serotonin antagonism. Unlike typical antipsychotics, it causes minimal extrapyramidal symptoms, but its risk of agranulocytosis necessitates restricted use and close monitoring.
MCQs (10–15)
- Clozapine primarily differs from typical antipsychotics because it:
a) Strongly blocks D₂ receptors
b) Selectively blocks NMDA receptors
c) Weakly blocks D₂ and strongly blocks 5-HT₂A
d) Inhibits MAO
Answer: c) Weakly blocks D₂ and strongly blocks 5-HT₂A
- Clozapine is most effective for:
a) Acute mania
b) Parkinson disease psychosis
c) Treatment-resistant schizophrenia
d) Anxiety disorders
Answer: c) Treatment-resistant schizophrenia
- The most serious adverse effect of clozapine is:
a) QT prolongation
b) Agranulocytosis
c) Tardive dyskinesia
d) Hyperprolactinemia
Answer: b) Agranulocytosis
- Clozapine has low extrapyramidal symptoms because of:
a) Weak D₂ blockade
b) GABA stimulation
c) NMDA antagonism
d) Acetylcholine release
Answer: a) Weak D₂ blockade
- Clozapine requires routine monitoring of:
a) Platelet count
b) Liver enzymes
c) Absolute neutrophil count
d) Serum potassium
Answer: c) Absolute neutrophil count
- Clozapine metabolism is mainly affected by:
a) CYP2C9
b) CYP1A2
c) CYP2E1
d) CYP3A5
Answer: b) CYP1A2
- Smoking reduces clozapine levels by:
a) Increasing renal excretion
b) Inhibiting absorption
c) Inducing CYP1A2
d) Blocking enterohepatic circulation
Answer: c) Inducing CYP1A2
- Clozapine has high affinity for which dopamine receptor?
a) D₁
b) D₂
c) D₃
d) D₄
Answer: d) D₄
- Which adverse effect is unique to clozapine?
a) Tardive dyskinesia
b) Agranulocytosis
c) Hyperprolactinemia
d) Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Answer: b) Agranulocytosis
- Clozapine improves negative symptoms mainly due to:
a) Dopamine depletion
b) Serotonin receptor blockade
c) GABA enhancement
d) Cholinesterase inhibition
Answer: b) Serotonin receptor blockade
FAQs (minimum 5)
- What is the primary mechanism of clozapine?
Combined weak dopamine D₂ blockade and strong serotonin 5-HT₂A antagonism. - Why does clozapine cause fewer EPS?
Because it minimally blocks D₂ receptors in the nigrostriatal pathway. - Why is clozapine reserved for refractory cases?
Due to the risk of agranulocytosis and need for frequent blood monitoring. - Does clozapine increase prolactin levels?
No, it causes minimal prolactin elevation. - Why does clozapine cause hypersalivation?
Due to paradoxical muscarinic receptor effects. - Can clozapine reduce suicide risk?
Yes, it is proven to reduce suicidal behavior in schizophrenia.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com - Tripathi KD. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology
https://www.jaypeebrothers.com - Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com