Table of Contents
1. Identification
Summary
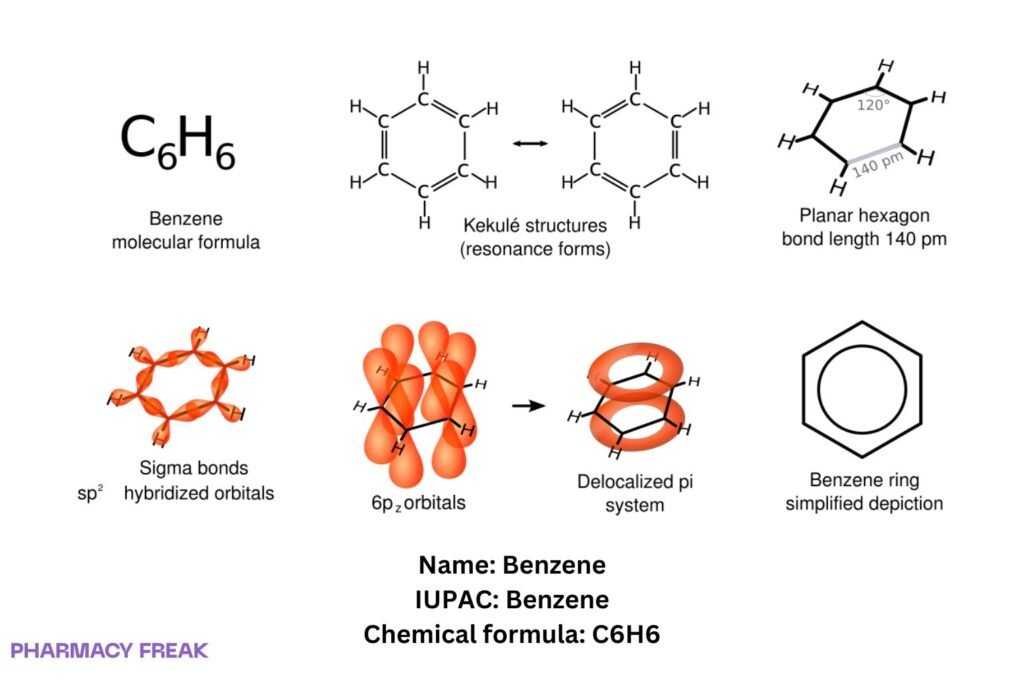
Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon (C₆H₆) consisting of a planar six-membered ring with delocalized π electrons; a foundational motif (“phenyl”) in organic chemistry and an industrial solvent/intermediate.
Brand Names
Not applicable.
Name
Benzene
Background
Endogenous to crude oil and combustion streams; widely used as a chemical feedstock; environmental and occupational toxicant with established leukemogenic potential.
Modality
Small molecule
Groups
Industrial chemical; environmental toxicant
Structure
Weight
~78.11 g/mol
Chemical Formula
C₆H₆
Synonyms
Benzol; Cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene (historic); Phene
External IDs
CAS: 71-43-2; PubChem CID: 241; UNII: J64922108F
2. Pharmacology
Indication
Not a therapeutic agent.
Associated Conditions
Occupational/environmental exposure linked to bone-marrow toxicity and hematologic malignancy risk.
Associated Therapies
Not applicable.
Contraindications & Blackbox Warnings
Not applicable (non-drug); regulatory guidance treats benzene as a known human carcinogen with strict exposure limits.
Pharmacodynamics
Central nervous system depressant at high acute doses; chronic exposure damages hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells.
Mechanism of action
Metabolic activation (e.g., phenolic/epoxide metabolites) generates reactive species that impair DNA, proteins, and marrow stromal signaling.
Absorption
Inhalational absorption predominant; dermal and oral uptake occur with liquid contact or contaminated water/foods.
Volume of distribution
Distributes into lipid-rich tissues; volatile, rapidly partitions to blood–air interface.
Protein binding
Reversible binding to plasma lipoproteins and tissue lipids; limited specific protein binding.
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic oxidative metabolism to phenol, catechol, hydroquinone, and ring-opened species; further conjugation (glucuronidation/sulfation).
Route of elimination
Pulmonary exhalation of parent; urinary excretion of conjugated metabolites.
Half-life
Short for parent compound (hours); metabolite kinetics depend on dose and route.
Clearance
Combination of pulmonary exhalation and hepatic biotransformation followed by renal elimination.
Adverse Effects
Acute: dizziness, headache, CNS depression, arrhythmia at very high levels.
Chronic: leukopenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia; increased leukemia risk.
Toxicity
High-level exposure: narcosis, ventricular dysrhythmias, death. Chronic low-level exposure: cumulative marrow injury with latency to malignancy.
Pathways
Phase I oxidation (CYP2E1-dominant) → phenolic/epoxide metabolites → Phase II conjugation; marrow redox stress and DNA damage responses.
Pharmacogenomic Effects/ADRs
Interindividual variability in CYP2E1/Phase II enzymes modifies metabolite burden; co-exposures (e.g., alcohol, toluene) alter activation.
3. Interactions
Drug Interactions
Not applicable as a medicine; solvent co-exposures and enzyme inducers/inhibitors can modify benzene metabolism/toxicity.
Food Interactions
Not applicable; ingestion concerns relate to contamination, not intended intake.
4. Categories
ATC Codes
None.
Drug Categories
Not a drug; aromatic hydrocarbon; environmental toxicant
Chemical Taxonomy
Monocyclic arene; planar conjugated ring; delocalized π system
Affected organisms
Humans and other exposed organisms (toxicology context)
5. Chemical Identifiers
UNII
J64922108F
CAS number
71-43-2
InChI Key
UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI
InChI=1S/C6H6/c1-2-4-6-5-3-1/h1-6H
IUPAC Name
Benzene
SMILES
c1ccccc1
6. References
PubChem Compound Summary: Benzene — formula C₆H₆, MW ~78.11, identifiers (CID 241), synonyms, structure. pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
NIST Chemistry WebBook — IUPAC InChI InChI=1S/C6H6/c1-2-4-6-5-3-1/h1-6H and InChIKey UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N; CAS 71-43-2. NIST WebBook+1
FDA GSRS/UNII — Benzene UNII J64922108F public record. precision.fda.gov
EPA IRIS — Benzene carcinogenicity and risk assessment overview. iris.epa.gov
FDA communications — benzene as known human carcinogen; contamination advisories for drug products. U.S. Food and Drug Administration+1

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com