Table of Contents
Introduction
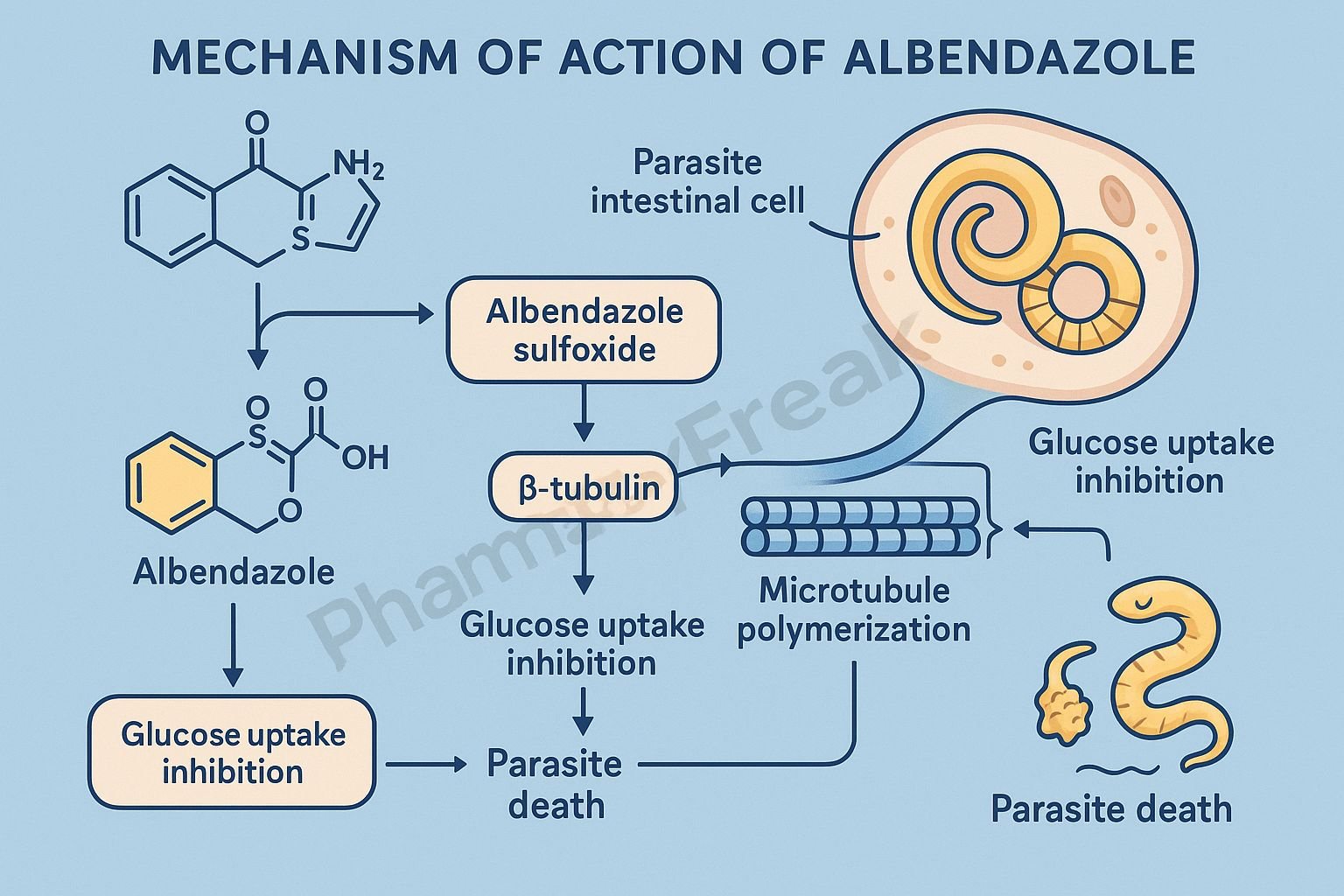
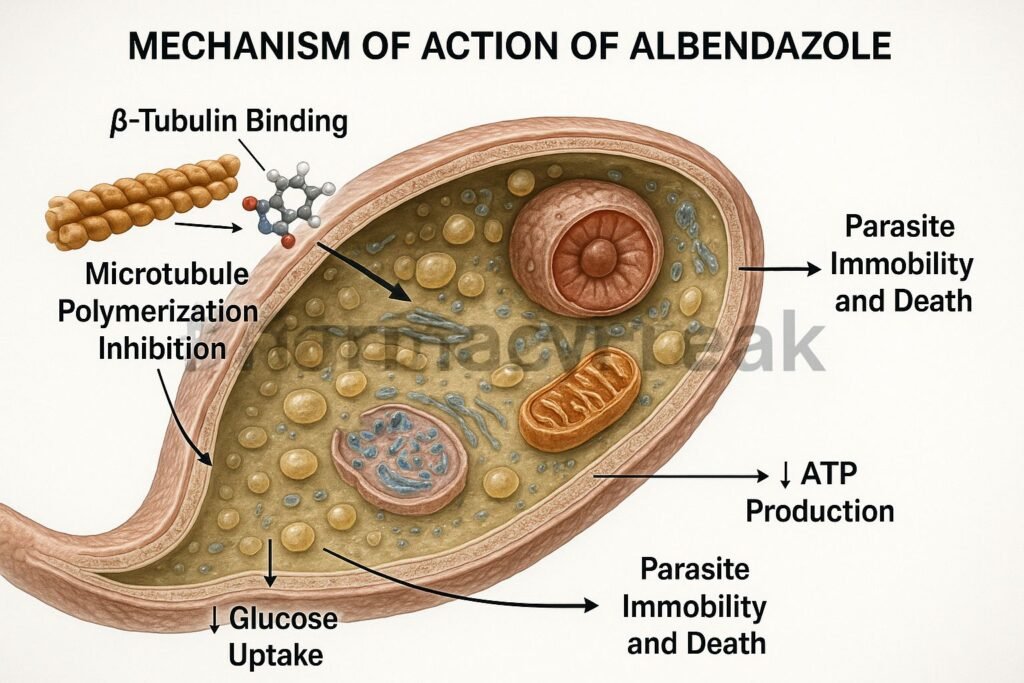
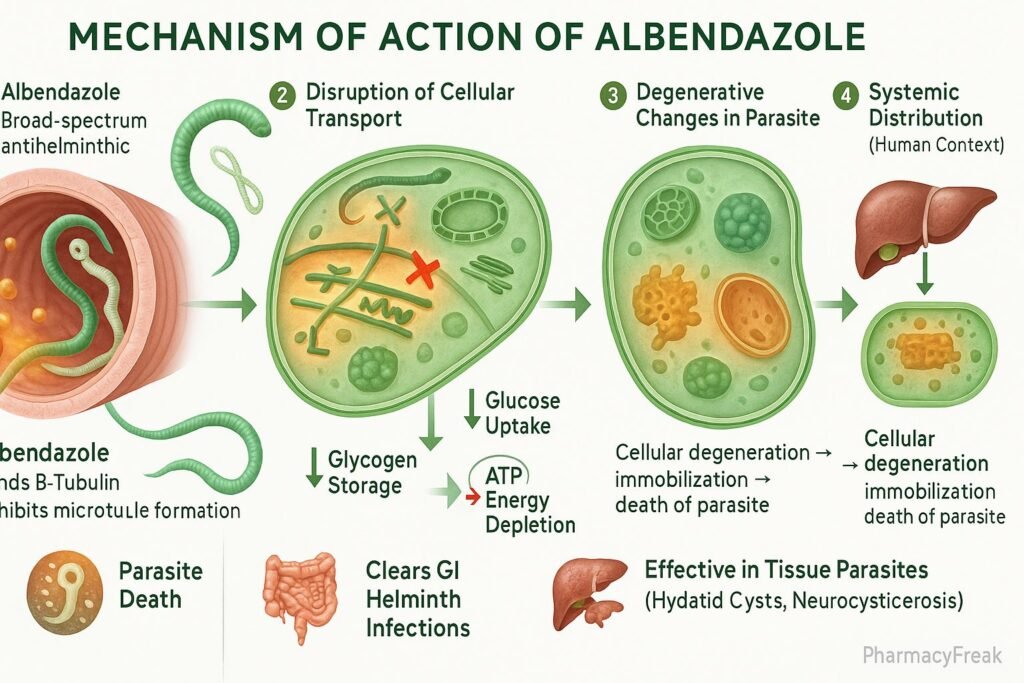
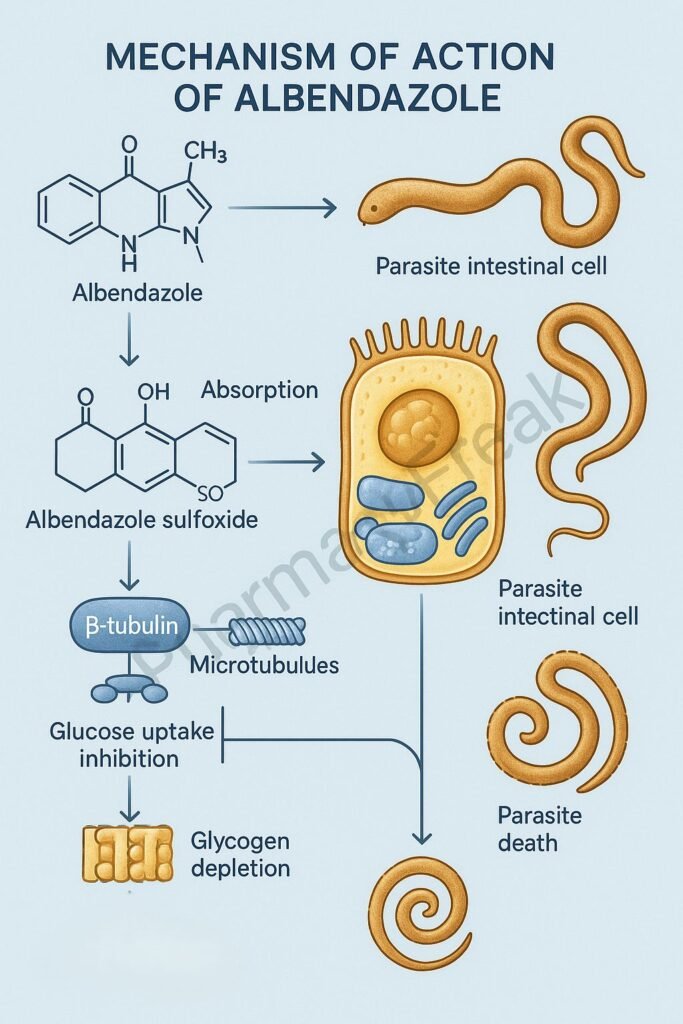
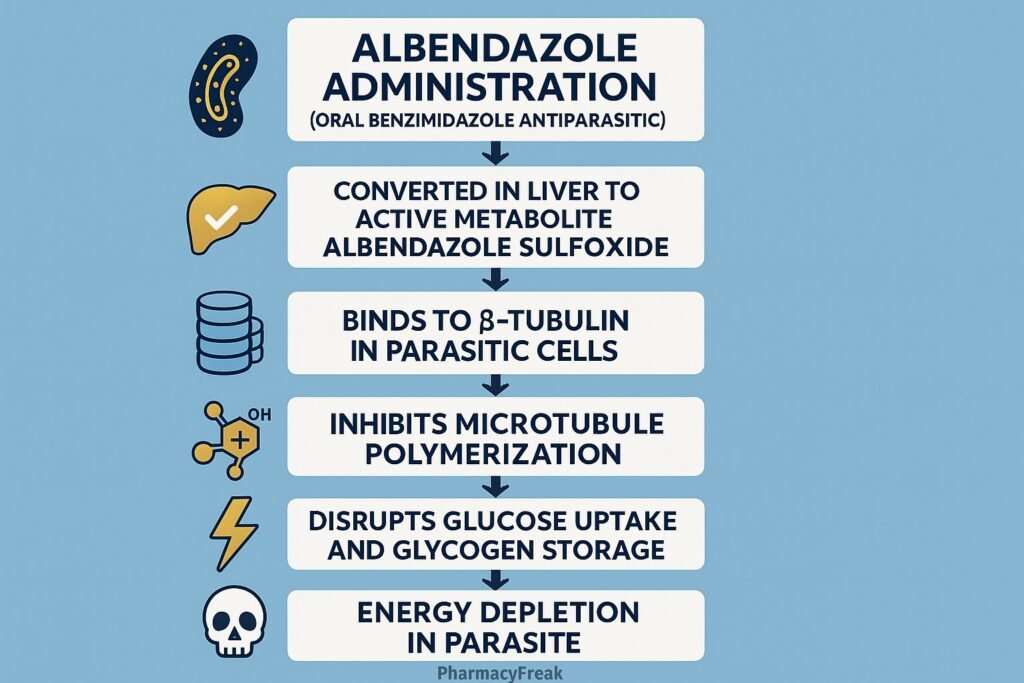
Albendazole is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic drug belonging to the benzimidazole class. Mechanism of Action of Albendazole involves inhibition of microtubule polymerization in parasitic worms, leading to impaired glucose uptake and depletion of energy stores. It is highly effective against a wide range of intestinal and tissue helminth infections such as ascariasis, hookworm, neurocysticercosis, and echinococcosis. Due to its broad efficacy, oral availability, and safety profile, albendazole is one of the most widely used antiparasitic drugs globally.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
- Binding to β-Tubulin
- Albendazole selectively binds to β-tubulin in parasite cells.
- This prevents the polymerization of tubulin into microtubules, which are essential for cell structure and intracellular transport.
- Inhibition of Microtubule Formation
- The disruption of microtubules affects glucose uptake and other essential nutrient transport processes in the parasite.
- Depletion of Glycogen Stores
- The parasite is unable to absorb glucose or convert stored glycogen into energy.
- This leads to energy depletion (ATP reduction) and impaired metabolic function.
- Degeneration of Cellular Structures
- Loss of cytoplasmic microtubules results in disintegration of intestinal cells of the helminth.
- The parasite eventually becomes immobilized and dies due to starvation.
- Overall Effect
- Inhibits microtubule synthesis → Blocks glucose uptake → ATP depletion → Parasite death.
Pharmacokinetics
- Absorption: Poor oral absorption; enhanced when taken with fatty meals.
- Distribution: Widely distributed; penetrates cerebrospinal fluid (useful in neurocysticercosis).
- Metabolism: Rapid hepatic metabolism to albendazole sulfoxide (active metabolite).
- Excretion: Primarily via urine and bile.
- Half-life: 8–12 hours (for albendazole sulfoxide).
Clinical Uses
- Intestinal helminth infections: Ascariasis, Enterobiasis, Trichuriasis, Hookworm, Strongyloidiasis.
- Tissue infections: Neurocysticercosis (Taenia solium larvae), Hydatid disease (Echinococcus granulosus).
- Mixed parasitic infections and mass deworming programs.
- Off-label: Larva migrans, giardiasis, microsporidiosis.
Adverse Effects
- Common: Abdominal pain, nausea, headache, dizziness.
- Less common: Elevated liver enzymes, reversible alopecia, fever.
- Serious: Bone marrow suppression, hepatotoxicity, pancytopenia (rare; usually with prolonged high-dose therapy).
- Contraindications: Pregnancy (especially first trimester), known hypersensitivity, and active liver disease.
Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Albendazole | Mebendazole | Praziquantel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drug class | Benzimidazole derivative | Benzimidazole derivative | Isoquinoline derivative |
| Mechanism | Inhibits microtubule formation | Inhibits microtubule formation | Increases calcium permeability |
| Spectrum of activity | Broad (intestinal & tissue) | Mainly intestinal worms | Trematodes & cestodes |
| Active metabolite | Albendazole sulfoxide | None significant | None |
| CNS penetration | High (useful in cysticercosis) | Low | Moderate |
MCQs
1. Albendazole belongs to which drug class?
a) Imidazothiazole derivative
b) Benzimidazole derivative
c) Isoquinoline derivative
d) Piperazine derivative
Answer: b) Benzimidazole derivative
2. The primary molecular target of albendazole is:
a) α-tubulin
b) β-tubulin
c) Microfilaments
d) Actin polymerase
Answer: b) β-tubulin
3. Albendazole causes death of parasites mainly by:
a) Inhibiting DNA synthesis
b) Blocking neuromuscular transmission
c) Depleting glycogen and ATP stores
d) Blocking calcium channels
Answer: c) Depleting glycogen and ATP stores
4. The active metabolite of albendazole is:
a) Albendazole sulfoxide
b) Albendazole sulfate
c) Albendazole hydroxide
d) Albendazole acetate
Answer: a) Albendazole sulfoxide
5. Albendazole absorption is enhanced when taken with:
a) Water
b) Milk
c) Fatty meals
d) Fruit juice
Answer: c) Fatty meals
6. Which of the following infections is treated with albendazole?
a) Amoebiasis
b) Neurocysticercosis
c) Malaria
d) Giardiasis only
Answer: b) Neurocysticercosis
7. Albendazole inhibits which metabolic process in helminths?
a) Protein synthesis
b) Glucose uptake
c) Lipid oxidation
d) Nucleic acid synthesis
Answer: b) Glucose uptake
8. Albendazole is contraindicated in:
a) Pregnancy
b) Hypertension
c) Diabetes
d) Asthma
Answer: a) Pregnancy
9. Which organ system is most affected by high-dose albendazole toxicity?
a) Liver
b) Kidney
c) Lungs
d) Pancreas
Answer: a) Liver
10. Albendazole is preferred over mebendazole in:
a) Simple enterobiasis
b) Neurocysticercosis and hydatid disease
c) Ascaris lumbricoides infection
d) Trichuriasis
Answer: b) Neurocysticercosis and hydatid disease
FAQs
Q1. How does albendazole kill worms?
It binds to β-tubulin and disrupts microtubule formation, leading to inhibition of glucose uptake and energy depletion in the parasite.
Q2. Is albendazole safe during pregnancy?
No, it should be avoided, especially during the first trimester due to potential teratogenic effects.
Q3. How should albendazole be taken for maximum absorption?
Take with a fatty meal to improve oral bioavailability.
Q4. What is the difference between albendazole and mebendazole?
Albendazole has better tissue penetration and is more effective against systemic infections.
Q5. Can albendazole be used in children?
Yes, it is safe in children above 2 years when used in appropriate doses.
Q6. What is the duration of therapy for neurocysticercosis?
Usually 7–28 days, depending on cyst burden and clinical response.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics
- Katzung’s Basic and Clinical Pharmacology
- WHO Guidelines for the Control of Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com