Table of Contents
Introduction
Triptans are a class of drugs primarily used in the acute treatment of migraine and cluster headaches. They are selective serotonin receptor agonists, specifically targeting the 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D subtypes. By reversing the pathophysiological mechanisms of migraine, triptans help relieve headache, nausea, photophobia, and phonophobia. Common drugs in this class include sumatriptan, rizatriptan, and zolmitriptan.
Mechanism of Action (Step-wise)
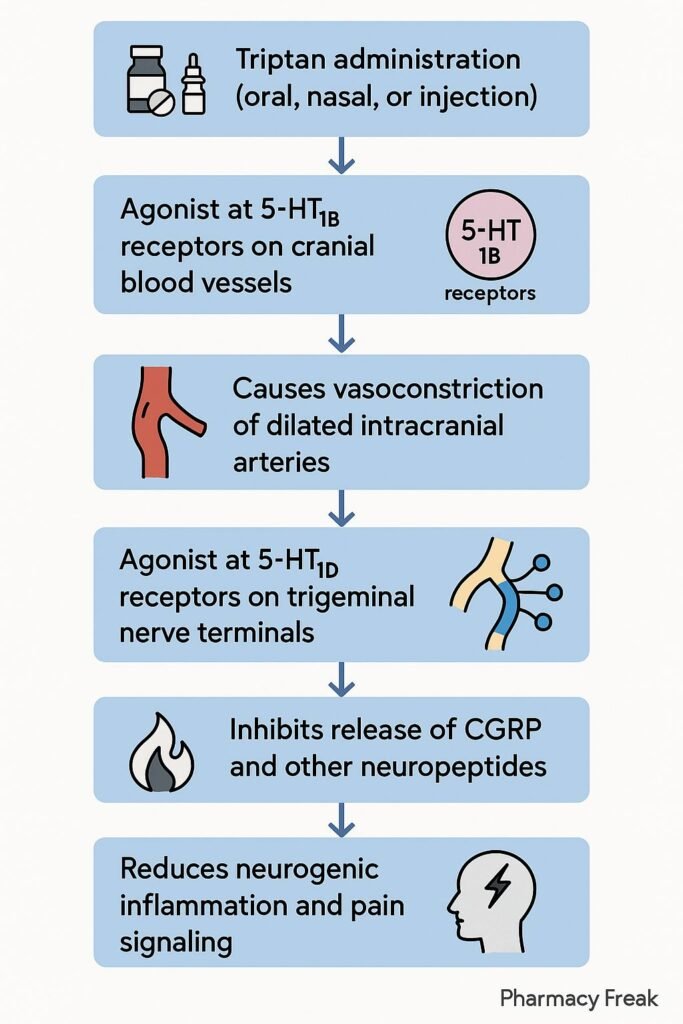
1. Activation of 5-HT1B/1D Receptors
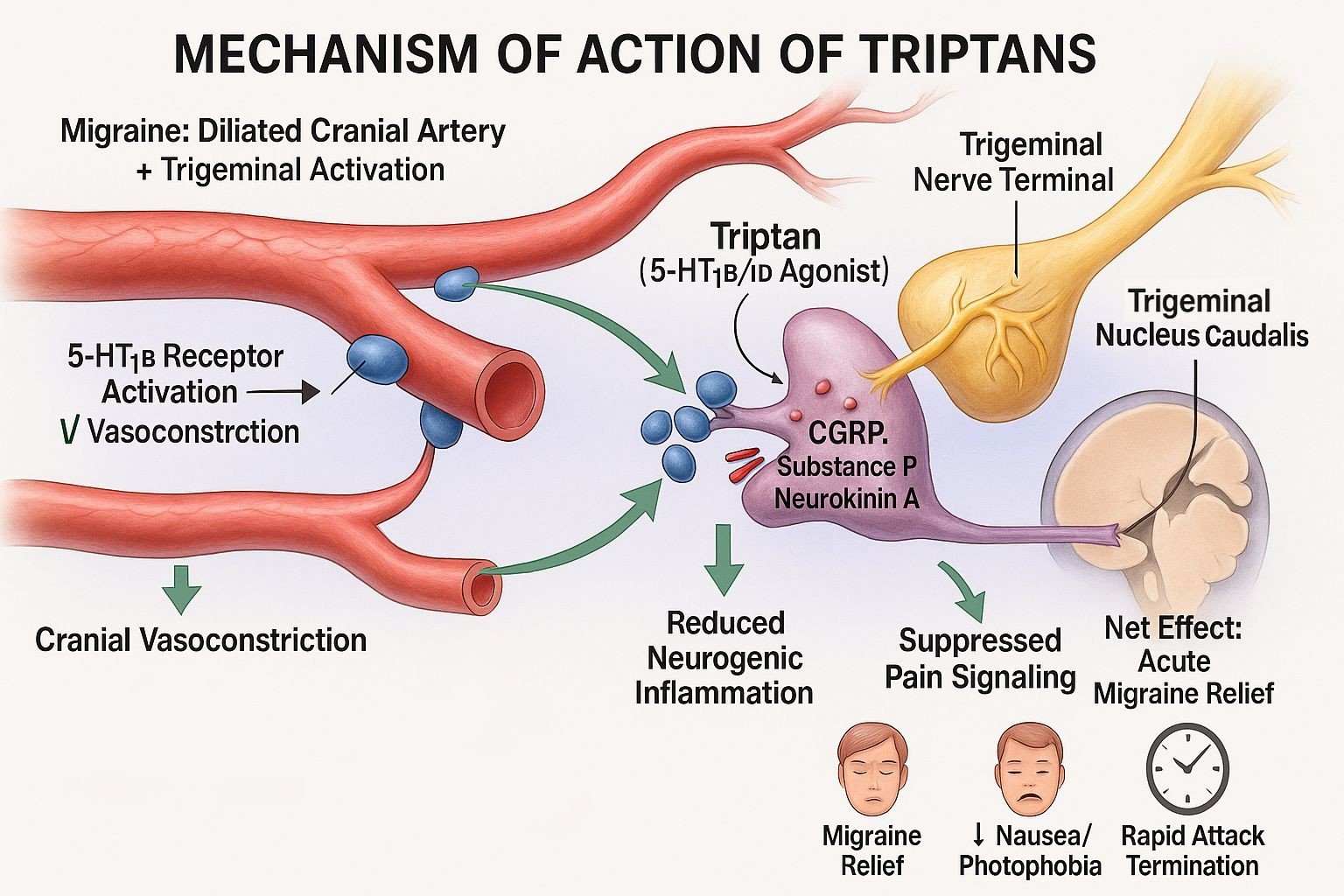
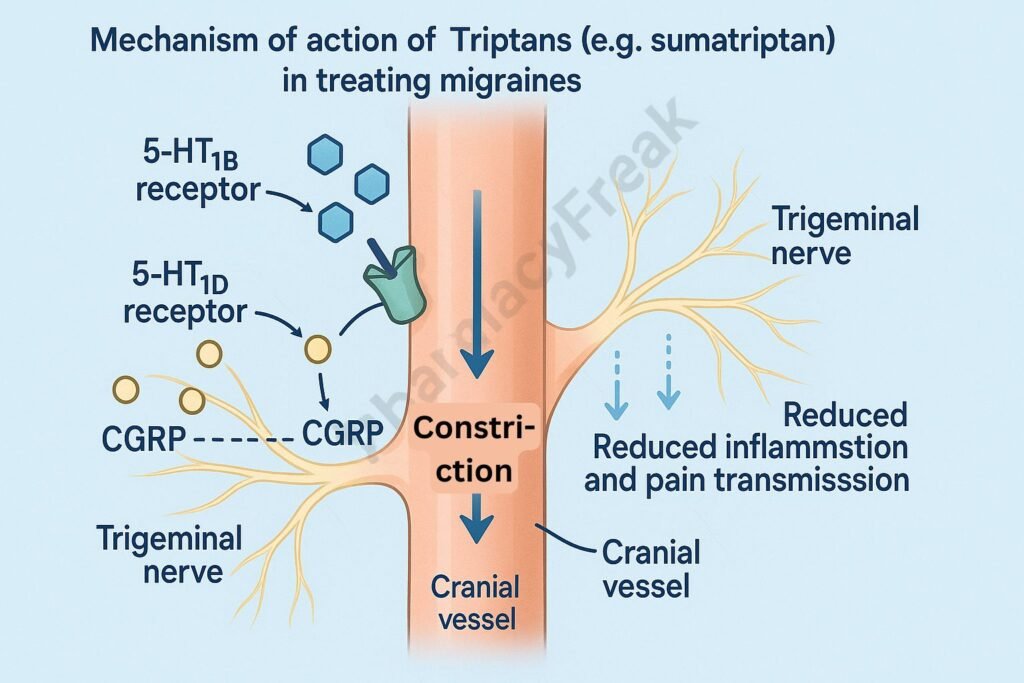
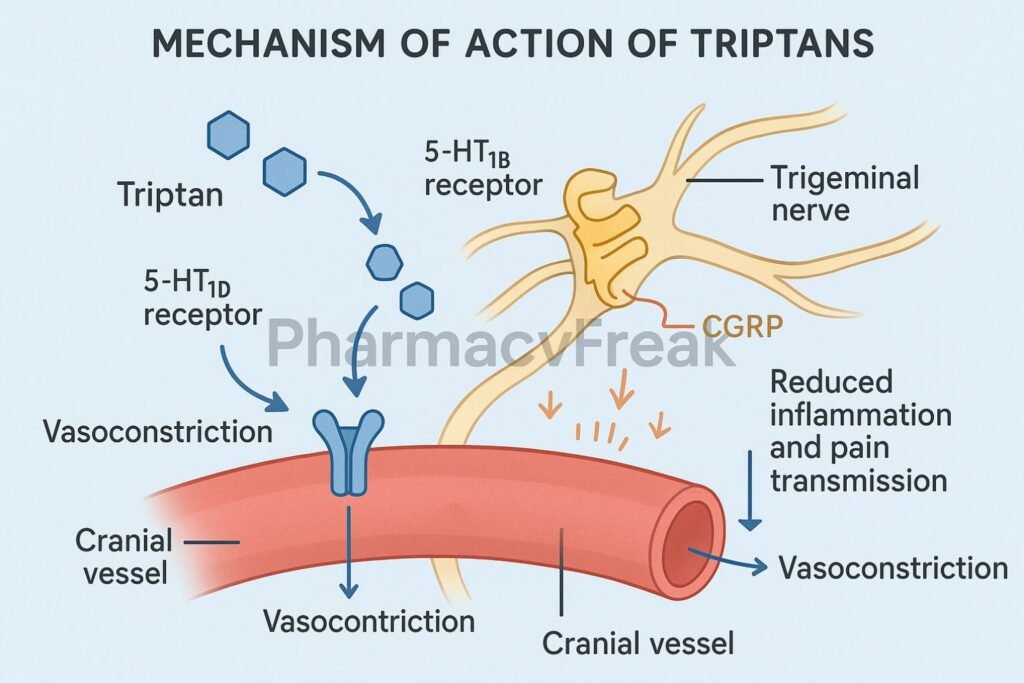
Triptans bind to serotonin (5-HT) 1B and 1D receptors located on cranial blood vessels and trigeminal nerve endings.
2. Cranial Vasoconstriction
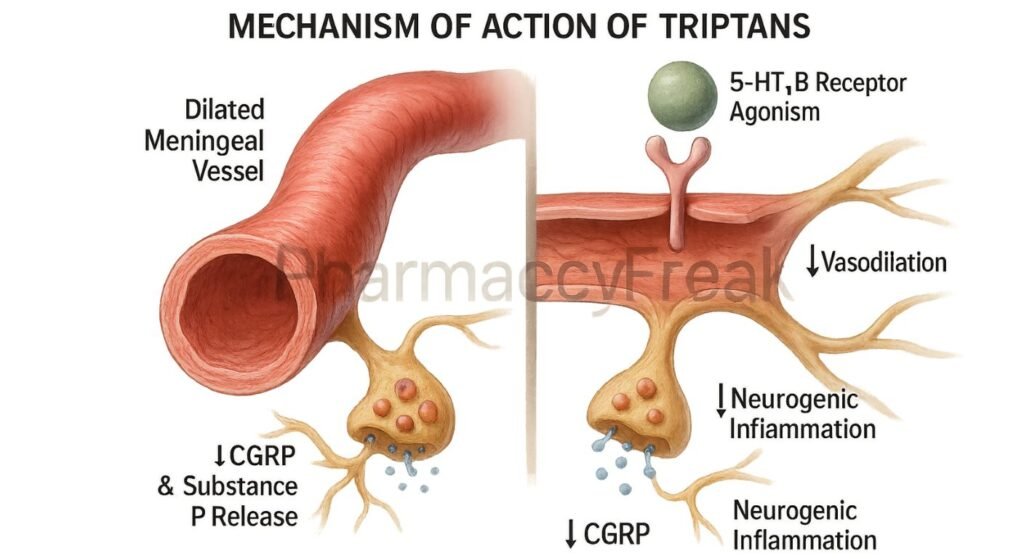
Stimulation of 5-HT1B receptors on vascular smooth muscle induces vasoconstriction of dilated intracranial arteries, reversing one key migraine trigger.
3. Inhibition of Neurotransmitter Release
Activation of 5-HT1D receptors on presynaptic trigeminal nerve terminals inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory neuropeptides such as CGRP, substance P, and neurokinin A.
4. Reduced Neurogenic Inflammation
By blocking neuropeptide release, triptans prevent vasodilation and plasma protein extravasation, which are features of neurogenic inflammation in migraine.
5. Inhibition of Pain Signal Transmission
Triptans reduce nociceptive transmission in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis and other brainstem regions, diminishing central sensitization and pain perception.
Pharmacokinetics
- Route of Administration: Oral, subcutaneous, intranasal
- Onset of Action: 10–30 minutes (SC/IN); 30–60 minutes (oral)
- Half-Life: Varies by agent (Sumatriptan: ~2 hrs; Naratriptan: ~6 hrs)
- Metabolism: Hepatic (MAO-A and CYP enzymes)
- Excretion: Primarily renal, some fecal
Clinical Uses
- Acute migraine attacks (with or without aura)
- Cluster headaches
- Short-term relief from menstrual migraines
- Off-label uses: migraine prophylaxis (in select cases)
Adverse Effects
- Chest tightness or pressure
- Dizziness and fatigue
- Nausea
- Injection site reactions (SC route)
- Serotonin syndrome (when combined with SSRIs/SNRIs)
- Contraindications: Ischemic heart disease, stroke, uncontrolled hypertension, basilar or hemiplegic migraine
Comparative Analysis
| Parameter | Triptans | NSAIDs |
|---|---|---|
| Target Receptor | 5-HT1B/1D agonist | COX-1/2 inhibitors |
| Vasoconstriction | Yes | No |
| Onset of Relief | Fast | Moderate |
| Best For | Moderate-to-severe migraine | Mild-to-moderate migraine |
| Cardiovascular Risk | Higher | Lower |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Triptans relieve migraine by activating which receptor?
a) 5-HT2A
b) 5-HT3
c) 5-HT1B/1D
d) D2
Answer: c) 5-HT1B/1D
2. Which neuropeptide is inhibited by triptans?
a) Endorphin
b) CGRP
c) GABA
d) Glutamate
Answer: b) CGRP
3. A contraindication for triptan use is:
a) Asthma
b) Depression
c) Ischemic heart disease
d) Diabetes
Answer: c) Ischemic heart disease
4. Which route provides fastest relief with triptans?
a) Oral
b) Intranasal
c) Subcutaneous
d) Rectal
Answer: c) Subcutaneous
5. Triptans act on pain pathways via:
a) Inhibiting MAO
b) Blocking calcium channels
c) Inhibiting trigeminal nerve transmission
d) Enhancing GABA
Answer: c) Inhibiting trigeminal nerve transmission
FAQs
Q1. Can triptans be used daily?
No, they are intended for acute treatment and not recommended for daily or frequent use.
Q2. Do triptans prevent migraines?
No, they are not typically used for prophylaxis, but for abortive therapy.
Q3. Can triptans cause dependence?
No physical dependence, but overuse may lead to medication-overuse headaches.
Q4. Are triptans safe in pregnancy?
Generally avoided unless absolutely necessary and under medical supervision.
Q5. What should be avoided when taking triptans?
Avoid SSRIs/SNRIs concurrently due to risk of serotonin syndrome.
References
- Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th Edition
- KD Tripathi, Essentials of Medical Pharmacology, 7th Edition
- Clinical Neurology and Headache Management Guidelines
- Triptan Prescribing Information
Related Internal Links

I am pursuing MBA in pharmaceutical management from NIPER Hyderabad with a strong academic record and proven success in national-level pharmacy entrance exams. I secured AIR 61 in NIPER 2024 (MS/M.Pharm) and AIR 27 in NIPER MBA, along with AIR 147 in GPAT 2024 and AIR 907 in GPAT 2023. I also achieved AIR 6 in AIIMS CRE-2025 for Drug Store Keeper and was selected as a Pharmacist (AIR 61) for ESIC. Additionally, I was the Runner-Up in Round 2 of the EY Case Study Competition.
At PharmacyFreak.com, I aim to guide future pharmacists through expert content, exam strategies, and insightful resources based on real experience and academic excellence.
Mail- harsh@pharmacyfreak.com