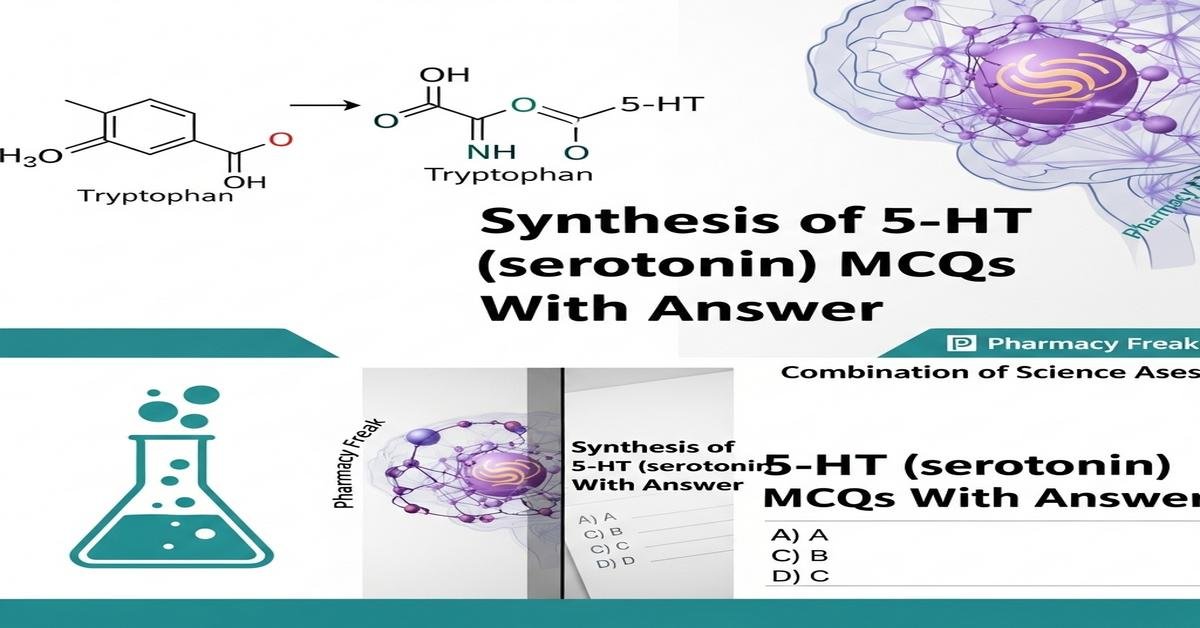
Synthesis of 5-HT (serotonin) MCQs With Answer
The synthesis of serotonin (5-HT) is a core topic for B. Pharm students, linking biochemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutics. This introduction covers the serotonin biosynthetic pathway from tryptophan, key enzymes such as tryptophan hydroxylase and aromatic L‑amino acid decarboxylase, essential cofactors (BH4, PLP), cellular sites of production, vesicular storage, reuptake, and metabolic breakdown by MAO-A to 5‑HIAA. Understanding these steps clarifies drug actions (SSRIs, MAO inhibitors), disease links (depression, carcinoid), and laboratory measurements. The following MCQs probe mechanism, regulation, clinical implications, and drug interactions to solidify your mastery. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which amino acid is the primary precursor for serotonin (5-HT) biosynthesis?
- Tryptophan
- Tyrosine
- Histidine
- Phenylalanine
Correct Answer: Tryptophan
Q2. What is the rate‑limiting enzyme in the serotonin synthesis pathway?
- Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH)
- Aromatic L‑amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)
- Monoamine oxidase (MAO)
- Vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT)
Correct Answer: Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH)
Q3. Tryptophan is converted to 5‑hydroxytryptophan (5‑HTP) by which reaction type?
- Hydroxylation
- Decarboxylation
- Methylation
- Oxidative deamination
Correct Answer: Hydroxylation
Q4. Which cofactor is required by tryptophan hydroxylase for activity?
- Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)
- Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
- Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
- Biotin
Correct Answer: Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)
Q5. The enzyme that decarboxylates 5‑HTP to serotonin is:
- Aromatic L‑amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)
- Monoamine oxidase A (MAO‑A)
- Phenylalanine hydroxylase
- Catechol‑O‑methyltransferase (COMT)
Correct Answer: Aromatic L‑amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)
Q6. Which cofactor is essential for AADC catalytic activity?
- Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
- Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)
- NADPH
- S‑adenosylmethionine (SAM)
Correct Answer: Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
Q7. Which enzyme isoform is predominantly expressed in the CNS for serotonin synthesis?
- TPH2
- TPH1
- TPH3
- TPH4
Correct Answer: TPH2
Q8. Most peripheral serotonin is synthesized in which cell type?
- Enterochromaffin cells of the gut
- Platelets
- Hepatocytes
- Adrenal medullary cells
Correct Answer: Enterochromaffin cells of the gut
Q9. Serotonin is stored in synaptic vesicles via which transporter?
- Vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT)
- SERT (serotonin transporter)
- DAT (dopamine transporter)
- NET (norepinephrine transporter)
Correct Answer: Vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT)
Q10. The primary mechanism for clearing serotonin from the synaptic cleft is:
- Reuptake by SERT (serotonin transporter)
- Metabolism by COMT
- Diffusion into cerebrospinal fluid
- Endocytosis by postsynaptic receptors
Correct Answer: Reuptake by SERT (serotonin transporter)
Q11. The major metabolic product of serotonin metabolism measured clinically is:
- 5‑Hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5‑HIAA)
- Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA)
- Homovanillic acid (HVA)
- 3‑Methoxytyramine (3‑MT)
Correct Answer: 5‑Hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5‑HIAA)
Q12. Which enzyme primarily oxidatively deaminates serotonin to 5‑HIAA?
- Monoamine oxidase A (MAO‑A)
- Monoamine oxidase B (MAO‑B)
- Monoamine oxidase C
- Catechol‑O‑methyltransferase (COMT)
Correct Answer: Monoamine oxidase A (MAO‑A)
Q13. Inhibition of which enzyme would directly reduce central serotonin synthesis?
- Tryptophan hydroxylase
- Monoamine oxidase A
- Acetylcholinesterase
- Catechol‑O‑methyltransferase (COMT)
Correct Answer: Tryptophan hydroxylase
Q14. The transporter responsible for serotonin uptake into platelets is:
- SERT (serotonin transporter)
- VMAT2
- P‑glycoprotein
- GLUT1
Correct Answer: SERT (serotonin transporter)
Q15. Which drug class increases synaptic serotonin by blocking its reuptake?
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) only acting on norepinephrine
- Benzodiazepines
Correct Answer: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Q16. p‑Chlorophenylalanine (PCPA) inhibits serotonin synthesis by targeting:
- Tryptophan hydroxylase
- Aromatic L‑amino acid decarboxylase
- Monoamine oxidase
- Vesicular monoamine transporter
Correct Answer: Tryptophan hydroxylase
Q17. The conversion of tryptophan to serotonin in the CNS mainly occurs in neurons located in:
- Raphe nuclei of the brainstem
- Substantia nigra
- Hippocampus only
- Locus coeruleus
Correct Answer: Raphe nuclei of the brainstem
Q18. Which vitamin deficiency can impair AADC activity leading to reduced serotonin?
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin D
Correct Answer: Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
Q19. Which molecule is required for BH4 regeneration critical to TPH activity?
- Dihydropteridine reductase (enzyme uses NADPH)
- Glutathione peroxidase
- Monoamine oxidase B
- Catechol‑O‑methyltransferase
Correct Answer: Dihydropteridine reductase (enzyme uses NADPH)
Q20. Which statement about peripheral serotonin is true?
- About 90% of total body serotonin is synthesized in the gut
- Peripheral serotonin is synthesized mainly in the brain
- Serotonin cannot be released from enterochromaffin cells
- Platelets synthesize serotonin de novo
Correct Answer: About 90% of total body serotonin is synthesized in the gut
Q21. Which receptor family are G‑protein coupled receptors except one ion channel subtype?
- 5‑HT receptors (mostly GPCRs; 5‑HT3 is ion channel)
- GABA receptors only
- NMDA receptors only
- Beta‑adrenergic receptors only
Correct Answer: 5‑HT receptors (mostly GPCRs; 5‑HT3 is ion channel)
Q22. Which 5‑HT receptor subtype is a ligand‑gated ion channel implicated in emesis?
- 5‑HT3
- 5‑HT1A
- 5‑HT2A
- 5‑HT4
Correct Answer: 5‑HT3
Q23. Excess systemic serotonin secretion from a tumor causes which syndrome?
- Carcinoid syndrome
- Sjorgren’s syndrome
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Conn’s syndrome
Correct Answer: Carcinoid syndrome
Q24. A major clinical test for carcinoid syndrome measures urinary levels of:
- 5‑HIAA
- HVA
- VMA
- Metanephrine
Correct Answer: 5‑HIAA
Q25. Co‑administration of MAO inhibitors with SSRIs can cause:
- Serotonin syndrome
- Parkinsonism
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypoglycemia
Correct Answer: Serotonin syndrome
Q26. Which enzyme’s activity determines the availability of BH4 for TPH function?
- GTP cyclohydrolase I (GTPCH)
- Methylmalonyl‑CoA mutase
- Tyrosine hydroxylase
- Acetyltransferase
Correct Answer: GTP cyclohydrolase I (GTPCH)
Q27. The pH compartmentalization that favors serotonin protonation and vesicular uptake is due to:
- Proton gradient created by vesicular H+ ATPase
- Mitochondrial membrane potential
- Cytosolic alkaline pH only
- Passive diffusion across membranes
Correct Answer: Proton gradient created by vesicular H+ ATPase
Q28. Which transporter moves serotonin from cytosol into synaptic vesicles?
- VMAT2
- SERT
- NET
- EAAT
Correct Answer: VMAT2
Q29. The biochemical conversion 5‑HT → 5‑HIAA primarily yields which type of functional group change?
- Oxidative deamination to an aldehyde then oxidation to carboxylic acid
- Methylation of indole ring
- Decarboxylation
- Sulfation exclusively
Correct Answer: Oxidative deamination to an aldehyde then oxidation to carboxylic acid
Q30. Which drug selectively blocks SERT and is used as an antidepressant?
- Fluoxetine
- Imipramine
- Phenelzine
- Haloperidol
Correct Answer: Fluoxetine
Q31. TPH requires molecular oxygen (O2) for which reason?
- It catalyzes an aromatic hydroxylation using O2
- It performs decarboxylation requiring O2
- It reduces oxygen to water as main product
- It uses O2 to regenerate PLP
Correct Answer: It catalyzes an aromatic hydroxylation using O2
Q32. Which laboratory finding suggests reduced central serotonin turnover?
- Low CSF 5‑HIAA levels
- High urinary VMA
- Elevated plasma dopamine
- High CSF HVA only
Correct Answer: Low CSF 5‑HIAA levels
Q33. Which genetic variation could directly affect serotonin synthesis enzyme activity?
- Mutations in TPH2 gene
- Polymorphism in glucokinase
- Deletion of COMT gene only affecting catechols
- Mutation in hemoglobin beta chain
Correct Answer: Mutations in TPH2 gene
Q34. Dietary tryptophan uptake into the brain competes with other large neutral amino acids via:
- L‑type amino acid transporter (LAT1)
- Glucose transporter GLUT4
- Sodium‑dependent bile acid transporter
- Organic anion transporter
Correct Answer: L‑type amino acid transporter (LAT1)
Q35. Which factor increases CNS serotonin synthesis by increasing precursor availability?
- High carbohydrate meal increasing plasma tryptophan ratio
- High fat meal decreasing tryptophan
- Acute physical trauma only
- Cold exposure exclusively
Correct Answer: High carbohydrate meal increasing plasma tryptophan ratio
Q36. Which pharmacological agent is used to deplete serotonin experimentally by inhibiting AADC?
- Benserazide or carbidopa (AADC inhibitors)
- Fluoxetine
- Selegiline
- Ondansetron
Correct Answer: Benserazide or carbidopa (AADC inhibitors)
Q37. The clinical effect of SSRIs is primarily due to:
- Increased synaptic serotonin leading to downstream adaptive receptor changes
- Direct stimulation of serotonin synthesis by TPH
- Inhibition of vesicular storage causing release
- Inhibition of serotonin metabolism by COMT
Correct Answer: Increased synaptic serotonin leading to downstream adaptive receptor changes
Q38. Which serotonin receptor subtype is strongly implicated in platelet aggregation?
- 5‑HT2A
- 5‑HT1B
- 5‑HT3
- 5‑HT4
Correct Answer: 5‑HT2A
Q39. Which statement about serotonin transporters is correct?
- SERT is sodium‑dependent and member of the SLC6 family
- SERT is ATP‑dependent and an ABC transporter
- SERT functions as a vesicular transporter like VMAT
- SERT exclusively transports serotonin out of the brain
Correct Answer: SERT is sodium‑dependent and member of the SLC6 family
Q40. Which process diverts tryptophan away from serotonin synthesis toward kynurenine pathway?
- Indoleamine 2,3‑dioxygenase (IDO) activation by inflammation
- Inhibition of MAO by drugs
- Activation of VMAT2
- Increased dietary vitamin B6
Correct Answer: Indoleamine 2,3‑dioxygenase (IDO) activation by inflammation
Q41. Which CNS disorder has been most directly linked to altered serotonergic neurotransmission?
- Major depressive disorder
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Osteoarthritis
- Myasthenia gravis
Correct Answer: Major depressive disorder
Q42. Which analytical measurement helps estimate whole body serotonin production clinically?
- 24‑hour urinary 5‑HIAA
- Plasma insulin level
- Serum albumin
- Urinary glucose
Correct Answer: 24‑hour urinary 5‑HIAA
Q43. Inhibition of dihydropteridine reductase would primarily impair which step?
- Regeneration of BH4 and thus TPH activity
- Conversion of 5‑HTP to 5‑HT directly
- Reuptake of serotonin by SERT
- Metabolism of serotonin to 5‑HIAA
Correct Answer: Regeneration of BH4 and thus TPH activity
Q44. Which drug is a 5‑HT3 antagonist used to prevent chemotherapy‑induced nausea?
- Ondansetron
- Fluoxetine
- Sumatriptan
- Buspirone
Correct Answer: Ondansetron
Q45. Sumatriptan relieves migraine by acting as an agonist at which receptors?
- 5‑HT1B/1D receptors
- 5‑HT3 receptors
- 5‑HT2C receptors
- 5‑HT4 receptors
Correct Answer: 5‑HT1B/1D receptors
Q46. Which process occurs after serotonin is released into the synaptic cleft?
- Binding to postsynaptic receptors and reuptake by presynaptic SERT
- Immediate conversion to dopamine
- Direct excretion into urine unchanged
- Binding only to peripheral receptors without reuptake
Correct Answer: Binding to postsynaptic receptors and reuptake by presynaptic SERT
Q47. Elevated serotonin in the gut primarily affects which physiological function?
- Gastrointestinal motility and secretion
- Renal filtration rate
- Bone resorption only
- Adipose lipolysis exclusively
Correct Answer: Gastrointestinal motility and secretion
Q48. Which enzyme inhibition would increase serotonin levels by decreasing degradation?
- MAO‑A inhibition
- AADC inhibition
- TPH inhibition
- GTPCH inhibition
Correct Answer: MAO‑A inhibition
Q49. Which statement best describes serotonin synthesis localization in platelets?
- Platelets uptake serotonin from plasma; they do not synthesize it de novo
- Platelets synthesize serotonin via TPH2 within platelet cytosol
- Platelets convert dopamine into serotonin directly
- Platelets store only metabolite 5‑HIAA
Correct Answer: Platelets uptake serotonin from plasma; they do not synthesize it de novo
Q50. Which therapeutic strategy could increase CNS serotonin synthesis clinically?
- Supplement dietary tryptophan or 5‑HTP precursors under supervision
- Administer MAO inhibitors that block TPH
- Give VMAT blockers to prevent vesicular uptake
- Provide high doses of vitamin C only
Correct Answer: Supplement dietary tryptophan or 5‑HTP precursors under supervision

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com