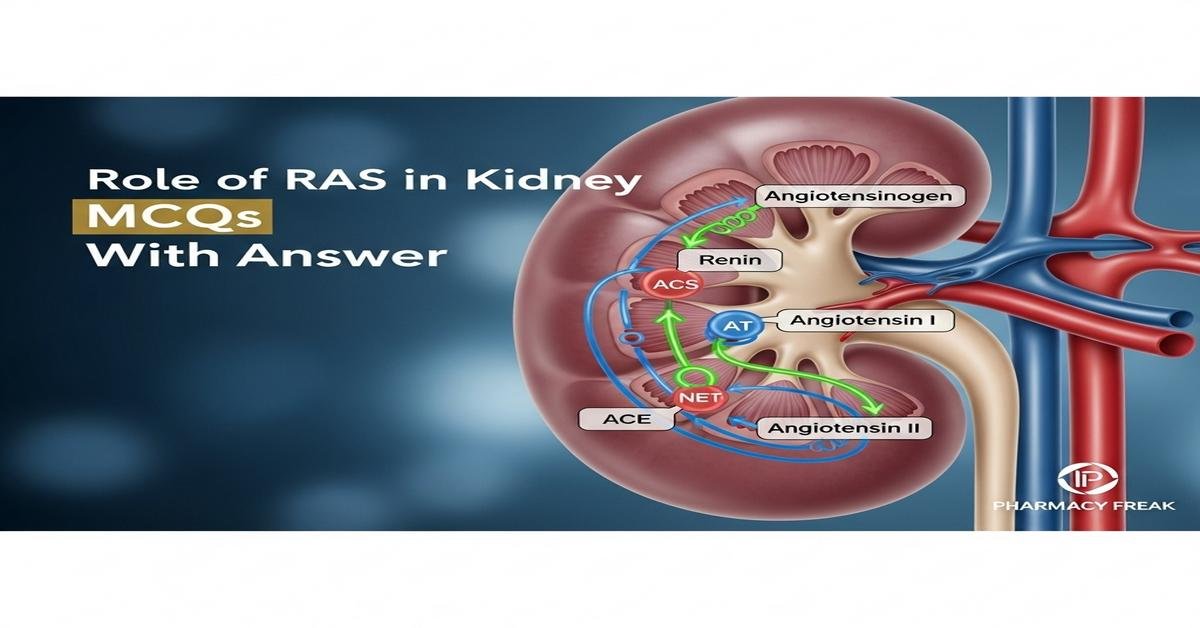
Role of RAS in kidney MCQs With Answer is an essential study area for B. Pharm students focusing on renal physiology and pharmacology. This introduction covers the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), its components—renin, angiotensinogen, ACE, angiotensin II, aldosterone—and their roles in kidney function, blood pressure regulation, sodium balance, and pathologies such as hypertensive and diabetic nephropathy. Understanding pharmacological modulation with ACE inhibitors, ARBs, direct renin inhibitors, and mineralocorticoid antagonists is crucial for therapeutics and adverse-effect management. Keywords: renin-angiotensin system, kidney, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, angiotensin II, aldosterone, renal hemodynamics, B. Pharm. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which enzyme converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II in the lungs and endothelial cells?
- Renin
- Angiotensinogen
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
- Aldosterone synthase
Correct Answer: Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
Q2. What is the primary trigger for renin release from juxtaglomerular cells?
- Increased renal perfusion pressure
- Decreased renal perfusion pressure
- High sodium delivery to macula densa
- Increased atrial natriuretic peptide
Correct Answer: Decreased renal perfusion pressure
Q3. Angiotensin II exerts most of its classic renal effects via which receptor?
- AT1 receptor
- AT2 receptor
- Mas receptor
- Mineralocorticoid receptor
Correct Answer: AT1 receptor
Q4. Which of the following is a direct renin inhibitor used in clinical practice?
- Enalapril
- Losartan
- Aliskiren
- Spironolactone
Correct Answer: Aliskiren
Q5. Activation of RAS causes which change in glomerular dynamics?
- Dilation of efferent arteriole
- Constriction of efferent arteriole
- Dilation of afferent arteriole
- Decrease in filtration fraction
Correct Answer: Constriction of efferent arteriole
Q6. Which drug class blocks the action of angiotensin II at AT1 receptors?
- ACE inhibitors
- Beta blockers
- Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Diuretics
Correct Answer: Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
Q7. ACE inhibitors increase bradykinin levels because ACE also degrades which peptide?
- Vasopressin
- Bradykinin
- Endothelin
- Renin
Correct Answer: Bradykinin
Q8. Which RAS component promotes aldosterone secretion from the adrenal cortex?
- Renin
- Angiotensin II
- Angiotensin I
- ACE2
Correct Answer: Angiotensin II
Q9. Aldosterone primarily increases sodium reabsorption in which nephron segment?
- Proximal tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
- Glomerulus
Correct Answer: Distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
Q10. A common adverse effect of ACE inhibitors due to increased bradykinin is:
- Hypokalemia
- Dry persistent cough
- Hypernatremia
- Gout flare
Correct Answer: Dry persistent cough
Q11. In diabetic nephropathy, RAS blockade helps primarily by:
- Increasing glomerular capillary pressure
- Reducing intraglomerular pressure and proteinuria
- Enhancing sodium retention
- Stimulating renin release
Correct Answer: Reducing intraglomerular pressure and proteinuria
Q12. Which lab parameter is most closely monitored when starting ACE inhibitors or ARBs?
- Serum calcium
- Serum potassium
- Serum amylase
- Blood glucose
Correct Answer: Serum potassium
Q13. Which physiological mechanism directly senses sodium chloride delivery to regulate renin?
- Baroreceptors in carotid sinus
- Macula densa of the distal tubule
- Atrial stretch receptors
- Glomerular mesangial cells
Correct Answer: Macula densa of the distal tubule
Q14. Which effect of angiotensin II increases systemic blood pressure?
- Systemic vasodilation
- Vasoconstriction of arterioles
- Decrease in cardiac contractility
- Increase in nitric oxide production
Correct Answer: Vasoconstriction of arterioles
Q15. ACE2 exerts counter-regulatory effects by converting angiotensin II into:
- Angiotensin III
- Angiotensin IV
- Angiotensin-(1-7)
- Renin
Correct Answer: Angiotensin-(1-7)
Q16. Which antihypertensive combination is contraindicated due to increased risk of hyperkalemia and renal impairment?
- ACE inhibitor with ARB
- ACE inhibitor with thiazide diuretic
- ARB with calcium channel blocker
- ACE inhibitor with beta blocker
Correct Answer: ACE inhibitor with ARB
Q17. Direct stimulation of mineralocorticoid receptors by aldosterone increases:
- Potassium excretion and sodium reabsorption
- Calcium excretion
- Glucose uptake
- Renin release
Correct Answer: Potassium excretion and sodium reabsorption
Q18. Which drug is a selective aldosterone receptor antagonist used to treat resistant hypertension and heart failure?
- Spironolactone
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Lisinopril
- Metoprolol
Correct Answer: Spironolactone
Q19. RAS activity in the kidney contributes to sodium reabsorption primarily by modulating which transporter?
- Na+/K+ ATPase and ENaC channels
- Glucose transporter GLUT2
- H+/K+ ATPase
- Cl-/HCO3- exchanger
Correct Answer: Na+/K+ ATPase and ENaC channels
Q20. Which patient population should NOT receive ACE inhibitors due to teratogenic risk?
- Pregnant women
- Children under 2 years
- Elderly males
- Patients with gout
Correct Answer: Pregnant women
Q21. Renin is an enzyme secreted as prorenin. Which organ synthesizes the precursor angiotensinogen?
- Kidney
- Liver
- Adrenal gland
- Pancreas
Correct Answer: Liver
Q22. Which test measures renin activity and is useful in evaluating primary aldosteronism?
- Plasma renin activity (PRA)
- Serum ACE level
- Urinary sodium excretion
- Serum creatinine
Correct Answer: Plasma renin activity (PRA)
Q23. An increase in efferent arteriolar resistance by angiotensin II causes which effect on GFR?
- Decrease GFR
- No change in GFR
- Increase GFR
- Complete loss of filtration
Correct Answer: Increase GFR
Q24. Which pharmacological effect explains why ACE inhibitors can cause hyperkalemia?
- They increase aldosterone secretion
- They reduce angiotensin II–stimulated aldosterone release
- They directly block potassium channels in kidney
- They increase dietary potassium absorption
Correct Answer: They reduce angiotensin II–stimulated aldosterone release
Q25. Tissue or local RAS in kidneys can act independently and involves which additional receptor implicated in fibrosis?
- Prorenin receptor (PRR)
- Beta-2 adrenergic receptor
- Vasopressin V2 receptor
- Dopamine D1 receptor
Correct Answer: Prorenin receptor (PRR)
Q26. Which of the following ACE inhibitors is a prodrug requiring hepatic activation?
- Lisinopril
- Captopril
- Enalapril
- Aliskiren
Correct Answer: Enalapril
Q27. Which antihypertensive is preferred in a patient with bilateral renal artery stenosis?
- ACE inhibitor immediately
- ARB immediately
- Caution with ACE inhibitors/ARBs due to risk of renal failure
- Start spironolactone without monitoring
Correct Answer: Caution with ACE inhibitors/ARBs due to risk of renal failure
Q28. Angiotensin II increases proximal tubular sodium reabsorption through stimulation of:
- Sodium–glucose cotransporter exclusively
- Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE3) activity
- Aquaporin channels directly
- Renal prostaglandin synthesis only
Correct Answer: Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE3) activity
Q29. Which ARB is commonly used as first-line therapy and is a prototype drug in this class?
- Valsartan
- Losartan
- Telmisartan
- Candesartan
Correct Answer: Losartan
Q30. Combination of neprilysin inhibitor with ARB (e.g., sacubitril/valsartan) augments natriuretic peptides but requires caution because:
- It causes severe hypokalemia routinely
- It may increase risk of angioedema and hypotension
- It eliminates aldosterone entirely
- It blocks renin release permanently
Correct Answer: It may increase risk of angioedema and hypotension
Q31. Which of the following is a correct mechanism by which NSAIDs can reduce the efficacy of RAS blockers?
- NSAIDs increase renin synthesis
- NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin-dependent renin release and renal perfusion, altering RAS effects
- NSAIDs enhance ACE activity directly
- NSAIDs increase angiotensin II receptor density
Correct Answer: NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin-dependent renin release and renal perfusion, altering RAS effects
Q32. In heart failure, RAS activation contributes to worsening by:
- Reducing systemic vascular resistance
- Promoting vasoconstriction, sodium retention, and remodeling
- Decreasing preload exclusively
- Increasing cardiac contractility beneficially
Correct Answer: Promoting vasoconstriction, sodium retention, and remodeling
Q33. ACE inhibitors are contraindicated in pregnancy because they can cause:
- Fetal renal dysgenesis and oligohydramnios
- Neonatal hypoglycemia
- Maternal hypernatremia only
- Teratogenic limb defects like thalidomide
Correct Answer: Fetal renal dysgenesis and oligohydramnios
Q34. Which monitoring parameter indicates worsening renal function after initiating RAS blockade?
- Decrease in serum potassium
- Rise in serum creatinine and fall in eGFR
- Drop in hematocrit
- Decrease in urinary protein excretion immediately
Correct Answer: Rise in serum creatinine and fall in eGFR
Q35. Angiotensin II’s effect on mesangial cells leads to:
- Mesangial relaxation and increased GFR
- Mesangial contraction reducing surface area for filtration
- Direct inhibition of renin production
- Activation of vitamin D synthesis
Correct Answer: Mesangial contraction reducing surface area for filtration
Q36. Which genetic polymorphism can affect ACE inhibitor response and ACE activity?
- ACE gene insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism
- BRCA1 mutation
- HLA-B27 allele
- CYP2D6 poor metabolizer status
Correct Answer: ACE gene insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism
Q37. Which statement about AT2 receptors is correct?
- AT2 receptors mediate most vasoconstrictor effects of angiotensin II
- AT2 receptors often mediate vasodilation, antiproliferative effects, and counterbalance AT1
- They are the primary mediators of aldosterone secretion
- They are blocked by spironolactone
Correct Answer: AT2 receptors often mediate vasodilation, antiproliferative effects, and counterbalance AT1
Q38. Which pharmacokinetic property of lisinopril differentiates it from many other ACE inhibitors?
- Requires hepatic activation
- Excreted unchanged by the kidney and not a prodrug
- Highly protein bound with biliary excretion
- Short half-life requiring multiple daily dosing
Correct Answer: Excreted unchanged by the kidney and not a prodrug
Q39. What is the mechanism of action of spironolactone in attenuating RAS effects?
- It blocks ACE
- It antagonizes mineralocorticoid receptors, reducing aldosterone effects
- It inhibits renin synthesis directly
- It blocks AT1 receptors
Correct Answer: It antagonizes mineralocorticoid receptors, reducing aldosterone effects
Q40. In acute renal hypoperfusion, initial RAS activation helps maintain GFR but chronic activation leads to:
- Renal protection with no adverse effects
- Progressive glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis
- Immediate resolution of hypertension
- Decreased sodium reabsorption long-term
Correct Answer: Progressive glomerulosclerosis and fibrosis
Q41. Which of the following is true about angiotensin III?
- It is inactive metabolite without biological effects
- It has some aldosterone-stimulating activity similar to angiotensin II
- It is the main substrate for renin
- It directly inhibits ACE
Correct Answer: It has some aldosterone-stimulating activity similar to angiotensin II
Q42. Which imaging or diagnostic clue might suggest renovascular hypertension due to RAS activation?
- Young patient with low renin levels
- Sudden onset severe hypertension with unilateral small kidney or asymmetric renal size
- Chronic hypotension with hyperkalemia only
- Normal renal arteries on Doppler ultrasound always
Correct Answer: Sudden onset severe hypertension with unilateral small kidney or asymmetric renal size
Q43. Which adverse effect is more associated with ARBs compared to ACE inhibitors?
- Higher incidence of cough
- More angioedema than ACE inhibitors
- Generally less cough but similar hyperkalemia risk
- Marked hypokalemia risk only
Correct Answer: Generally less cough but similar hyperkalemia risk
Q44. RAS blockade reduces progression of chronic kidney disease mainly by:
- Raising systemic blood pressure
- Lowering intraglomerular pressure and reducing proteinuria
- Increasing aldosterone levels
- Enhancing sodium retention long-term
Correct Answer: Lowering intraglomerular pressure and reducing proteinuria
Q45. Which of the following best describes the role of prorenin in kidney pathology?
- Prorenin is inactive and irrelevant to disease
- Prorenin binding to PRR may activate profibrotic signaling independent of angiotensin II
- Prorenin directly degrades aldosterone
- Prorenin only functions in the liver
Correct Answer: Prorenin binding to PRR may activate profibrotic signaling independent of angiotensin II
Q46. Inhibiting ACE increases levels of which peptide that can contribute to angioedema?
- Angiotensin II
- Bradykinin
- Aldosterone
- Renin
Correct Answer: Bradykinin
Q47. Which statement about angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) is correct?
- They combine neprilysin inhibition with ACE inhibition
- They combine neprilysin inhibition with ARB to enhance natriuretic peptides and block angiotensin II effects
- They are monotherapy renin inhibitors
- They only block aldosterone receptors
Correct Answer: They combine neprilysin inhibition with ARB to enhance natriuretic peptides and block angiotensin II effects
Q48. Which mechanism explains why RAS inhibitors can worsen renal function in hypovolemic patients?
- They increase efferent arteriolar constriction causing filtration loss
- They prevent angiotensin II–mediated efferent arteriolar constriction, reducing GFR when renal perfusion is low
- They directly damage glomerular basement membrane
- They stimulate excessive aldosterone in hypovolemia
Correct Answer: They prevent angiotensin II–mediated efferent arteriolar constriction, reducing GFR when renal perfusion is low
Q49. Which electrolyte disturbance is most commonly associated with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists like spironolactone?
- Hypokalemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hyponatremia only
Correct Answer: Hyperkalemia
Q50. For B. Pharm students, understanding RAS pharmacology is crucial because it directly informs:
- Only basic chemistry concepts
- Clinical decision-making, drug selection, dosing, interactions and adverse-effect management in renal and cardiovascular disease
- Techniques for aseptic compounding only
- None of the therapeutic considerations
Correct Answer: Clinical decision-making, drug selection, dosing, interactions and adverse-effect management in renal and cardiovascular disease

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com