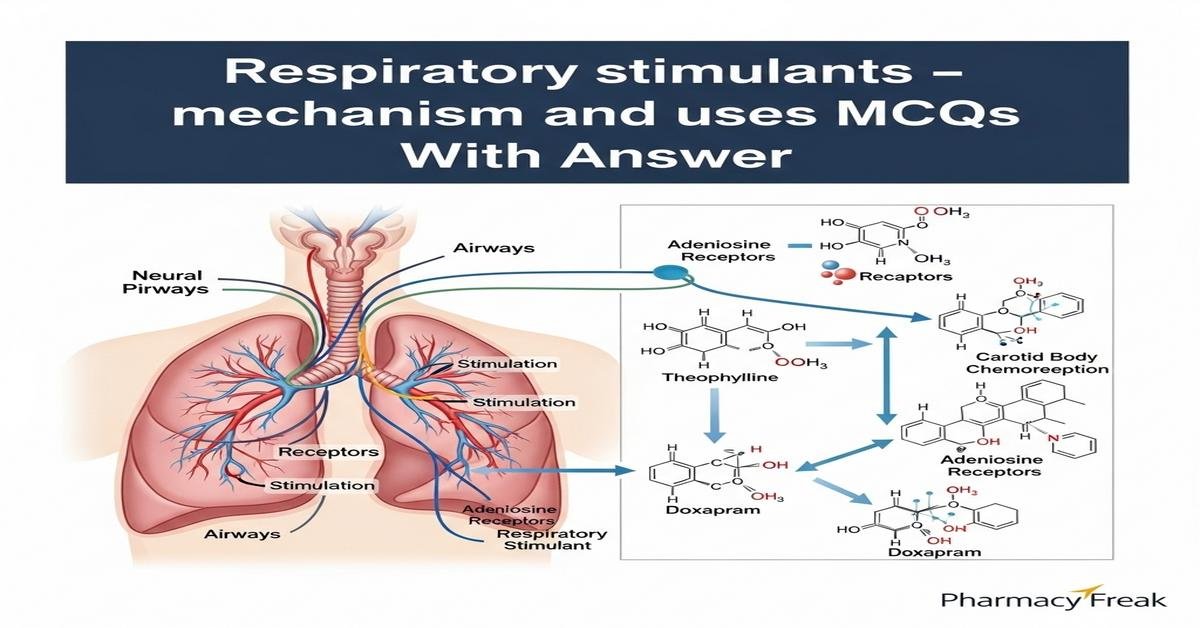
Respiratory stimulants are drugs that increase ventilatory drive by acting on central and peripheral chemoreceptors or by altering acid–base balance. This concise review explains mechanisms and clinical uses of key agents — doxapram, methylxanthines (caffeine, theophylline/aminophylline), acetazolamide, almitrine and progestogens — emphasizing pharmacology, indications such as apnea of prematurity, opioid-induced respiratory depression, and high-altitude breathing disorders, plus adverse effects, monitoring and drug interactions. B. Pharm students will benefit from mechanism-based insights into receptor targets, signaling pathways (adenosine antagonism, phosphodiesterase inhibition, carbonic anhydrase blockade), pharmacokinetics and therapeutic monitoring. Focus is on mechanism, dosing, toxicities and clinical decision-making. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which of the following best describes the principal mechanism of action of doxapram?
- Selective inhibition of adenosine A1 receptors in the medulla
- Stimulation of carotid body peripheral chemoreceptors and central medullary respiratory centers
- Nonselective beta-adrenergic agonism increasing bronchodilation
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibition producing metabolic alkalosis
Correct Answer: Stimulation of carotid body peripheral chemoreceptors and central medullary respiratory centers
Q2. Which methylxanthine is the preferred first-line treatment for apnea of prematurity?
- Theophylline
- Aminophylline
- Doxapram
Correct Answer: Caffeine citrate
Q3. The primary cellular actions of theophylline that contribute to respiratory stimulation include:
- Activation of GABA-A receptors and increase in chloride influx
- Adenosine receptor antagonism and phosphodiesterase inhibition raising intracellular cAMP
- Direct agonism of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the carotid body
- Blockade of NMDA receptors in the respiratory center
Correct Answer: Adenosine receptor antagonism and phosphodiesterase inhibition raising intracellular cAMP
Q4. Acetazolamide stimulates ventilation primarily by:
- Directly activating central chemoreceptors in the medulla
- Inhibiting carbonic anhydrase to induce metabolic acidosis and secondary hyperventilation
- Blocking peripheral chemoreceptor function to increase tidal volume
- Increasing sensitivity of carotid bodies to oxygen by upregulating ion channels
Correct Answer: Inhibiting carbonic anhydrase to induce metabolic acidosis and secondary hyperventilation
Q5. Which agent is a peripheral chemoreceptor stimulant used historically for persistent hypoxemia in COPD but associated with peripheral neuropathy with long-term use?
- Almitrine
- Medroxyprogesterone
- Theophylline
- Caffeine
Correct Answer: Almitrine
Q6. Theophylline therapeutic plasma concentration range most commonly targeted to maximize efficacy and minimize toxicity is:
- 1–5 µg/mL
- 5–10 µg/mL
- 10–20 µg/mL
- 30–40 µg/mL
Correct Answer: 10–20 µg/mL
Q7. A major adverse effect that limits the use of methylxanthines at high plasma levels is:
- Hypoglycemia and insulin secretion
- Renal failure due to tubular necrosis
- Seizures and serious cardiac arrhythmias
- Severe constipation and paralytic ileus
Correct Answer: Seizures and serious cardiac arrhythmias
Q8. Which interaction increases theophylline plasma concentration and risk of toxicity?
- Cigarette smoking
- Rifampicin coadministration
- Fluoroquinolone antibiotics (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
- High-protein, low-carbohydrate diet
Correct Answer: Fluoroquinolone antibiotics (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
Q9. In opioid-induced respiratory depression, the recommended immediate pharmacologic intervention is:
- IV doxapram bolus
- High-dose theophylline infusion
- Administration of naloxone (opioid antagonist)
- Oral caffeine
Correct Answer: Administration of naloxone (opioid antagonist)
Q10. Which respiratory stimulant is most appropriate for long-term management of central hypoventilation syndromes or obesity hypoventilation?
- A single dose of doxapram
- Progestogens such as medroxyprogesterone
- IV aminophylline continuous infusion
- Acetazolamide only as needed
Correct Answer: Progestogens such as medroxyprogesterone
Q11. Which statement about caffeine pharmacology is correct?
- Caffeine is a selective dopamine D2 receptor agonist
- Caffeine has a longer half-life in preterm neonates than in adults
- Caffeine primarily acts by stimulating peripheral serotonin receptors
- Caffeine is contraindicated for apnea of prematurity
Correct Answer: Caffeine has a longer half-life in preterm neonates than in adults
Q12. Doxapram is contraindicated or used cautiously in patients with which of the following conditions?
- Severe coronary artery disease or uncontrolled hypertension
- Well-controlled asthma on inhaled steroids
- Mild chronic kidney disease stage 2
- History of seasonal allergic rhinitis
Correct Answer: Severe coronary artery disease or uncontrolled hypertension
Q13. Which mechanism explains why acetazolamide helps prevent acute mountain sickness?
- It directly increases oxygen binding to hemoglobin
- It causes metabolic acidosis that increases ventilation and arterial oxygenation
- It stimulates erythropoietin release to increase red cell mass acutely
- It blocks peripheral chemoreceptor signaling to reduce dyspnea
Correct Answer: It causes metabolic acidosis that increases ventilation and arterial oxygenation
Q14. Which monitoring parameter is most important when using theophylline or aminophylline?
- Serum potassium concentration weekly
- Serum calcium every 2 days
- Plasma theophylline concentration and ECG monitoring for arrhythmias
- Liver function tests every hour
Correct Answer: Plasma theophylline concentration and ECG monitoring for arrhythmias
Q15. Which of the following is a correct pairing of drug and its dominant receptor or target?
- Caffeine — muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist
- Theophylline — adenosine receptor antagonist and phosphodiesterase inhibitor
- Acetazolamide — beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonist
- Almitrine — central GABA-B receptor agonist
Correct Answer: Theophylline — adenosine receptor antagonist and phosphodiesterase inhibitor
Q16. For acute postoperative respiratory depression due to residual anesthetic, which statement is most accurate?
- Theophylline is the immediate drug of choice
- Doxapram may be used as a short-acting stimulant while treating the underlying cause
- Long-term acetazolamide infusion is recommended
- Oral caffeine should be given to all postoperative patients
Correct Answer: Doxapram may be used as a short-acting stimulant while treating the underlying cause
Q17. Which of these clinical uses is NOT a typical indication for respiratory stimulants?
- Apnea of prematurity
- Opioid overdose respiratory depression (initial management)
- Long-term sole therapy for COPD stable hypercapnia without addressing underlying disease
- Prevention of acute mountain sickness
Correct Answer: Long-term sole therapy for COPD stable hypercapnia without addressing underlying disease
Q18. Smoking has what effect on theophylline plasma levels and why?
- Increases levels due to inhibition of CYP3A4
- Decreases levels due to induction of CYP1A2 enzymes
- No effect because theophylline is renally excreted unchanged
- Causes unpredictable fluctuations due to nicotine displacement
Correct Answer: Decreases levels due to induction of CYP1A2 enzymes
Q19. A neonate receiving caffeine citrate for apnea should be monitored for which common side effect?
- Hypotension and bradycardia
- Feeding intolerance, tachycardia and jitteriness
- Severe hyperglycemia requiring insulin
- Ototoxicity with permanent hearing loss
Correct Answer: Feeding intolerance, tachycardia and jitteriness
Q20. Which statement about almitrine’s effect on ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) matching is correct?
- Almitrine uniformly worsens V/Q mismatch by increasing perfusion to nonventilated areas
- Almitrine enhances hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction improving V/Q matching in some patients
- Almitrine is a potent bronchodilator that corrects V/Q mismatch
- Almitrine reduces hemoglobin oxygen affinity to improve tissue oxygen delivery
Correct Answer: Almitrine enhances hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction improving V/Q matching in some patients
Q21. Which pharmacokinetic property of caffeine is especially relevant in preterm infants?
- Extremely high protein binding leading to decreased free drug
- Prolonged half-life due to immature hepatic metabolism
- Rapid renal clearance making dosing hourly
- Complete metabolism to inactive metabolites in gut flora
Correct Answer: Prolonged half-life due to immature hepatic metabolism
Q22. Which adverse effect is characteristically associated with acetazolamide use?
- Metabolic alkalosis and hypoventilation
- Metabolic acidosis, paresthesias and renal bicarbonate wasting
- Hyperkalemia and fluid retention
- Severe neutropenia within hours of first dose
Correct Answer: Metabolic acidosis, paresthesias and renal bicarbonate wasting
Q23. Which drug class provides the most direct antagonism of opioid-induced respiratory depression?
- Methylxanthines
- Respiratory analeptics such as doxapram
- Opioid receptor antagonists like naloxone
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors like acetazolamide
Correct Answer: Opioid receptor antagonists like naloxone
Q24. Which monitoring is especially important when initiating doxapram therapy in an adult patient?
- Serum albumin concentration weekly
- Continuous cardiac and respiratory monitoring due to risk of arrhythmia and hypertension
- Thyroid function tests before the first dose
- Fasting glucose monitoring hourly
Correct Answer: Continuous cardiac and respiratory monitoring due to risk of arrhythmia and hypertension
Q25. Which of the following is a correct clinical pearl about methylxanthines?
- Methylxanthines have no drug interactions and require no monitoring
- Theophylline toxicity may present with nausea, vomiting, tremor, and seizures
- Methylxanthines are ineffective in neonatal apnea because they cannot cross the blood-brain barrier
- The therapeutic index of theophylline is wide, so levels are not helpful
Correct Answer: Theophylline toxicity may present with nausea, vomiting, tremor, and seizures
Q26. Which mechanism explains why respiratory stimulants might worsen gas exchange in some COPD patients?
- They uniformly increase hemoglobin concentration reducing oxygen delivery
- Increased ventilation may blunt hypoxic drive, worsening V/Q mismatch and CO2 retention in some patients
- They induce bronchoconstriction causing atelectasis
- They cause immediate pulmonary edema in COPD
Correct Answer: Increased ventilation may blunt hypoxic drive, worsening V/Q mismatch and CO2 retention in some patients
Q27. A B. Pharm student counseling about theophylline should advise that common precipitants of toxicity include:
- Initiation of ciprofloxacin or macrolide antibiotics and liver disease
- Starting tobacco smoking and phenobarbital therapy
- Increased caffeine intake and vitamin C supplementation
- High carbohydrate diets and exercise
Correct Answer: Initiation of ciprofloxacin or macrolide antibiotics and liver disease
Q28. Which statement about the role of central versus peripheral chemoreceptors is accurate regarding respiratory stimulants?
- Central chemoreceptors respond mainly to arterial O2 changes, peripheral to CO2
- Peripheral chemoreceptors (carotid bodies) respond to hypoxia and many stimulants target them to increase drive
- Only central chemoreceptors mediate responses to pH and CO2; peripheral bodies have no role
- Drugs cannot selectively influence peripheral chemoreceptor function
Correct Answer: Peripheral chemoreceptors (carotid bodies) respond to hypoxia and many stimulants target them to increase drive
Q29. Which of the following is the most appropriate role for acetazolamide in respiratory pharmacotherapy?
- Immediate reversal of opioid overdose in emergency room
- Chronic bronchodilator therapy in asthma
- Prevention and treatment of acute mountain sickness and as adjunct to stimulate ventilation in central sleep apnea
- Primary treatment for COPD exacerbation with hypercapnia
Correct Answer: Prevention and treatment of acute mountain sickness and as adjunct to stimulate ventilation in central sleep apnea
Q30. For a patient on chronic theophylline therapy, which clinical sign would most strongly suggest theophylline toxicity requiring urgent evaluation?
- Transient mild headache with no other symptoms
- Persistent vomiting, severe agitation, and generalized tonic-clonic seizure
- Temporary mild insomnia for one night
- Localized muscle pain after exercise
Correct Answer: Persistent vomiting, severe agitation, and generalized tonic-clonic seizure

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com