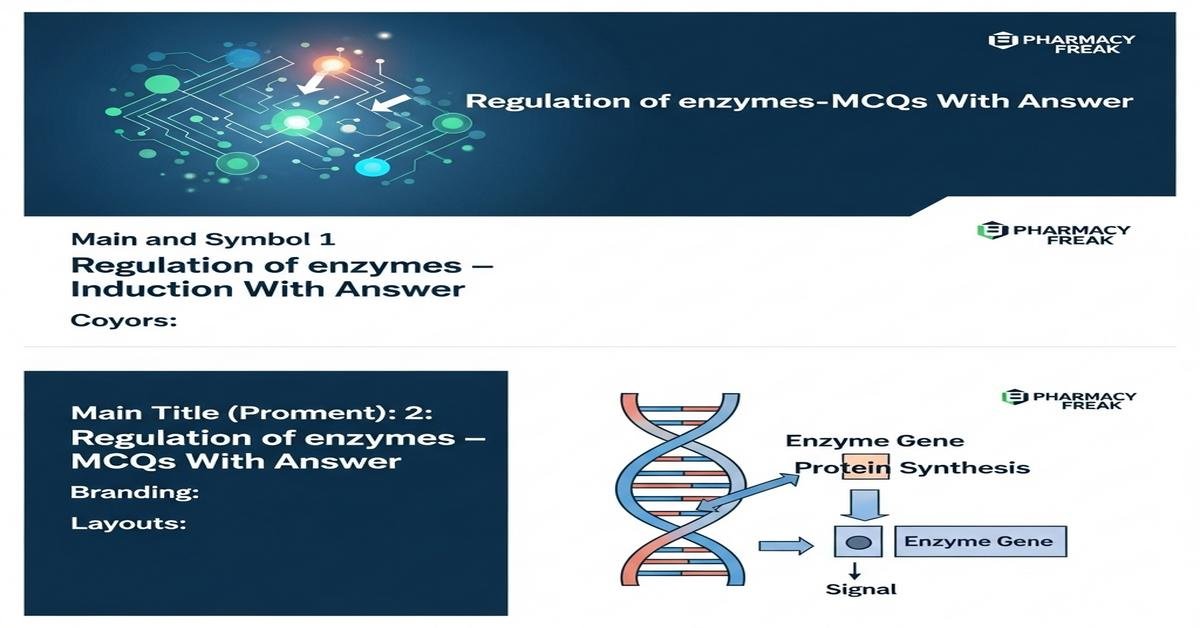
Regulation of enzymes – induction MCQs With Answer
Understanding the regulation of enzymes, especially enzyme induction, is crucial for B. Pharm students studying pharmacology and drug metabolism. This introduction covers mechanisms like transcriptional activation, nuclear receptors (PXR, CAR, AhR), post‑translational modulation, and clinical implications such as drug‑drug interactions, altered pharmacokinetics, and therapeutic failure. Key topics include hepatic CYP450 induction, isoform specificity, autoinduction, mechanism‑based inactivation, and methods to assess induction (RT‑PCR, reporter assays). Mastering these concepts helps predict metabolic changes, optimize dosing, and ensure patient safety. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which nuclear receptor is most commonly associated with induction of CYP3A enzymes?
- PXR (Pregnane X receptor)
- AhR (Aryl hydrocarbon receptor)
- GR (Glucocorticoid receptor)
- ER (Estrogen receptor)
Correct Answer: PXR (Pregnane X receptor)
Q2. Enzyme induction typically results in which change to drug clearance?
- Increased clearance
- Decreased clearance
- No change in clearance
- Immediate toxic accumulation
Correct Answer: Increased clearance
Q3. Which drug is a classic inducer of hepatic microsomal enzymes and can reduce effectiveness of oral contraceptives?
- Rifampicin
- Ketoconazole
- Fluconazole
- Ciprofloxacin
Correct Answer: Rifampicin
Q4. Autoinduction refers to:
- A drug increasing its own metabolism over time
- A drug inhibiting its own absorption
- One drug inducing metabolism of another drug only
- Enzyme degradation by proteasomes
Correct Answer: A drug increasing its own metabolism over time
Q5. Which of the following is a mechanism-based (suicide) inhibitor rather than an inducer?
- Clopidogrel
- Rifampicin
- Phenobarbital
- Carbamazepine
Correct Answer: Clopidogrel
Q6. Activation of AhR commonly induces which CYP family?
- CYP1A
- CYP2D
- CYP3A
- CYP2E
Correct Answer: CYP1A
Q7. Which laboratory technique is most appropriate to measure mRNA levels of an induced enzyme?
- RT‑PCR
- ELISA for protein
- Mass spectrometry for metabolites
- Histology
Correct Answer: RT‑PCR
Q8. Phenobarbital induces drug‑metabolizing enzymes primarily through activation of which receptor?
- CAR (Constitutive Androstane Receptor)
- PXR
- AhR
- PPARα
Correct Answer: CAR (Constitutive Androstane Receptor)
Q9. Enzyme induction usually affects which kinetic parameter of a drug metabolized by that enzyme?
- Vmax increases
- Km increases
- Km decreases dramatically
- No change to Vmax or Km
Correct Answer: Vmax increases
Q10. Which clinical consequence is most likely when a patient starts a potent CYP3A inducer while on a narrow therapeutic index drug metabolized by CYP3A?
- Loss of therapeutic effect due to subtherapeutic levels
- Acute toxicity due to accumulation
- Immediate allergic reaction
- Unchanged drug effect
Correct Answer: Loss of therapeutic effect due to subtherapeutic levels
Q11. Carbamazepine is known for which of the following enzyme regulation phenomena?
- Autoinduction of its own metabolism
- Pure competitive inhibition of CYP2C9
- Only phase II enzyme inhibition
- No effect on drug‑metabolizing enzymes
Correct Answer: Autoinduction of its own metabolism
Q12. Which method directly quantifies protein levels of an induced enzyme in liver tissue?
- Western blot
- qPCR for mRNA
- Reporter gene assay
- In silico docking
Correct Answer: Western blot
Q13. Stimulation of gene transcription of metabolic enzymes depends primarily on:
- Activation of transcription factors/nuclear receptors
- Direct enzyme proteolysis
- Competitive substrate binding
- Renal excretion rates
Correct Answer: Activation of transcription factors/nuclear receptors
Q14. Which hepatic phase II enzyme is commonly inducible and important for conjugation reactions?
- UDP‑glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)
- Acetylcholinesterase
- DNA polymerase
- Lactate dehydrogenase
Correct Answer: UDP‑glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)
Q15. Induction of CYP2E1 is clinically important because it can increase toxicity of which compound?
- Acetaminophen (paracetamol) via reactive metabolite formation
- Warfarin due to decreased INR
- Insulin via altered glucose uptake
- Digoxin due to P‑glycoprotein changes
Correct Answer: Acetaminophen (paracetamol) via reactive metabolite formation
Q16. Which experimental assay uses a luciferase reporter to assess induction via a specific promoter?
- Reporter gene assay
- ELISA
- Chromatography
- NMR spectroscopy
Correct Answer: Reporter gene assay
Q17. Drug‑drug interactions from enzyme induction are usually most apparent after:
- Several days to weeks
- Within minutes
- Only after a year
- Only in renal impairment
Correct Answer: Several days to weeks
Q18. Which of the following can act as an inducer of CYP1A enzymes often through environmental exposure?
- Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
- Beta‑blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- Statins
Correct Answer: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
Q19. Induction that increases both enzyme amount and activity is best described as affecting which level?
- Transcriptional and translational levels
- Only substrate availability
- Only renal clearance
- Only post‑translational proteolysis
Correct Answer: Transcriptional and translational levels
Q20. Which transporter expression can be induced along with metabolic enzymes, affecting drug disposition?
- P‑glycoprotein (P‑gp, ABCB1)
- SERCA pump
- Na+/K+ ATPase
- Hemoglobin
Correct Answer: P‑glycoprotein (P‑gp, ABCB1)
Q21. A patient on chronic phenobarbital therapy may require which dose adjustment of warfarin (a CYP inducer effect)?
- Increase warfarin dose due to increased metabolism
- Decrease warfarin dose due to reduced metabolism
- No change in warfarin dose
- Stop warfarin immediately
Correct Answer: Increase warfarin dose due to increased metabolism
Q22. Which hepatic feature is NOT a mechanism for enzyme induction?
- Increased proteasomal degradation of the enzyme
- Enhanced gene transcription
- Stabilization of mRNA
- Enhanced translation
Correct Answer: Increased proteasomal degradation of the enzyme
Q23. Which CYP isoform is primarily responsible for metabolizing many psychotropic drugs and is inducible by certain drugs?
- CYP3A4
- CYP2D6
- CYP1A2 only
- CYP7A1
Correct Answer: CYP3A4
Q24. Which term describes induction that continues even after the inducing drug is stopped until the enzyme is degraded?
- Persistent induction due to increased enzyme half‑life
- Immediate reversible induction
- Competitive inhibition
- Allosteric modulation
Correct Answer: Persistent induction due to increased enzyme half‑life
Q25. Which of the following is an example of a dietary inducer affecting drug metabolism?
- St. John’s wort inducing CYP3A4
- Grapefruit juice inhibiting CYP3A4
- Milk increasing absorption of tetracyclines
- Folic acid deficiency
Correct Answer: St. John’s wort inducing CYP3A4
Q26. Induction of enzymes can lead to formation of toxic metabolites; which concept best describes this risk?
- Bioactivation
- Prodrug inactivation
- First‑pass inhibition
- Renal trapping
Correct Answer: Bioactivation
Q27. Which analytical approach measures enzyme activity directly by quantifying metabolite formation?
- In vitro microsomal metabolic assay
- qPCR for mRNA
- Western blot for protein
- Immunohistochemistry
Correct Answer: In vitro microsomal metabolic assay
Q28. Which of these drugs is a known inducer of CYP2C9 and may reduce levels of drugs like warfarin?
- Rifampicin
- Cimetidine
- Ketoconazole
- Fluvoxamine
Correct Answer: Rifampicin
Q29. Which statement about transcriptional induction by nuclear receptors is TRUE?
- Nuclear receptors bind response elements on DNA to increase transcription
- Nuclear receptors degrade mRNA directly
- Nuclear receptors phosphorylate enzymes to activate them
- Nuclear receptors primarily act in the cytosol to sequester drugs
Correct Answer: Nuclear receptors bind response elements on DNA to increase transcription
Q30. Which factor can limit the extent of enzyme induction clinically?
- Genetic polymorphism reducing inducible expression
- Excessive hydration
- Dietary sugar intake only
- Ambient temperature
Correct Answer: Genetic polymorphism reducing inducible expression
Q31. Which is the best description of phenoconversion in the context of enzyme regulation?
- A drug‑induced change in phenotype of metabolism (e.g., normal to poor metabolizer)
- Permanent genetic mutation of CYP genes
- Conversion of prodrug to active drug in plasma
- Enzyme glycosylation in the ER
Correct Answer: A drug‑induced change in phenotype of metabolism (e.g., normal to poor metabolizer)
Q32. Which of the following is a consequence of induction of hepatic UGT enzymes?
- Increased glucuronidation and faster clearance of substrates
- Decreased conjugation and accumulation of parent drug
- Reduced renal filtration of drugs
- Inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase
Correct Answer: Increased glucuronidation and faster clearance of substrates
Q33. A selective inducer of CYP3A4 will most likely affect which class of drugs?
- Calcium channel blockers metabolized by CYP3A4
- Drugs exclusively renally excreted unchanged
- Insulin formulations
- Inhaled anesthetics only
Correct Answer: Calcium channel blockers metabolized by CYP3A4
Q34. Which clinical monitoring is important when starting an inducer in a patient on a narrow therapeutic index drug?
- Therapeutic drug monitoring (plasma concentrations)
- Only blood pressure checks
- Daily ECG for all drugs
- No monitoring required
Correct Answer: Therapeutic drug monitoring (plasma concentrations)
Q35. Which pharmacological strategy can overcome decreased drug exposure due to enzyme induction?
- Increase dose or choose an alternative not metabolized by induced enzyme
- Stop all other medications immediately
- Switch to intravenous formulations only
- Give a loading dose of the inducer
Correct Answer: Increase dose or choose an alternative not metabolized by induced enzyme
Q36. Which experimental evidence would best demonstrate that induction is transcriptional rather than post‑translational?
- Increased mRNA levels measured by qPCR
- Increased enzyme phosphorylation with unchanged mRNA
- Decreased protein degradation with unchanged mRNA
- Immediate enzyme activity change within minutes
Correct Answer: Increased mRNA levels measured by qPCR
Q37. Which of the following is least likely to be induced by typical xenobiotic inducers?
- DNA polymerase involved in replication
- Phase I CYP enzymes
- Phase II conjugating enzymes
- Drug transporters like P‑gp
Correct Answer: DNA polymerase involved in replication
Q38. Induction via PXR often leads to cross‑induction of which of the following?
- Both CYP3A enzymes and P‑glycoprotein
- Only mitochondrial enzymes
- Only renal transporters unrelated to drug efflux
- Hemostatic factors in plasma
Correct Answer: Both CYP3A enzymes and P‑glycoprotein
Q39. Which of these is a biomarker that may indicate liver enzyme induction or liver injury?
- Serum ALT/AST levels
- Serum creatinine only
- Urinary glucose exclusively
- Serum amylase only
Correct Answer: Serum ALT/AST levels
Q40. Which property of an inducer determines its ability to upregulate nuclear receptors?
- Affinity for and activation of the nuclear receptor ligand‑binding domain
- Ability to inhibit renal transporters
- Only its water solubility
- Its taste and smell
Correct Answer: Affinity for and activation of the nuclear receptor ligand‑binding domain
Q41. Which phase of drug metabolism is most directly affected by CYP induction?
- Phase I (oxidation/reduction/hydrolysis)
- Phase II conjugation only
- Absorption in the gut lumen
- Renal tubular secretion
Correct Answer: Phase I (oxidation/reduction/hydrolysis)
Q42. Which of the following is true about drug interaction onset with enzyme inducers compared to inhibitors?
- Inducer effects are slower to appear and to resolve than inhibitor effects
- Inducer effects appear immediately and resolve slowly
- Inducer effects are always reversible within hours
- Inhibitor effects are always slower than inducer effects
Correct Answer: Inducer effects are slower to appear and to resolve than inhibitor effects
Q43. Which laboratory model uses primary cells that retain drug‑metabolizing enzyme expression to study induction?
- Primary human hepatocytes
- HEK293 overexpressing albumin
- CHO cells without receptors
- Red blood cell cultures
Correct Answer: Primary human hepatocytes
Q44. Which of the following drugs is most likely to decrease plasma concentrations of an opioid metabolized by CYP3A4?
- St. John’s wort
- Fluoxetine
- Ketoconazole
- Grapefruit juice
Correct Answer: St. John’s wort
Q45. Which statement best differentiates induction from inhibition?
- Induction increases enzyme amount/activity over time; inhibition decreases enzyme activity rapidly
- Induction decreases enzyme expression; inhibition increases gene transcription
- Both always act immediately and are irreversible
- Induction only occurs in kidneys; inhibition only in liver
Correct Answer: Induction increases enzyme amount/activity over time; inhibition decreases enzyme activity rapidly
Q46. The clinical term ‘therapeutic failure’ due to enzyme induction most often means:
- Drug plasma levels fall below effective concentration
- Patient experiences immediate hypersensitivity
- Drug causes acute renal failure
- Drug accumulation causes overdose
Correct Answer: Drug plasma levels fall below effective concentration
Q47. Which concept explains why two drugs metabolized by different CYPs may still interact through induction?
- Cross‑induction of multiple CYP isoforms by the same nuclear receptor
- Renal competition for excretion only
- Binding to albumin only affects one drug
- They cannot interact if different CYPs are involved
Correct Answer: Cross‑induction of multiple CYP isoforms by the same nuclear receptor
Q48. In drug development, which study design assesses potential enzyme induction risk before clinical trials?
- In vitro induction studies using human hepatocytes
- Phase IV post‑marketing surveillance only
- Randomized controlled trial without preclinical data
- Single dose toxicity in mice only
Correct Answer: In vitro induction studies using human hepatocytes
Q49. Which of the following best describes ‘mechanism‑based inactivation’ relative to induction?
- Irreversible inhibition of an enzyme by a metabolite, decreasing activity
- Increasing enzyme gene transcription permanently
- Enhancing mRNA stability to produce more enzyme
- Stimulating ribosomal translation of enzymes
Correct Answer: Irreversible inhibition of an enzyme by a metabolite, decreasing activity
Q50. For a B. Pharm student, understanding enzyme induction is most important for:
- Predicting and managing drug interactions and optimizing therapy
- Designing sterile compounding techniques only
- Learning only about physical pharmacy measurements
- Choosing packaging materials for drugs
Correct Answer: Predicting and managing drug interactions and optimizing therapy

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com