Large intestine anatomy and functions MCQs With Answer
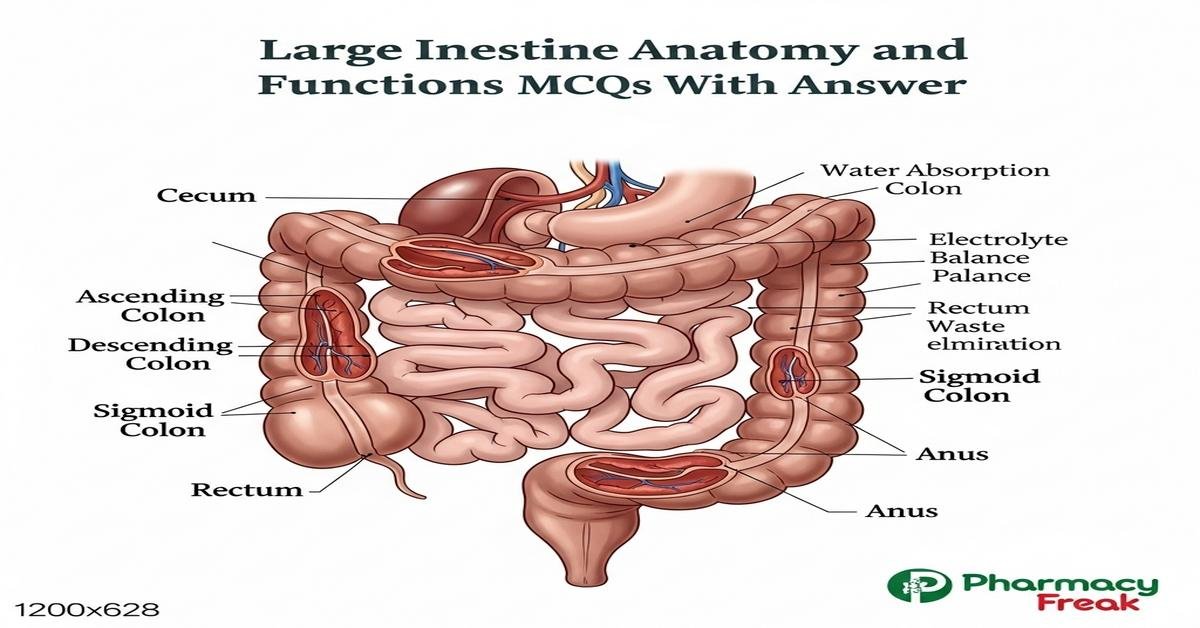
The large intestine anatomy and functions are essential topics for B. Pharm students preparing for pharmacology, pathology, and clinical pharmacy exams. This concise introduction covers colon segments (cecum, ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid, rectum, anal canal), key histological features (taenia coli, haustra, goblet cells), major physiological roles (water and electrolyte absorption, fermentation, short-chain fatty acid production, vitamin K synthesis), blood supply, innervation, and relevant drug actions affecting motility and secretion. These focused MCQs will strengthen clinical reasoning and drug therapy understanding related to colonic disorders, constipation, diarrhea, and microbiome interactions. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which segment of the large intestine directly receives chyme from the ileum?
- Cecum
- Ascending colon
- Sigmoid colon
- Rectum
Correct Answer: Cecum
Q2. Which characteristic is typical of the colonic mucosa compared with small intestine?
- Presence of villi
- Abundant goblet cells
- Paneth cells throughout
- Long microvilli on enterocytes
Correct Answer: Abundant goblet cells
Q3. Taenia coli are:
- Three longitudinal bands of smooth muscle on the colon
- Circular muscle rings forming haustra
- Folds in the rectal mucosa
- Small fatty appendices on the serosa
Correct Answer: Three longitudinal bands of smooth muscle on the colon
Q4. Which vessel supplies the descending colon?
- Superior mesenteric artery
- Inferior mesenteric artery
- Celiac trunk
- Internal iliac artery
Correct Answer: Inferior mesenteric artery
Q5. Which nerve provides parasympathetic innervation to the distal colon and rectum?
- Vagus nerve
- Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2–S4)
- Greater splanchnic nerve
- Hypogastric nerve
Correct Answer: Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2–S4)
Q6. Haustra of the colon are formed primarily by:
- Contraction of circular muscle forming fixed folds
- Contraction of taenia coli creating sacculations
- Tumors causing localized bulging
- Appendices epiploicae pulling the wall
Correct Answer: Contraction of taenia coli creating sacculations
Q7. The main absorptive function of the colon is:
- Protein digestion and absorption
- Water and electrolyte absorption
- Bile salt reabsorption
- Vitamin D synthesis
Correct Answer: Water and electrolyte absorption
Q8. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced by colonic bacteria primarily come from fermentation of:
- Proteins only
- Complex carbohydrates and fibers
- Simple sugars absorbed in small intestine
- Fatty acids from bile
Correct Answer: Complex carbohydrates and fibers
Q9. Which vitamin is synthesized by colonic microbiota and absorbed locally?
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin B12 in large amounts
- Vitamin D
Correct Answer: Vitamin K
Q10. The ileocecal valve functionally prevents:
- Retrograde flow of colonic contents into the ileum
- Passage of bile into the colon
- Absorption of vitamin K
- Movement of feces into rectum
Correct Answer: Retrograde flow of colonic contents into the ileum
Q11. Which histological structure is prominent in the colon but not in the small intestine?
- Crypts of Lieberkühn with abundant goblet cells
- Peyer’s patches
- Villi
- Brunner’s glands
Correct Answer: Crypts of Lieberkühn with abundant goblet cells
Q12. The rectum stores feces and is distinguished by which feature in the anal canal?
- Pectinate (dentate) line marking epithelial transition
- Peyer’s patches cluster
- Taenia coli continuation
- Presence of villi
Correct Answer: Pectinate (dentate) line marking epithelial transition
Q13. Mass movements in the colon are primarily triggered by:
- Fasting state and sympathetic stimulation
- Gastric and duodenal reflexes after meals
- Large protein meals only
- Defecation reflex suppression
Correct Answer: Gastric and duodenal reflexes after meals
Q14. Which ion transport mechanism in the colon is stimulated by aldosterone?
- Chloride secretion via CFTR
- Sodium absorption via epithelial sodium channels (ENaC)
- Potassium absorption into lumen
- Bicarbonate secretion into lumen
Correct Answer: Sodium absorption via epithelial sodium channels (ENaC)
Q15. In the context of drug delivery, the colon is a target for sustained release because:
- It has high proteolytic activity that degrades most drugs
- Transit time is relatively slow and microbiota can activate prodrugs
- Vascular uptake is minimal
- pH is highly acidic throughout
Correct Answer: Transit time is relatively slow and microbiota can activate prodrugs
Q16. Which of the following is a bulk-forming laxative acting in the colon?
- Bisacodyl
- Psyllium (ispaghula husk)
- Polyethylene glycol (osmotic)
- Docusate sodium (stool softener)
Correct Answer: Psyllium (ispaghula husk)
Q17. Loperamide reduces diarrhea mainly by:
- Increasing intestinal secretion of chloride
- Acting as a peripheral μ-opioid receptor agonist to decrease motility
- Antibiotic activity against E. coli
- Neutralizing gastric acid
Correct Answer: Acting as a peripheral μ-opioid receptor agonist to decrease motility
Q18. The most common site of appendicitis pain is related to irritation of which structure?
- Descending colon
- Cecum and parietal peritoneum near McBurney’s point
- Sigmoid colon near pelvic brim
- Rectum posterolaterally
Correct Answer: Cecum and parietal peritoneum near McBurney’s point
Q19. Diverticulosis commonly affects which part of the colon?
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon evenly
- Sigmoid colon
- Cecum only
Correct Answer: Sigmoid colon
Q20. Which statement about the appendix is true?
- It is a blind-ended tube arising from the sigmoid colon
- It contains lymphoid tissue and is considered part of gut-associated lymphoid tissue
- It secretes large amounts of digestive enzymes
- It is supplied by the inferior mesenteric artery
Correct Answer: It contains lymphoid tissue and is considered part of gut-associated lymphoid tissue
Q21. Which layer of the colon wall houses the myenteric (Auerbach) plexus?
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Between circular and longitudinal muscle layers (muscularis externa)
- Serosa only
Correct Answer: Between circular and longitudinal muscle layers (muscularis externa)
Q22. Colonic ischemia most often results from compromise of which blood supply in the watershed area?
- Jejunal arterial arcades
- Splenic artery distal branches
- Watershed between superior and inferior mesenteric arteries (e.g., splenic flexure)
- Internal pudendal artery
Correct Answer: Watershed between superior and inferior mesenteric arteries (e.g., splenic flexure)
Q23. Which of the following is characteristic of ulcerative colitis (UC) rather than Crohn’s disease?
- Transmural inflammation with skip lesions
- Continuous mucosal inflammation starting from rectum
- Perianal fistulas common
- Granulomas on histology
Correct Answer: Continuous mucosal inflammation starting from rectum
Q24. Which diagnostic test is most appropriate to visualize the entire colonic mucosa?
- Upper GI endoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Abdominal ultrasound
- HIDA scan
Correct Answer: Colonoscopy
Q25. Which pharmacologic class is contraindicated in acute severe ulcerative colitis due to risk of toxic megacolon?
- Systemic corticosteroids
- Antimotility agents like loperamide
- Aminosalicylates
- Biologic anti-TNF agents
Correct Answer: Antimotility agents like loperamide
Q26. The dentate (pectinate) line in the anal canal is clinically important because it:
- Marks the transition from smooth to skeletal muscle in the rectum
- Indicates change in epithelial type and differing nerve supply
- Shows the site of taenia coli termination
- Is the origin of the rectal venous plexus only
Correct Answer: Indicates change in epithelial type and differing nerve supply
Q27. Which enzyme-derived drug activation depends on colonic bacteria?
- Proton pump inhibitors
- Sulfasalazine (activated to 5-ASA and sulfapyridine)
- Metformin
- Warfarin
Correct Answer: Sulfasalazine (activated to 5-ASA and sulfapyridine)
Q28. Which of the following best describes colonic motility pattern called “haustral shuttling”?
- Rapid peristalsis propelling contents to rectum continuously
- Localized mixing movements that facilitate absorption within haustra
- Complete inhibition of contraction after meal
- Retrograde movement toward the ileum
Correct Answer: Localized mixing movements that facilitate absorption within haustra
Q29. The portal venous drainage of the colon ultimately goes to the:
- Systemic circulation via inferior vena cava directly
- Liver via the portal vein
- Aorta through mesenteric arteries
- Pulmonary circulation
Correct Answer: Liver via the portal vein
Q30. Which of the following is a stimulant laxative that acts on enteric nerves to increase motility?
- Bisacodyl
- Methylcellulose (bulk-forming)
- Lactulose (osmotic)
- Mineral oil (lubricant)
Correct Answer: Bisacodyl
Q31. Which substance is primarily absorbed in the colon and used by colonocytes as an energy source?
- Glucose from dietary sugars
- Butyrate (a short-chain fatty acid)
- Amino acids from proteins
- Free fatty acids from bile micelles
Correct Answer: Butyrate (a short-chain fatty acid)
Q32. Pseudomembranous colitis is most commonly associated with which organism after antibiotic use?
- Escherichia coli
- Clostridioides difficile
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Helicobacter pylori
Correct Answer: Clostridioides difficile
Q33. Which colonic movement aids defecation by increasing intrarectal pressure?
- Haustral shuttling
- Segmental contraction only
- Mass peristaltic movements
- Reverse peristalsis
Correct Answer: Mass peristaltic movements
Q34. The omental appendices (appendices epiploicae) are:
- Glandular mucosal folds in the rectum
- Fat-filled peritoneal pouches attached to colon serosa
- Sphincter muscles at the anal canal
- Vascular arcades supplying the mesentery
Correct Answer: Fat-filled peritoneal pouches attached to colon serosa
Q35. Constipation caused by anticholinergic drugs is due to:
- Increased colonic secretions
- Decreased parasympathetic-mediated colonic motility
- Direct damage to colonic mucosa
- Increased activity of pelvic splanchnic nerves
Correct Answer: Decreased parasympathetic-mediated colonic motility
Q36. The proximal two-thirds of the transverse colon develops embryologically from the:
- Hindgut
- Midgut
- Cloaca
- Allantois
Correct Answer: Midgut
Q37. In ischemic colitis, which symptom is most characteristic?
- Painless, chronic constipation
- Sudden abdominal pain with bloody diarrhea
- Upper abdominal burning relieved by antacids
- Jaundice without abdominal pain
Correct Answer: Sudden abdominal pain with bloody diarrhea
Q38. Which layer contains abundant lymphoid aggregates in the colon?
- Muscularis externa
- Mucosa and submucosa (GALT)
- Serosa only
- Adventitia exclusively
Correct Answer: Mucosa and submucosa (GALT)
Q39. Which drug is used to treat refractory constipation by activating guanylate cyclase-C on enterocytes?
- Lubiprostone
- Linaclotide
- Loperamide
- Bisacodyl
Correct Answer: Linaclotide
Q40. The clinical sign of rebound tenderness in right lower quadrant suggests irritation of:
- Left colon serosa
- Peritoneum overlying the cecum and appendix
- Rectum mucosa only
- Transverse colon flexure
Correct Answer: Peritoneum overlying the cecum and appendix
Q41. Which of the following is true about colonic epithelial renewal?
- Villi contain stem cells renewing enterocytes
- Crypt base stem cells proliferate and migrate upward to replace epithelium
- Enterocytes live for several years in colon
- There is no regenerative capacity in colon
Correct Answer: Crypt base stem cells proliferate and migrate upward to replace epithelium
Q42. A colonoscopic biopsy showing non-caseating granulomas suggests which diagnosis?
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
- Ischemic colitis
- Pseudomembranous colitis
Correct Answer: Crohn’s disease
Q43. Which electrolyte disturbance is commonly seen with severe secretory diarrhea originating from the colon?
- Hypernatremia and metabolic alkalosis
- Hyponatremia and metabolic acidosis with loss of bicarbonate
- Hyperkalemia due to renal retention
- Hypocalcemia with elevated bicarbonate
Correct Answer: Hyponatremia and metabolic acidosis with loss of bicarbonate
Q44. The gastrocolic reflex primarily causes:
- Relaxation of the colon after eating
- Increased colonic motility and mass movements after a meal
- Decreased secretions in colon
- Closure of ileocecal valve
Correct Answer: Increased colonic motility and mass movements after a meal
Q45. Carcinoma of the colon most commonly arises from:
- Normal mucosa without precursor lesions
- Adenomatous polyps (adenoma-carcinoma sequence)
- Appendiceal mucoceles only
- Transmural inflammatory scars exclusively
Correct Answer: Adenomatous polyps (adenoma-carcinoma sequence)
Q46. Which receptor type on enteric neurons mediates increased secretion and motility in secretory diarrhea?
- Adrenergic β2 receptors
- Serotonin (5-HT3/5-HT4) receptors and enteric cholinergic receptors
- GABA-B receptors
- Opioid μ receptors centrally only
Correct Answer: Serotonin (5-HT3/5-HT4) receptors and enteric cholinergic receptors
Q47. Which statement about the distal colon’s blood supply is correct?
- It is supplied entirely by the superior mesenteric artery
- The sigmoid arteries, branches of the inferior mesenteric artery, supply the sigmoid colon
- The rectum is supplied only by branches of the superior rectal artery
- The colon has no collateral blood supply
Correct Answer: The sigmoid arteries, branches of the inferior mesenteric artery, supply the sigmoid colon
Q48. Bowel sounds in colonic obstruction are typically:
- Hyperactive high-pitched early, then diminished
- Always normal
- Absent from the onset
- Only heard in the small intestine
Correct Answer: Hyperactive high-pitched early, then diminished
Q49. Which laboratory test aids in identifying inflammatory bowel disease activity originating in the colon?
- Fecal calprotectin
- Serum lipase only
- Serum amylase only
- Urine ketones
Correct Answer: Fecal calprotectin
Q50. The anal sphincter complex includes which muscle under voluntary control?
- Internal anal sphincter (smooth muscle)
- External anal sphincter (skeletal muscle)
- Taenia coli
- Puborectalis only involuntary
Correct Answer: External anal sphincter (skeletal muscle)

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com