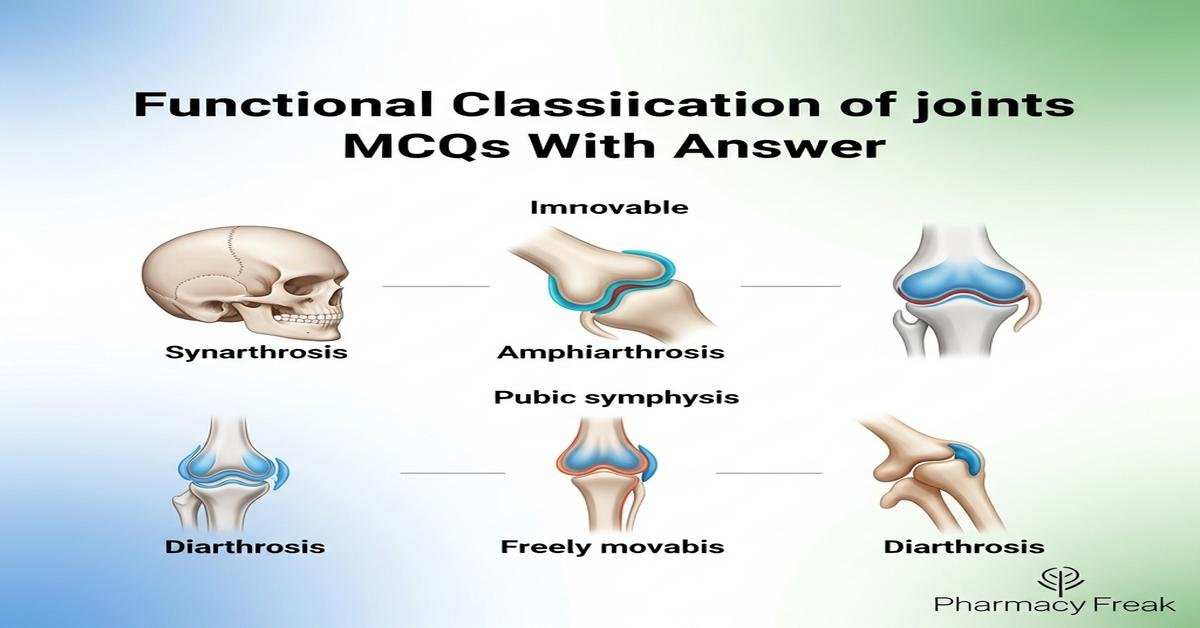
Understanding the functional classification of joints is essential for B. Pharm students studying musculoskeletal physiology, drug delivery to joints, and therapy of joint disorders. This concise guide and quiz—Functional classification of joints MCQs With Answer—covers synarthrosis (immovable), amphiarthrosis (slightly movable) and diarthrosis/synovial (freely movable), synovial joint types, joint components like synovial membrane, articular cartilage and ligaments, and clinical-pharmacological aspects such as intra-articular drug administration and inflammation. Emphasis is placed on joint mobility, examples, biomechanics and implications for pharmacotherapy. Answers are provided to aid self-assessment and revision. Now let’s test your knowledge with 30 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which of the following is NOT a functional classification of joints?
- Synarthrosis
- Amphiarthrosis
- Diarthrosis
- Arthroscopy
Correct Answer: Arthroscopy
Q2. Which functional class describes freely movable joints?
- Synarthrosis
- Amphiarthrosis
- Diarthrosis
- Synchondrosis
Correct Answer: Diarthrosis
Q3. Which of the following is an example of a synarthrosis?
- Pubic symphysis
- Sutures of the skull
- Knee joint
- Intervertebral disc
Correct Answer: Sutures of the skull
Q4. The pubic symphysis is functionally classified as which type of joint?
- Synarthrosis
- Amphiarthrosis
- Diarthrosis
- Synovial hinge
Correct Answer: Amphiarthrosis
Q5. Which feature is characteristic of synovial (diarthrotic) joints?
- Direct bone fusion with no cavity
- Presence of a joint cavity lined by a synovial membrane
- Fibrocartilaginous connection without a cavity
- Epiphyseal plate cartilage only
Correct Answer: Presence of a joint cavity lined by a synovial membrane
Q6. Which synovial joint type permits the greatest range of motion?
- Hinge joint
- Pivot joint
- Plane (gliding) joint
- Ball-and-socket joint
Correct Answer: Ball-and-socket joint
Q7. Which joint is a classic example of a pivot synovial joint?
- Humeroulnar (elbow) joint
- Proximal radioulnar joint
- Carpometacarpal joint of thumb
- Hip joint
Correct Answer: Proximal radioulnar joint
Q8. Hinge joints primarily allow which movements?
- Rotation and circumduction
- Flexion and extension
- Gliding only
- Abduction and adduction
Correct Answer: Flexion and extension
Q9. Which structure is responsible for producing synovial fluid?
- Articular cartilage
- Synovial membrane (synovium)
- Fibrous capsule only
- Periosteum
Correct Answer: Synovial membrane (synovium)
Q10. Articular surfaces of synovial joints are covered by which type of cartilage?
- Elastic cartilage
- Fibrocartilage
- Hyaline cartilage
- Calcified cartilage
Correct Answer: Hyaline cartilage
Q11. Which joint contains menisci (fibrocartilaginous pads) that improve congruency?
- Wrist (radiocarpal) joint
- Shoulder (glenohumeral) joint
- Knee joint
- Elbow joint
Correct Answer: Knee joint
Q12. An example of a plane (gliding) synovial joint is:
- Elbow (humeroulnar) joint
- Intercarpal joints of the wrist
- Hip joint
- Temporomandibular joint
Correct Answer: Intercarpal joints of the wrist
Q13. Which synovial joint type is exemplified by the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb?
- Hinge joint
- Saddle joint
- Pivot joint
- Condyloid joint
Correct Answer: Saddle joint
Q14. A condyloid (ellipsoidal) joint allows which combination of movements?
- Only rotation
- Flexion/extension and abduction/adduction
- Gliding only
- Hinge-type flexion and extension only
Correct Answer: Flexion/extension and abduction/adduction
Q15. Which statement best describes synarthroses?
- Freely movable synovial joints
- Slightly movable cartilaginous joints
- Immovable fibrous joints such as skull sutures
- Joints with fibrocartilaginous discs only
Correct Answer: Immovable fibrous joints such as skull sutures
Q16. Amphiarthroses are primarily united by which tissue type?
- Fibrous tissue only
- Cartilaginous tissue
- Synovial membrane
- Bone fusion
Correct Answer: Cartilaginous tissue
Q17. The term “arthrosis” in joint classification generally refers to:
- A surgical incision
- A type of ligament
- A joint
- An enzyme in synovial fluid
Correct Answer: A joint
Q18. Which joint is the most common site for intra-articular corticosteroid injections in clinical practice?
- Interphalangeal joints of toes
- Knee joint
- Sacroiliac joint
Correct Answer: Knee joint
Q19. Primary functions of synovial fluid include:
- Structural support of bone marrow only
- Lubrication and nourishment of articular cartilage
- Blood supply to articular cartilage
- Secretion of calcified matrix
Correct Answer: Lubrication and nourishment of articular cartilage
Q20. In joint inflammation, increased synovial membrane permeability typically causes:
- Reduced synovial fluid volume
- Joint effusion (increased synovial fluid in cavity)
- Rapid bone fusion
- Decreased lymphatic drainage only
Correct Answer: Joint effusion (increased synovial fluid in cavity)
Q21. Which disease primarily involves autoimmune inflammation of the synovium?
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout (acute tophaceous gout excluded)
- Septic bursitis only
Correct Answer: Rheumatoid arthritis
Q22. Structures that restrict excessive movement and stabilize joints are:
- Tendons only
- Ligaments
- Synovial villi
- Articular cartilage alone
Correct Answer: Ligaments
Q23. Which structures in the knee are intracapsular but extrasynovial?
- Medial and lateral menisci
- Cruciate (ACL and PCL) ligaments
- Patellar tendon
- Bursa
Correct Answer: Cruciate (ACL and PCL) ligaments
Q24. Which synovial joint type is typically biaxial (permits movement in two planes)?
- Pivot joint
- Condyloid (ellipsoidal) joint
- Ball-and-socket joint
- Hinge joint
Correct Answer: Condyloid (ellipsoidal) joint
Q25. Which synovial property most influences residence time of intra-articular drugs?
- Thickness of articular cartilage only
- Synovial membrane vascularity and lymphatic drainage
- Number of ligaments around the joint
- Bone density of adjoining bones
Correct Answer: Synovial membrane vascularity and lymphatic drainage
Q26. The epiphyseal growth plate is an example of which cartilaginous joint subtype?
- Syndesmosis
- Synostosis
- Synchondrosis
- Symphysis
Correct Answer: Synchondrosis
Q27. The intervertebral joints (between vertebral bodies) functionally classify as:
- Synarthroses
- Amphiarthroses
- Diarthroses
- Synostoses
Correct Answer: Amphiarthroses
Q28. Which joint contains an articular disc separating the joint cavity into compartments?
- Hip joint
- Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
- Interphalangeal joint
- Subtalar joint
Correct Answer: Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
Q29. For acute synovitis pain and inflammation, which drug class is commonly first-line pharmacotherapy?
- Antibiotics
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Anticoagulants
- Antihistamines
Correct Answer: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Q30. Which movement decreases the angle between the anterior surfaces of two bones (e.g., bending the elbow)?
- Extension
- Abduction
- Flexion
- Rotation
Correct Answer: Flexion

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com