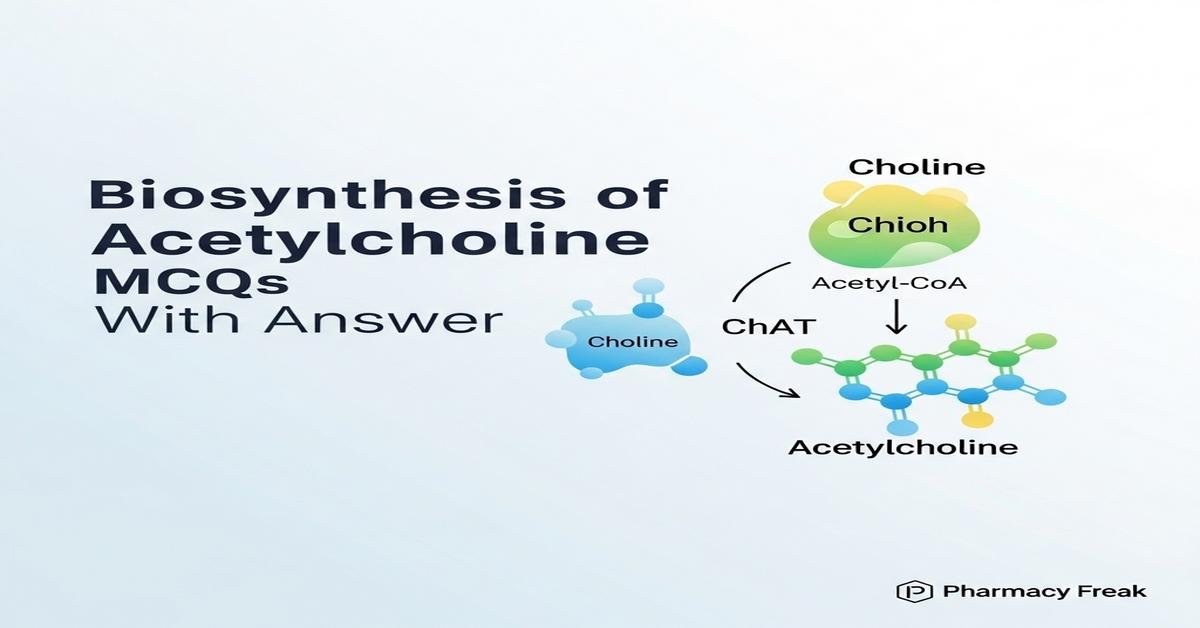
Introduction:
The biosynthesis of acetylcholine MCQs with answer is an essential review resource for B. Pharm students studying neurotransmitter chemistry, cholinergic pharmacology, and neuropharmacology. This concise, exam-focused introduction covers key concepts: choline uptake, acetyl-CoA supply, choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) catalysis, vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) packaging, synaptic release mechanisms, and acetylcholinesterase metabolism. Questions emphasize regulatory steps, pharmacological inhibitors (hemicholinium, vesamicol, organophosphates), clinical implications in Alzheimer’s disease and neuromuscular disorders, and experimental assays. The MCQs target applied knowledge, mechanism-based reasoning, and drug action relevant to B. Pharm curricula. Now let’s test your knowledge with 50 MCQs on this topic.
Q1. Which enzyme catalyzes the formation of acetylcholine from choline and acetyl-CoA?
- Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
- Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
- Choline kinase
- Choline dehydrogenase
Correct Answer: Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
Q2. What is the primary rate-limiting step in neuronal acetylcholine synthesis?
- Availability of acetyl-CoA in the cytosol
- Choline uptake via high-affinity transporter (CHT1)
- Vesicular packaging by VAChT
- Release triggered by Ca2+ influx
Correct Answer: Choline uptake via high-affinity transporter (CHT1)
Q3. Which transporter is responsible for high-affinity choline uptake into cholinergic nerve terminals?
- SLC5A7 (CHT1)
- SLC18A3 (VAChT)
- SLC6A3 (DAT)
- SLC1A3 (GLAST)
Correct Answer: SLC5A7 (CHT1)
Q4. Which compound specifically inhibits high-affinity choline uptake and reduces acetylcholine synthesis?
- Hemicholinium-3
- Vesamicol
- Botulinum toxin
- Neostigmine
Correct Answer: Hemicholinium-3
Q5. Where in the neuron does choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) primarily catalyze ACh synthesis?
- In the cytosol of the presynaptic terminal
- Inside synaptic vesicles
- In the postsynaptic membrane
- Within the mitochondrial matrix
Correct Answer: In the cytosol of the presynaptic terminal
Q6. Which molecule provides the acetyl group for acetylcholine synthesis?
- Acetyl-CoA
- Acetate
- Acetyl phosphate
- Acetoacetate
Correct Answer: Acetyl-CoA
Q7. Which protein transports acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?
- Vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT)
- Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
- High-affinity choline transporter (CHT1)
- Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Correct Answer: Vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT)
Q8. VAChT function depends on which gradient generated by vesicular H+-ATPase?
- Proton electrochemical gradient (H+ gradient)
- Sodium gradient
- Potassium gradient
- Chloride gradient
Correct Answer: Proton electrochemical gradient (H+ gradient)
Q9. Which drug inhibits VAChT and prevents acetylcholine packaging into vesicles?
- Vesamicol
- Hemicholinium-3
- Neostigmine
- Tubocurarine
Correct Answer: Vesamicol
Q10. Release of acetylcholine from synaptic vesicles is primarily triggered by which ion?
- Calcium (Ca2+)
- Sodium (Na+)
- Potassium (K+)
- Magnesium (Mg2+)
Correct Answer: Calcium (Ca2+)
Q11. Botulinum toxin impairs acetylcholine release by cleaving which class of proteins?
- SNARE proteins
- Ion channels
- G-protein coupled receptors
- Acetylcholinesterase molecules
Correct Answer: SNARE proteins
Q12. What is the primary enzyme responsible for rapid hydrolysis of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft?
- Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
- Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE)
- Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
- Monoamine oxidase (MAO)
Correct Answer: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Q13. Which inhibitor class increases synaptic acetylcholine by blocking its breakdown?
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., neostigmine, physostigmine)
- Calcium channel blockers
- Beta blockers
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Correct Answer: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., neostigmine, physostigmine)
Q14. Organophosphate poisoning leads to accumulation of acetylcholine primarily by inhibiting which enzyme?
- Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
- Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
- Vesicular monoamine transporter
- High-affinity choline transporter
Correct Answer: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
Q15. Which clinical agent is used to reactivate AChE after organophosphate inhibition if given early?
- Pralidoxime (2-PAM)
- Atropine
- Propranolol
- Gabapentin
Correct Answer: Pralidoxime (2-PAM)
Q16. In cholinergic neurons, which substrate is recycled back into the terminal after acetylcholine breakdown?
- Choline
- Acetate
- Acetyl-CoA
- Serine
Correct Answer: Choline
Q17. Which of the following is NOT a direct precursor of acetylcholine?
- Glutamate
- Choline
- Acetyl-CoA
- Dietary choline sources (e.g., lecithin)
Correct Answer: Glutamate
Q18. How does hemicholinium-3 affect synaptic transmission?
- Blocks choline uptake and reduces ACh synthesis
- Blocks AChE and increases ACh levels
- Blocks VAChT and prevents packaging
- Enhances ACh release by increasing Ca2+ entry
Correct Answer: Blocks choline uptake and reduces ACh synthesis
Q19. Which genetic defect would most directly reduce acetylcholine synthesis?
- Mutation in choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
- Mutation in acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
- Mutation in muscarinic receptors
- Mutation in postsynaptic AChR
Correct Answer: Mutation in choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
Q20. What is the main location of cholinergic neurons involved in cognitive function affected in Alzheimer’s disease?
- Nucleus basalis of Meynert
- Substantia nigra pars compacta
- Red nucleus
- Cerebellar Purkinje cells
Correct Answer: Nucleus basalis of Meynert
Q21. Which analytical assay directly measures activity of choline acetyltransferase?
- Radiolabeled acetyl-CoA incorporation into ACh
- HPLC measurement of dopamine
- ELISA for acetylcholinesterase protein
- Western blot for VAChT
Correct Answer: Radiolabeled acetyl-CoA incorporation into ACh
Q22. Which compound is a clinically used reversible AChE inhibitor that improves cholinergic transmission in myasthenia gravis?
- Neostigmine
- Hemicholinium-3
- Vesamicol
- Botulinum toxin
Correct Answer: Neostigmine
Q23. Which synaptic location primarily expresses vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT)?
- Membrane of cholinergic synaptic vesicles
- Postsynaptic density
- Mitochondrial membrane
- Axonal plasma membrane
Correct Answer: Membrane of cholinergic synaptic vesicles
Q24. Which statement best describes choline biosynthesis in the liver relevant to whole-body choline supply?
- Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PEMT) synthesizes some choline de novo
- Choline is exclusively obtained from diet and cannot be synthesized
- Choline is produced by acetylcholinesterase activity
- VAChT synthesizes choline in vesicles
Correct Answer: Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PEMT) synthesizes some choline de novo
Q25. Which clinical syndrome is caused by antibodies against postsynaptic nicotinic ACh receptors, reducing neuromuscular transmission?
- Myasthenia gravis
- Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
- Parkinson’s disease
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
Correct Answer: Myasthenia gravis
Q26. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome primarily impairs which presynaptic mechanism affecting ACh release?
- Voltage-gated calcium channels
- Acetylcholinesterase activity
- Choline uptake transporter
- VAChT function
Correct Answer: Voltage-gated calcium channels
Q27. Which of the following increases acetyl-CoA availability in cholinergic neurons for ACh synthesis?
- Glycolysis and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity
- Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
- Blockade of VAChT
- Hemicholinium therapy
Correct Answer: Glycolysis and pyruvate dehydrogenase activity
Q28. Which isoform of cholinesterase is more abundant in plasma and can hydrolyze ACh but is not the primary synaptic enzyme?
- Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE)
- Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
- Monoamine oxidase (MAO)
- Carboxylesterase
Correct Answer: Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE)
Q29. Which drug class would increase synaptic acetylcholine levels and is used in Alzheimer’s disease management?
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., donepezil)
- Muscarinic antagonists (e.g., atropine)
- Beta-adrenergic agonists
- NMDA receptor antagonists only
Correct Answer: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., donepezil)
Q30. Which of the following best describes the fate of acetate after acetylcholine hydrolysis?
- Diffuses away and is metabolized by surrounding cells
- Specifically taken up by VAChT for reuse
- Converted back to acetylcholine by AChE
- Stored in synaptic vesicles
Correct Answer: Diffuses away and is metabolized by surrounding cells
Q31. Which receptor subtype is activated at the neuromuscular junction by acetylcholine?
- Nicotinic muscle-type (nAChR) receptors
- Muscarinic M2 receptors
- Dopaminergic D2 receptors
- GABA-A receptors
Correct Answer: Nicotinic muscle-type (nAChR) receptors
Q32. Which structural feature is essential in choline for recognition by CHT1 and ChAT?
- Quaternary ammonium group
- Carboxyl group
- Sulfhydryl group
- Aromatic ring
Correct Answer: Quaternary ammonium group
Q33. Chronic inhibition of acetylcholinesterase would lead to which homeostatic response in cholinergic neurons?
- Downregulation of presynaptic ACh release and receptor desensitization
- Upregulation of ChAT expression immediately
- Increased VAChT expression within minutes
- Permanent increase in choline synthesis
Correct Answer: Downregulation of presynaptic ACh release and receptor desensitization
Q34. A selective inhibitor of ChAT would be expected to cause which effect?
- Reduced acetylcholine synthesis and cholinergic signaling
- Increased levels of acetylcholine in synapses
- Enhanced vesicular storage of acetylcholine
- Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
Correct Answer: Reduced acetylcholine synthesis and cholinergic signaling
Q35. Which technique can localize ChAT-expressing neurons in brain tissue sections?
- Immunohistochemistry for ChAT protein
- Electron microscopy of synaptic vesicles only
- Patch-clamp recording of glial cells
- In situ hybridization for AChE mRNA
Correct Answer: Immunohistochemistry for ChAT protein
Q36. Which dietary nutrient deficiency can limit acetylcholine synthesis?
- Choline deficiency
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Iron deficiency
- Vitamin C deficiency
Correct Answer: Choline deficiency
Q37. Inhibition of which enzyme would primarily decrease acetyl-CoA available for ACh synthesis in neurons?
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- Acetylcholinesterase
- Choline acetyltransferase
- Vesicular H+-ATPase
Correct Answer: Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Q38. Which experimental drug would increase extracellular acetylcholine by blocking its vesicular storage?
- Vesamicol
- Hemicholinium-3
- Pralidoxime
- Atropine
Correct Answer: Vesamicol
Q39. Which population of neurons uses acetylcholine as a primary neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system?
- Preganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons
- All postganglionic sympathetic neurons exclusively
- Only enteric neurons
- Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra
Correct Answer: Preganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons
Q40. Which drug is a muscarinic receptor antagonist that blocks acetylcholine action at parasympathetic effector organs?
- Atropine
- Neostigmine
- Donepezil
- Vesamicol
Correct Answer: Atropine
Q41. Which cellular organelle provides ATP needed for vesicular H+-ATPase activity during ACh packaging?
- Mitochondria
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosomes
- Peroxisomes
Correct Answer: Mitochondria
Q42. Which technique is commonly used to quantify acetylcholine levels in tissue or synaptosomes?
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection
- Immunoprecipitation of AChE
- Western blot for ChAT only
- Patch-clamp electrophysiology
Correct Answer: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection
Q43. In the central nervous system, which receptor subtype mediates slow modulatory effects of acetylcholine?
- Muscarinic receptors (GPCRs)
- Nicotinic receptors (ion channels)
- NMDA receptors
- GABA-B receptors
Correct Answer: Muscarinic receptors (GPCRs)
Q44. Which adverse effect is most likely with excessive acetylcholine due to AChE inhibition?
- Bradycardia and bronchoconstriction
- Tachycardia and bronchodilation
- Hyperglycemia and diuresis
- Paralysis of smooth muscle relaxation
Correct Answer: Bradycardia and bronchoconstriction
Q45. Which molecule serves as a diagnostic marker for cholinergic neuron integrity in some imaging studies?
- VAChT expression or radiolabeled ligands for VAChT
- Serotonin transporter ligands
- Tyrosine hydroxylase antibodies
- Dopamine receptor imaging
Correct Answer: VAChT expression or radiolabeled ligands for VAChT
Q46. Which statement about choline transporters is correct?
- CHT1 is a sodium-dependent high-affinity choline transporter crucial for ACh synthesis
- CHT1 is a vesicular transporter that packages ACh
- CHT1 is primarily found in postsynaptic membranes
- CHT1 degrades acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
Correct Answer: CHT1 is a sodium-dependent high-affinity choline transporter crucial for ACh synthesis
Q47. Which pharmacological intervention increases available acetylcholine by inhibiting peripheral AChE and is used to reverse neuromuscular blockade?
- Neostigmine administration
- Hemicholinium-3 administration
- Vesamicol administration
- Atropine alone
Correct Answer: Neostigmine administration
Q48. Which factor most directly couples action potential arrival to acetylcholine release?
- Opening of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels at the presynaptic terminal
- Activation of postsynaptic muscarinic receptors
- Diffusion of acetylcholine from the postsynaptic cell
- Increased activity of acetylcholinesterase
Correct Answer: Opening of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels at the presynaptic terminal
Q49. Which therapeutic strategy targets increased central acetylcholine to improve cognition in dementia?
- Use of centrally acting acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., rivastigmine)
- Administration of hemicholinium-3
- Blockade of VAChT with vesamicol
- Use of peripheral muscarinic agonists only
Correct Answer: Use of centrally acting acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., rivastigmine)
Q50. In research, knockdown of VAChT expression would primarily produce which outcome?
- Reduced vesicular ACh storage and impaired synaptic cholinergic transmission
- Increased choline uptake into terminals
- Enhanced acetylcholine synthesis by ChAT
- Direct inhibition of acetylcholinesterase
Correct Answer: Reduced vesicular ACh storage and impaired synaptic cholinergic transmission

I am a Registered Pharmacist under the Pharmacy Act, 1948, and the founder of PharmacyFreak.com. I hold a Bachelor of Pharmacy degree from Rungta College of Pharmaceutical Science and Research. With a strong academic foundation and practical knowledge, I am committed to providing accurate, easy-to-understand content to support pharmacy students and professionals. My aim is to make complex pharmaceutical concepts accessible and useful for real-world application.
Mail- Sachin@pharmacyfreak.com